El Paso Water
- water-resources
- El Paso, Texas
Construction Type
Drainage
Project Delivery Method
Design-Bid-Build
Project Components
Analysis, hydraulic design, sediment basin design
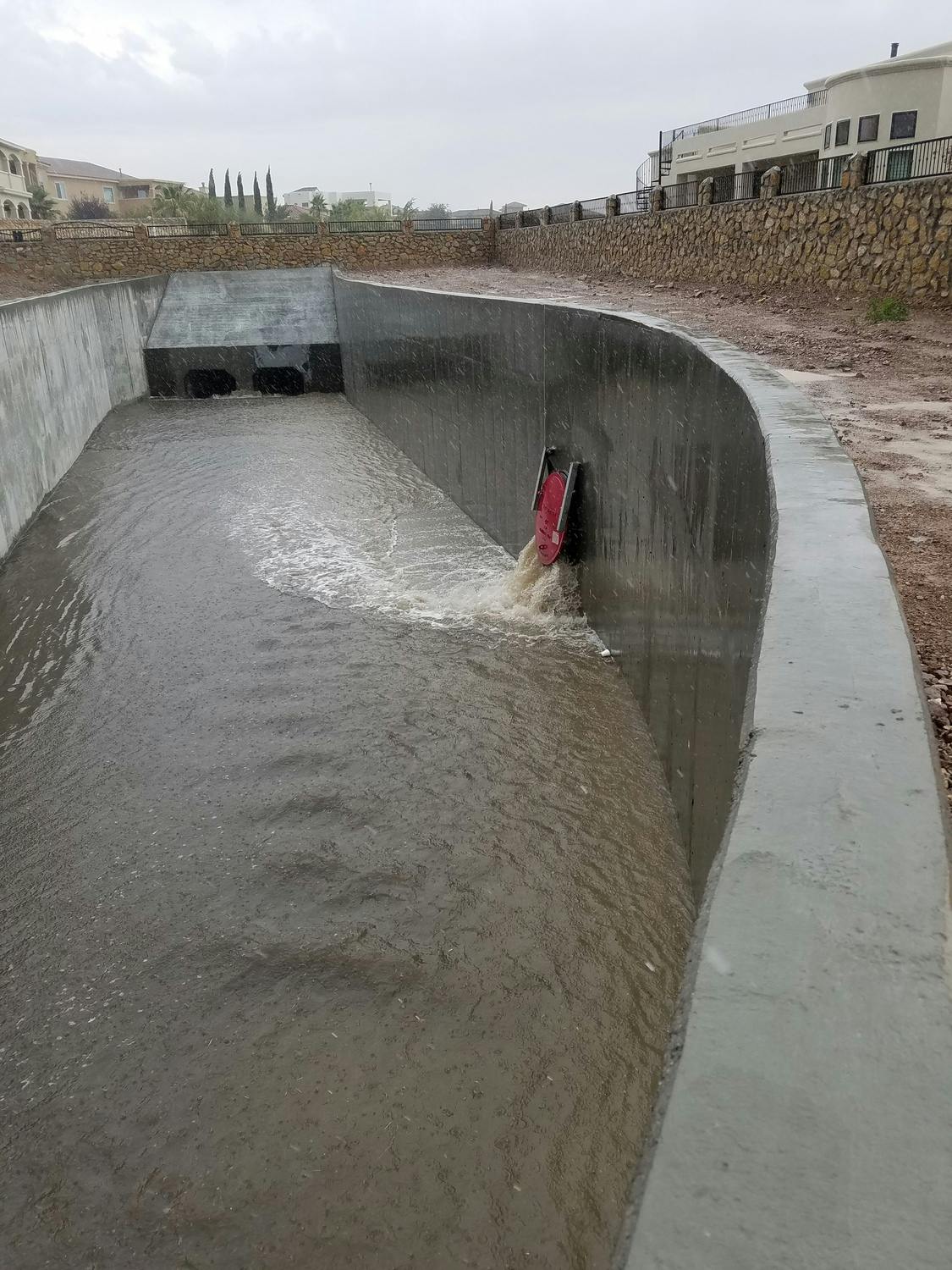
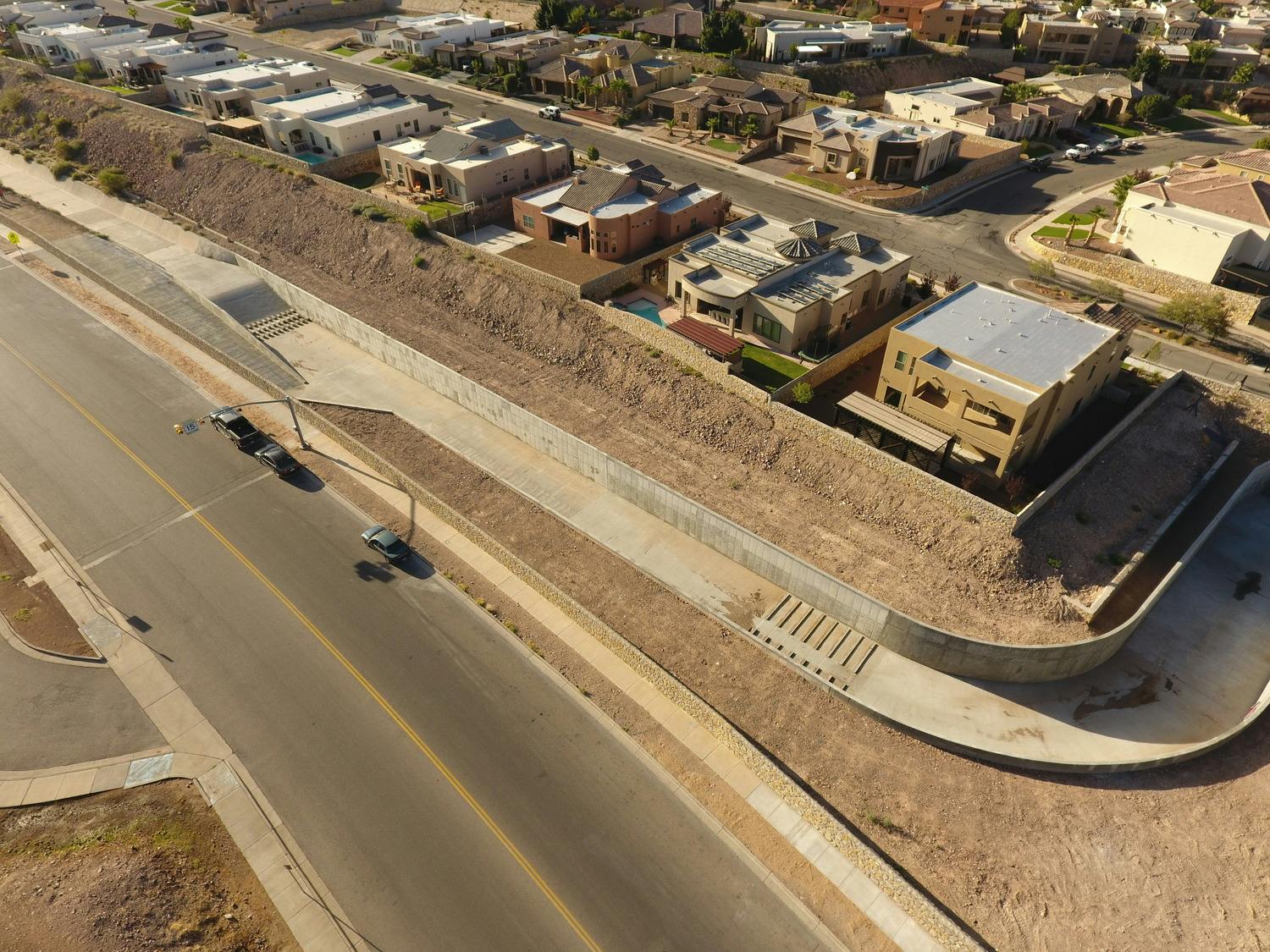
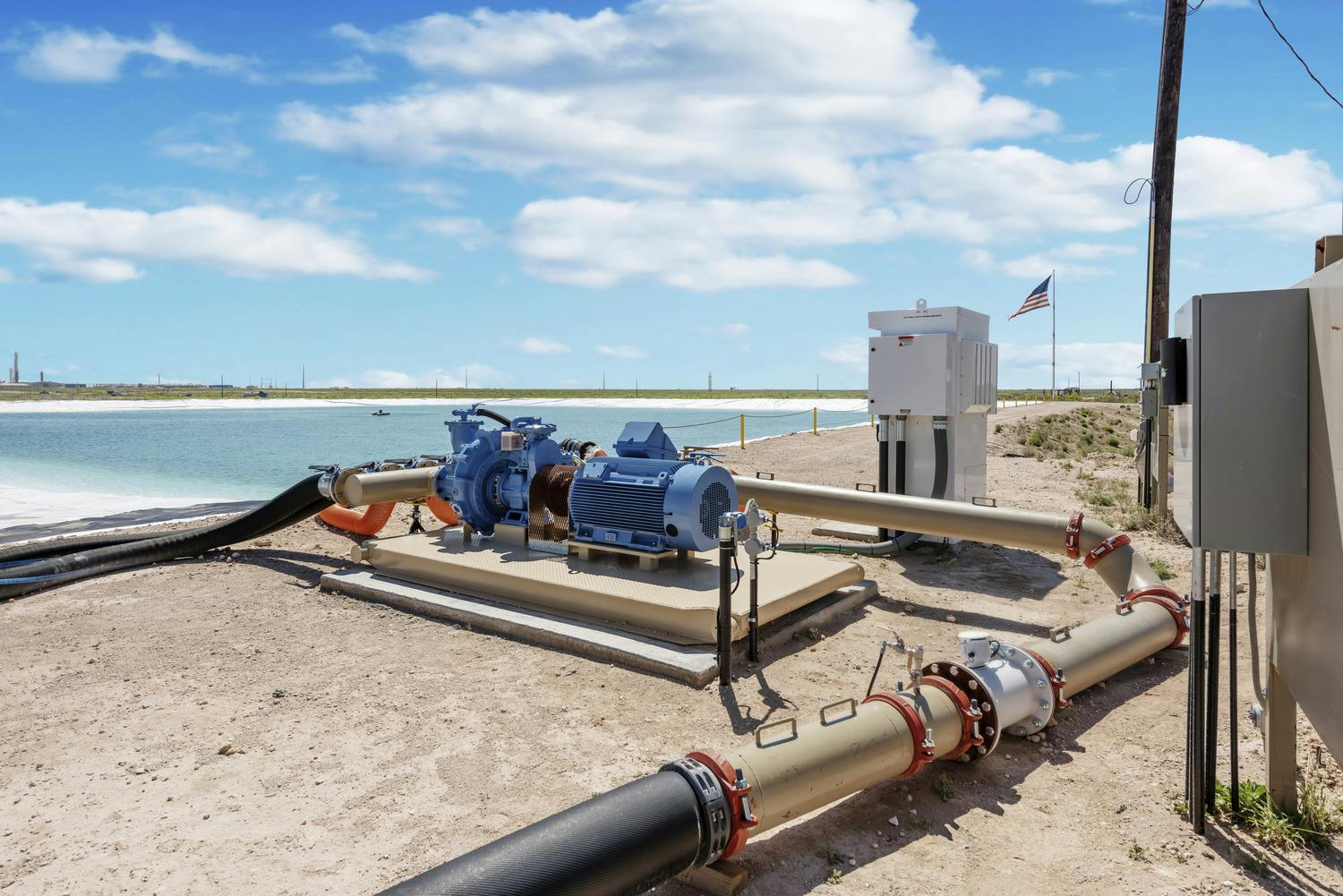
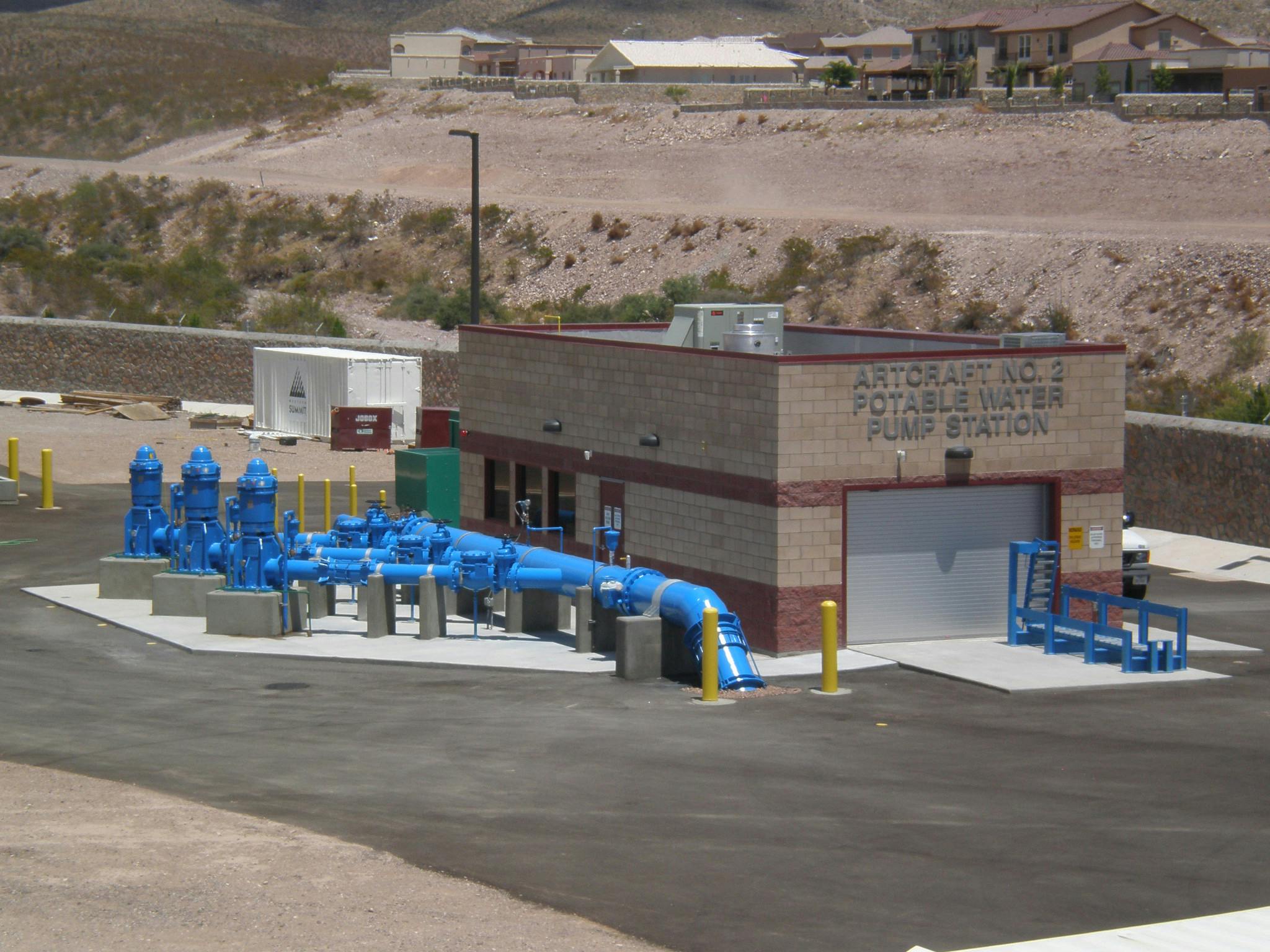
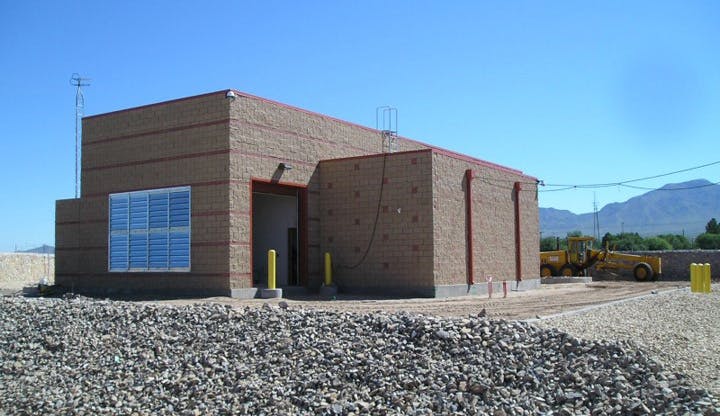
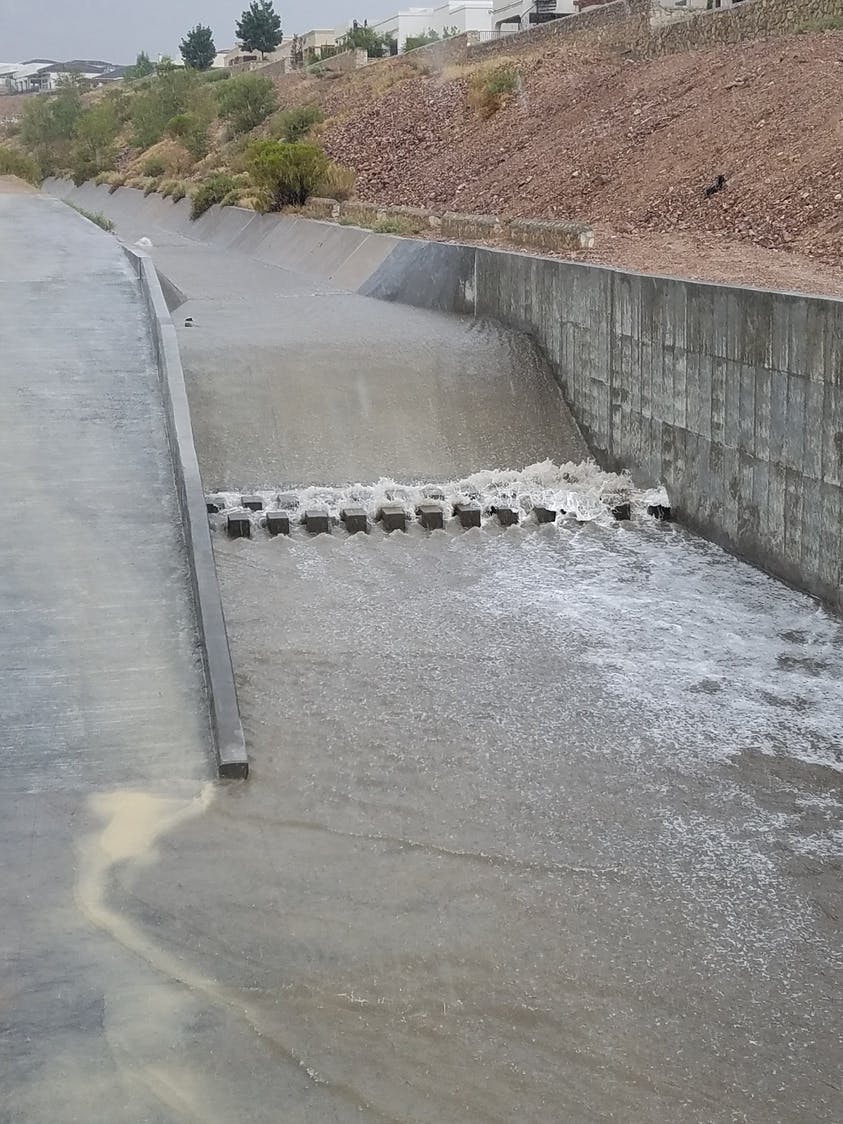
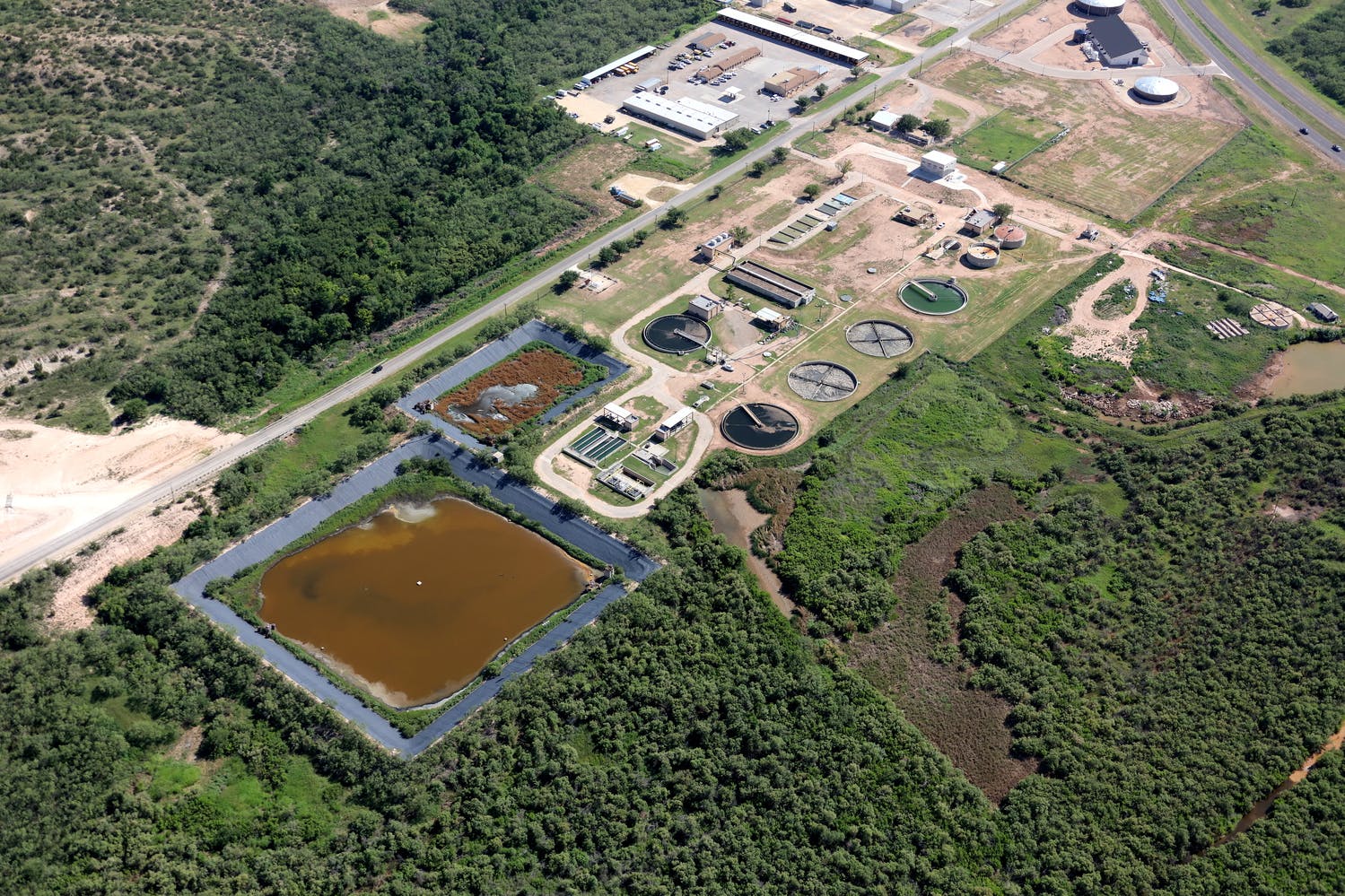
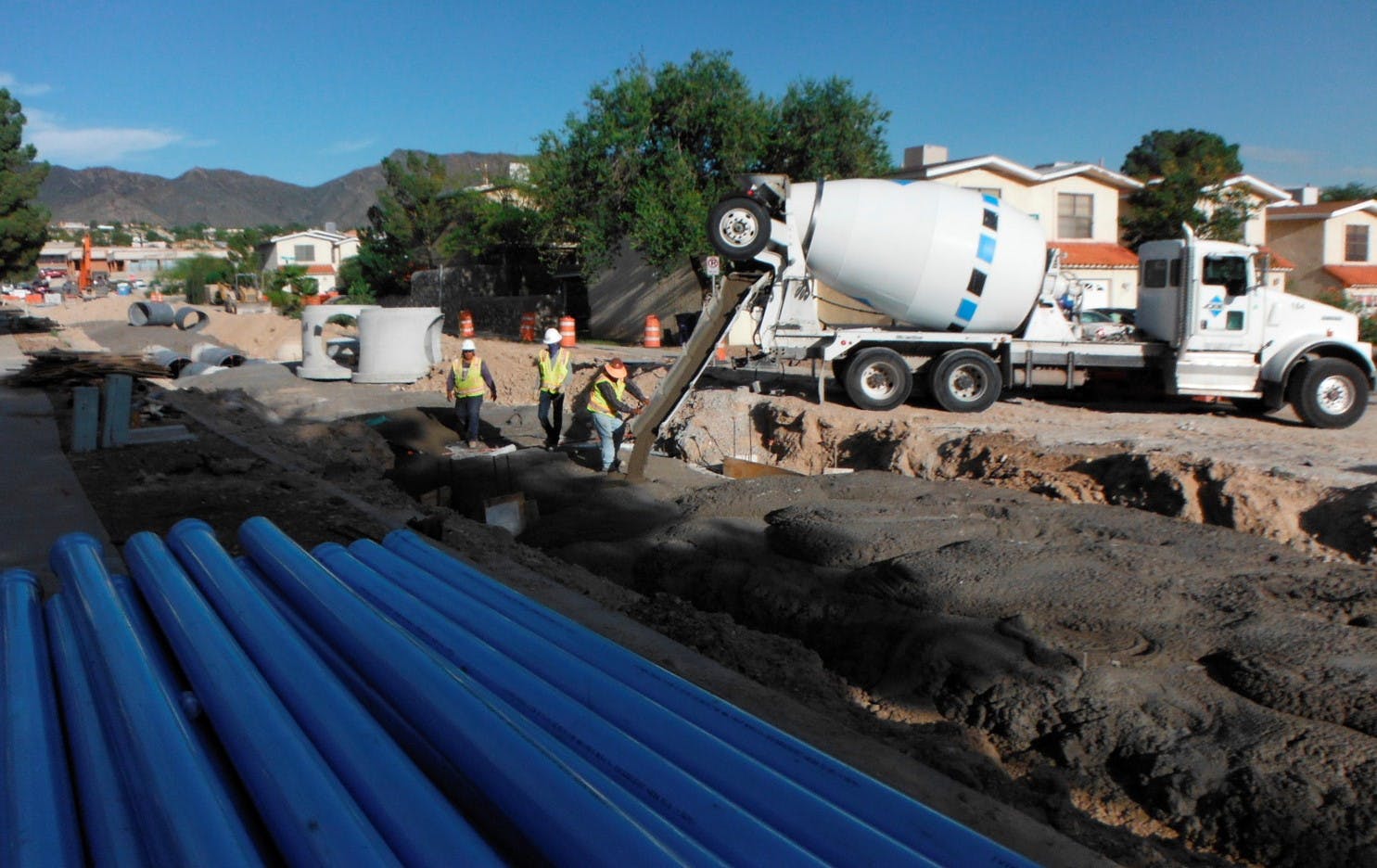
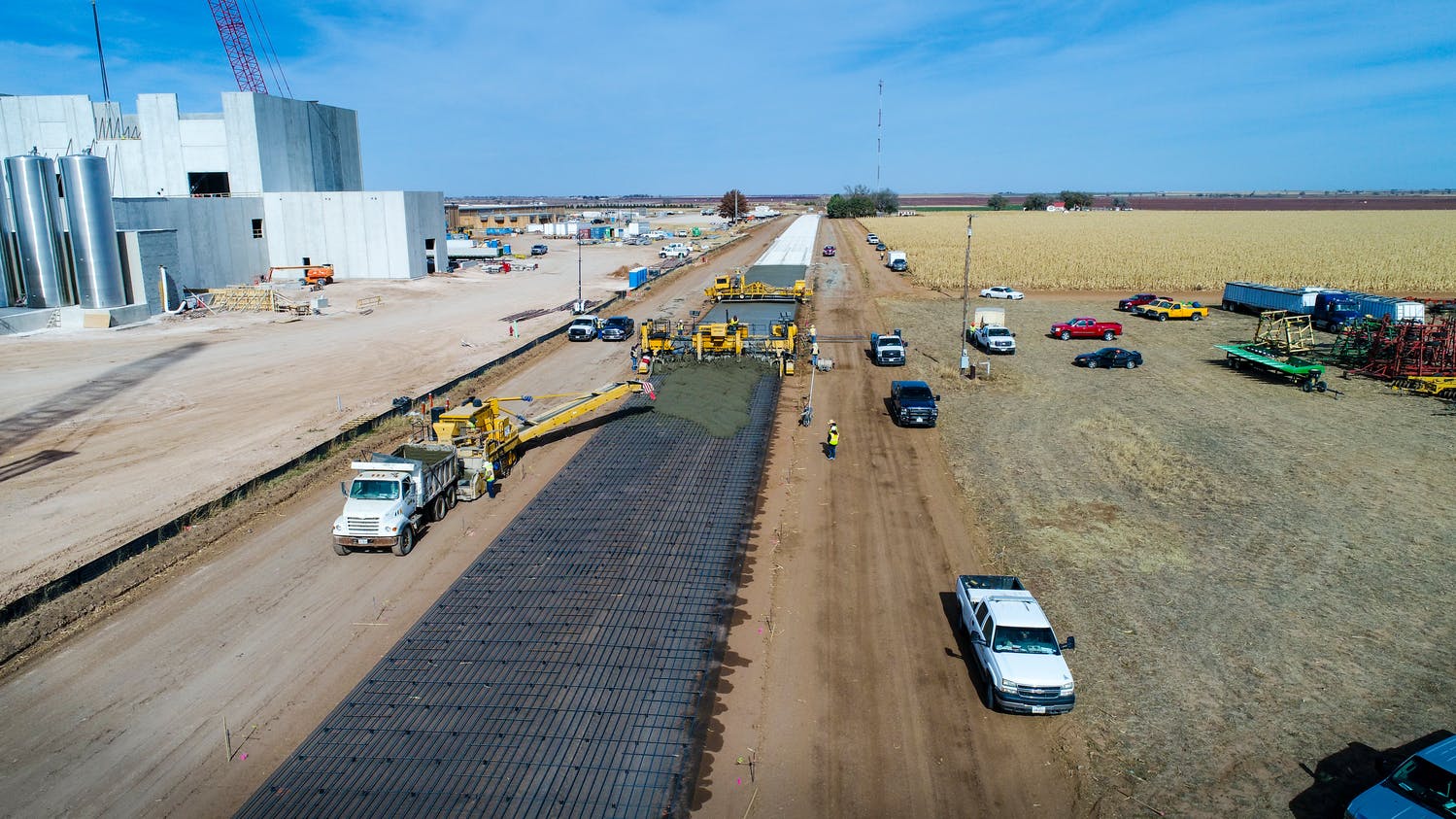
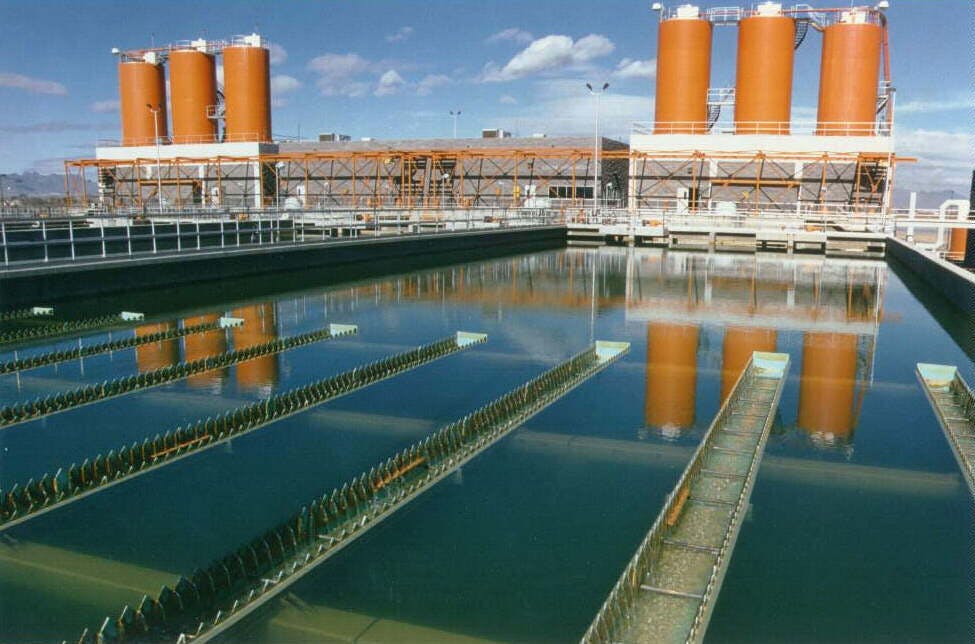
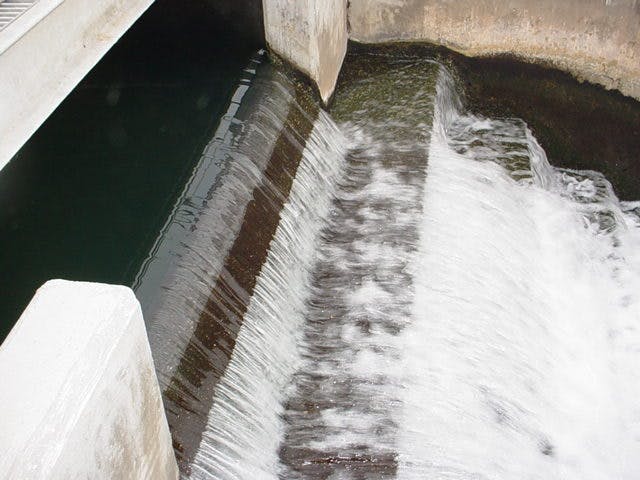
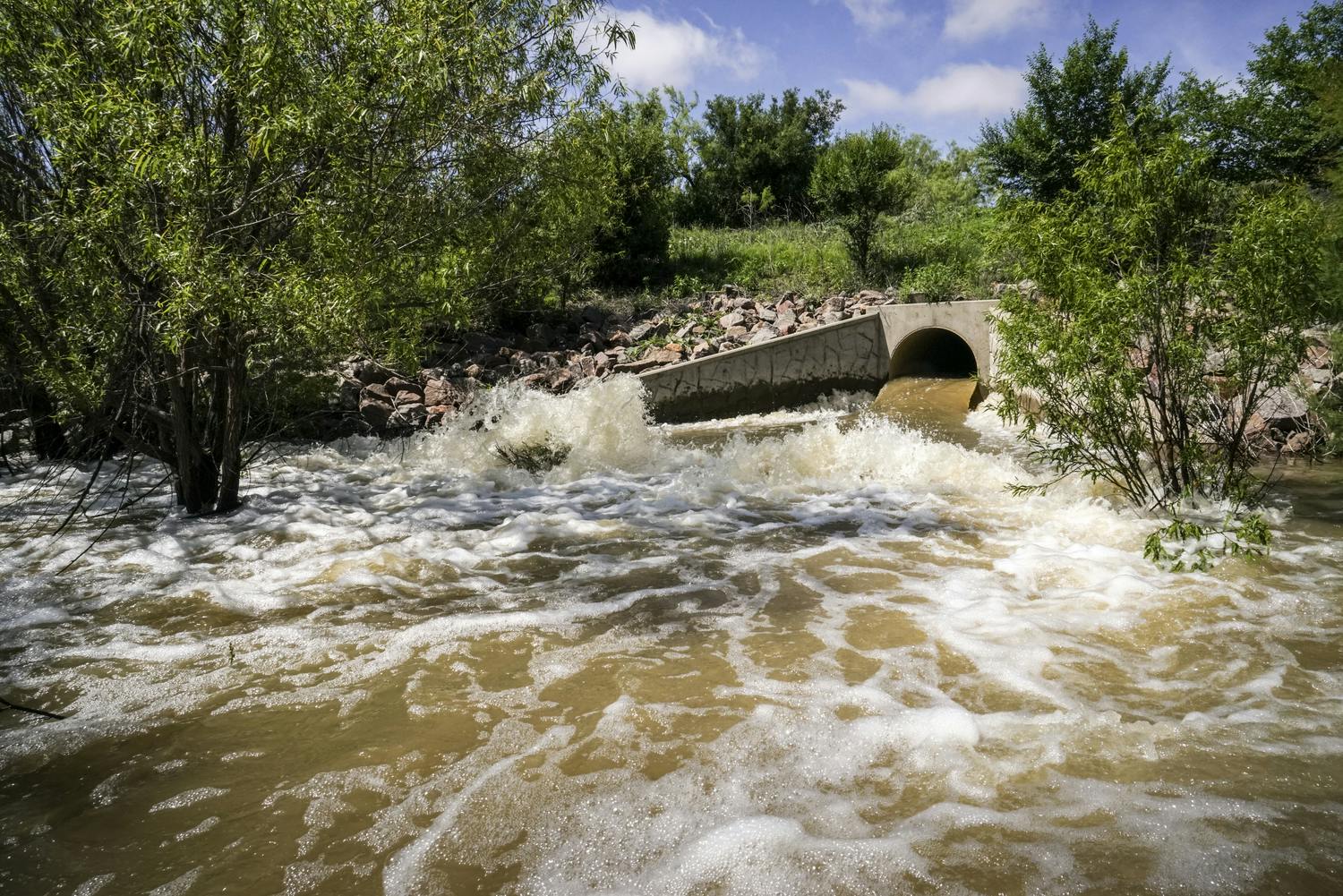
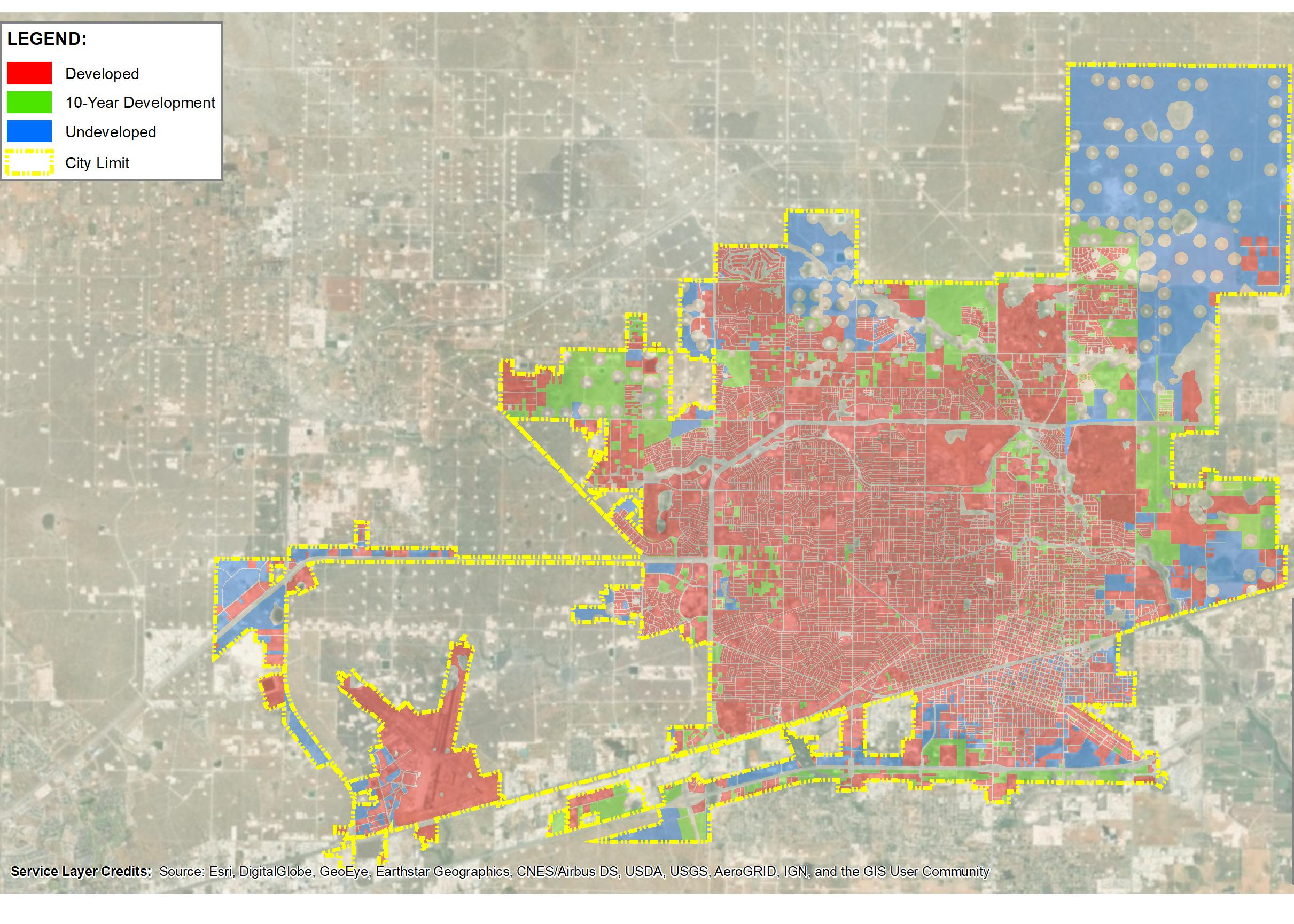
El Paso’s varied terrain and urbanization into the mountainous areas has increased the hydrologic and hydraulic characteristics so much that the City of El Paso sought Parkhill’s expertise after a high-intensity rainstorm event caused structural damage to a concrete channel and exposed a danger to property and people in the area. The local FEMA flood maps and computer models for Arroyo 1, known as Bear Ridge Channel locally, showed that the Bear Ridge Channel should have contained the 4.2-in of rain during the 24-hour 100-year storm event within the concrete channel banks.
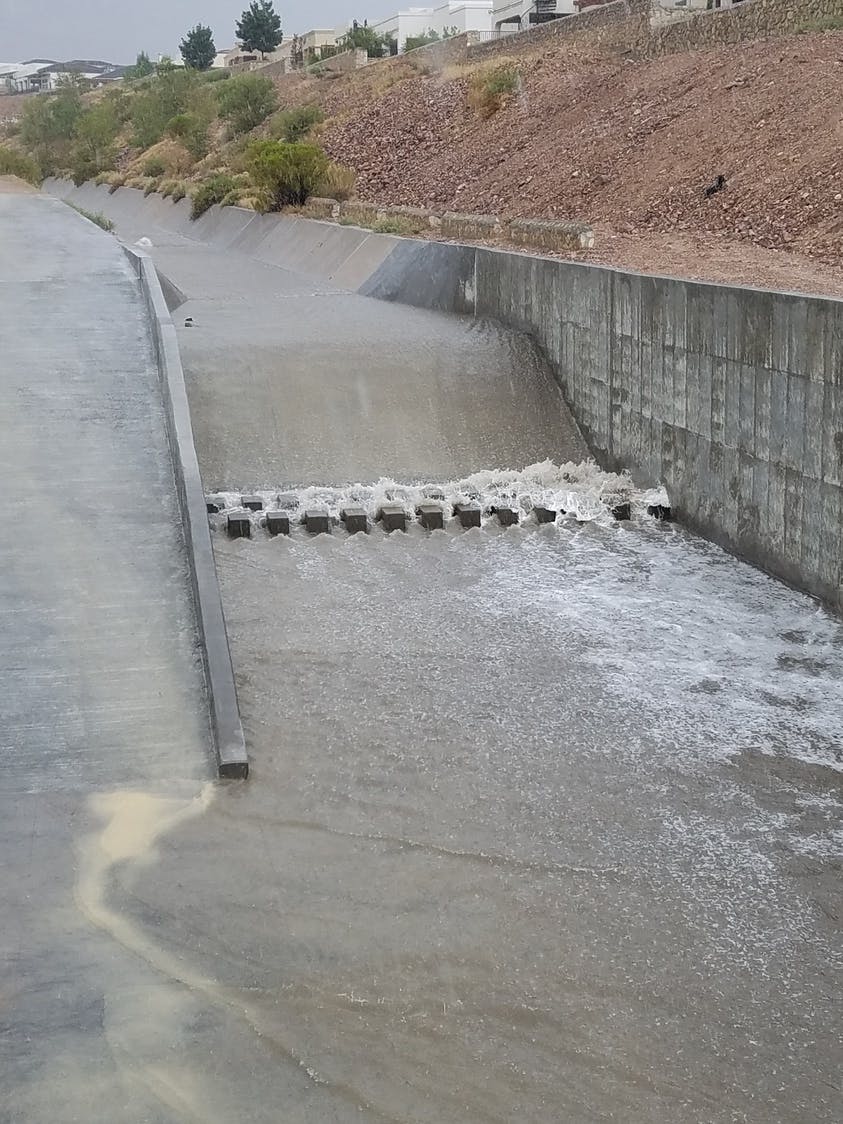
The computer simulations were incorrect, and reality showed that smaller storm events would leave the channel banks. The problem was a 35-ft radius, 90-degree bend in the channel. Parkhill’s analysis of the channel showed deficiencies in the existing constructed channel, both in geometric design and hydraulic design. Parkhill identified two areas in need of improvement: in the headwaters of the concrete-lined channel and 90-degree bend. Parkhill proposed two design alternatives to improve the channel conveyance at the 90-degree bend.
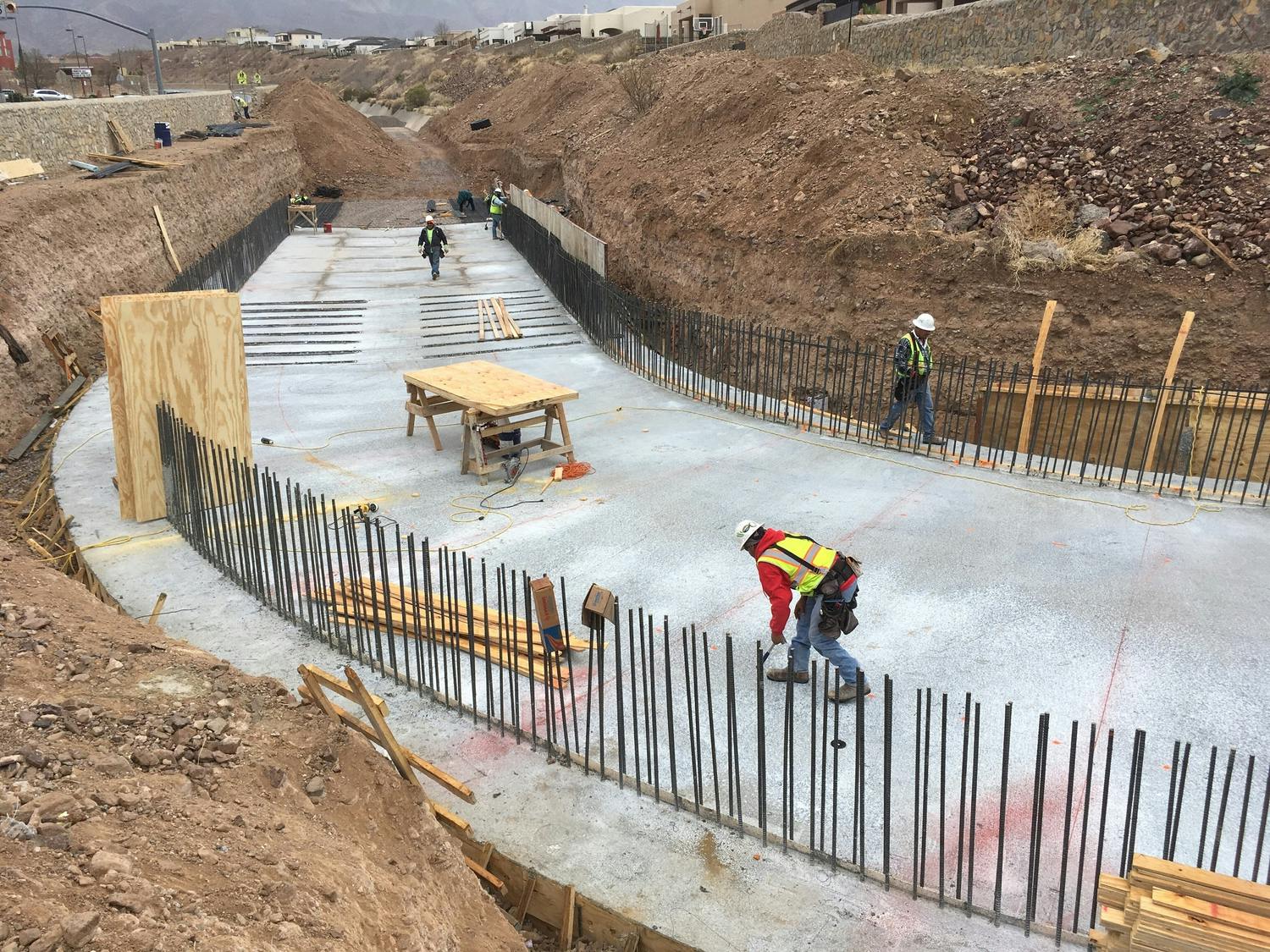
The chosen alternative consisted of a stilling basin to improve the geometric and hydraulic deficiencies in the original design. The conveyance of stormwater is now contained within the channel banks and is allowed to pass around the 90-degree bend and through the downstream culvert crossing. A sediment basin is being designed to reduce the sediment loads and restrict the flow rates into the concrete channel at the headwaters of the concrete channel.
Services Provided
Construction administration
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
City of Borger
- water-resources
- Borger, Texas
Project Size
Seven wells with a total production capacity of approximately 6.5 million gallons per day; six miles of 12-inch to 36-inch collection pipeline; a 5 mgd booster pump station; two 1 million-gallon ground storage tanks; a hybrid standpipe; and an approximately 15-mile transmission pipeline ranging in diameter from 16 to 24 inches
Construction Type
New water supply
Project Components
Hydraulic analysis, structural, electrical, SCADA, architectural, and civil work
The City of Borger engaged the services of Parkhill to engineer a water system for a new source of potable groundwater in reaction to increasing water demands, reduced water availability due to drought conditions and the prospect of a new $720 million facility adding to Borger’s strong industrial economy.
The Borger Northwest Wellfield project was designed to produce an initial firm capacity of 5 million gallons per day (MGD), with a future capacity of 10 MGD. Hydrogeology for this wellfield was challenging, but Parkhill’s design team was able to determine locations for high-producing water wells using electromagnetic resistivity techniques adapted from the oil drilling industry. Additionally, this system is unique in that it pumps water directly from the wellfield into the city’s water distribution system.
Because of the highly specialized construction requirements of this project, Parkhill’s team divided it into specialized components that lowered construction costs for the wellfield. With the money saved by splitting up the construction, Parkhill was able to include a second, one-million-gallon storage tank in the facility that currently provides redundancy for operations and will ease future expansion of the system.
Awards
2017 Texas Engineering Excellence Award Water and Wastewater Gold Medal Winner – American Council of Engineering Companies of Texas
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
El Paso Water
- water-resources
- El Paso, Texas
Project Size
2 miles
Project Delivery Method
CMAR
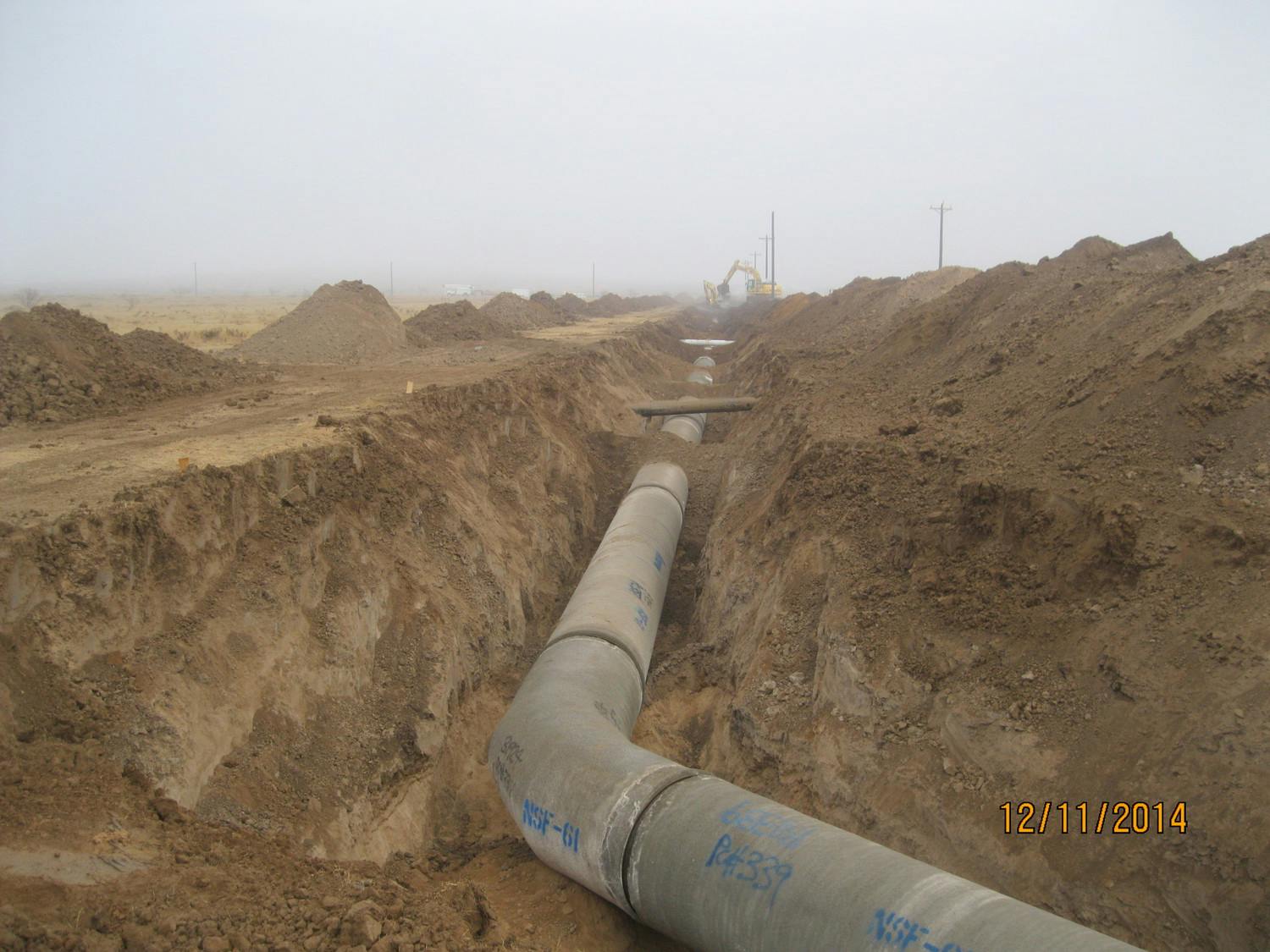
Over the past several years, El Paso Water has seen issues with leaks and breakages in the pipeline along Doniphan Drive, a major traffic route in El Paso’s Upper Valley. The Doniphan Rehabilitation Project was designed to fix almost two miles of 24-inch sewer main on El Paso’s West Side and provided a quality development that would reduce excessive costs.
The line lies just outside of the Union Pacific Railroad right of way and just behind the existing curb line of Doniphan Drive. A large portion of it was made of leaky clay pipes, a material that has not been used since before the 1980s because it makes the joints hard to seal. The line was also located within the groundwater table, and since it was in poor condition, increased infiltration into the system and forced El Paso Water to process additional flow.
To solve these issues, the line was segmented into three portions between the intersections of Mesa and Doniphan and Frontera and Doniphan. This line was receiving small amounts of flow from businesses along Doniphan and some residents east of Doniphan.
The middle portion, from Teramar to Coupland, has in the past few years been replacing approximately 3,600 linear feet of the clay pipe with PVC. However, the other two sections of the line still had numerous cracks and voids in the pipe. This led to groundwater infiltration and required El Paso Water to perform the additional treatment of the sewage.
Opencut construction was a method the team considered, but it would have reduced Doniphan, a principal arterial, to one lane in either direction. With average annual daily traffic values ranging between 12,000 and 21,000 vehicles per day, this was not a feasible option. Instead, El Paso Water chose cured-in-place pipe (CIPP). Installing CIPP is like inserting a “sock” into the inside of a bigger pipeline for little to no disruption to traffic.
This was a fast-track project. El Paso Water used the Texas BuyBoard to streamline the negotiation of prices allowing them to bypass the typical bid phase process, which shortened the overall construction time.
The project entailed the evaluation and pressure cleaning of the line in all three sections and the overhauling of 24 utility holes. The contractor lined the first and last portions (equaling about 6,000 feet) with 12-millimeter CIPP. After each segment of CIPP was installed, the line was videotaped by a miniature remote-control robot camera and reviewed for final quality assurance.
This was a high-profile project. Extraordinary care had to be taken due to its location along a busy thoroughfare and adjacent to Country Club Road, where there is also frequent traffic. The rehabilitation has given El Paso Water a quality development that will reduce needless treatment and excessive costs. The project was completed on time and under budget.
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
BRH Garver Construction
- water-resources
- El Paso, Texas
Project Size
66-inch-diameter, 570-foot-long tunnel and a second 315-foot tunnel
Construction Type
New Large Diameter Pipeline/Tunneling
Project Delivery Method
Design-Build
Project Components
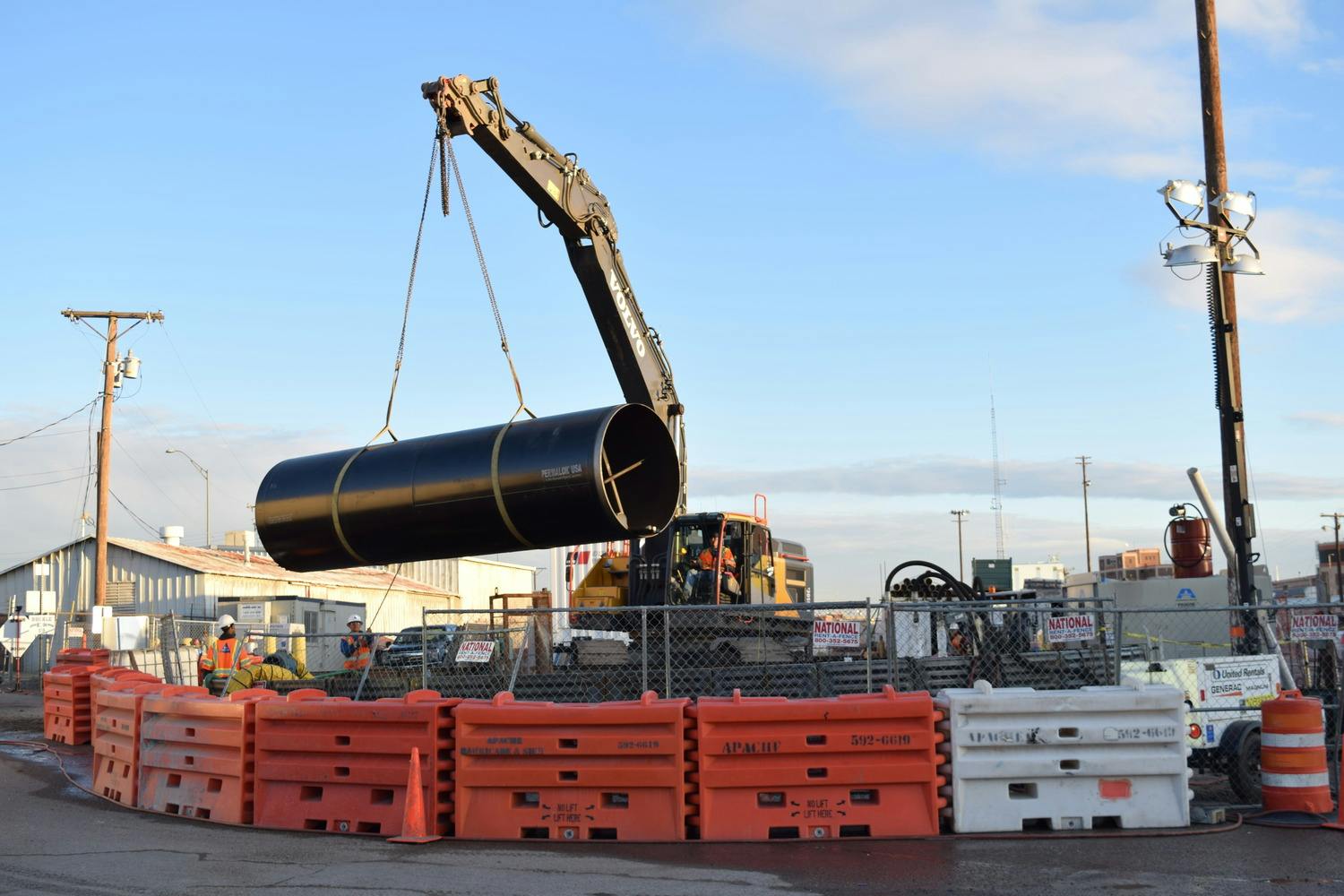
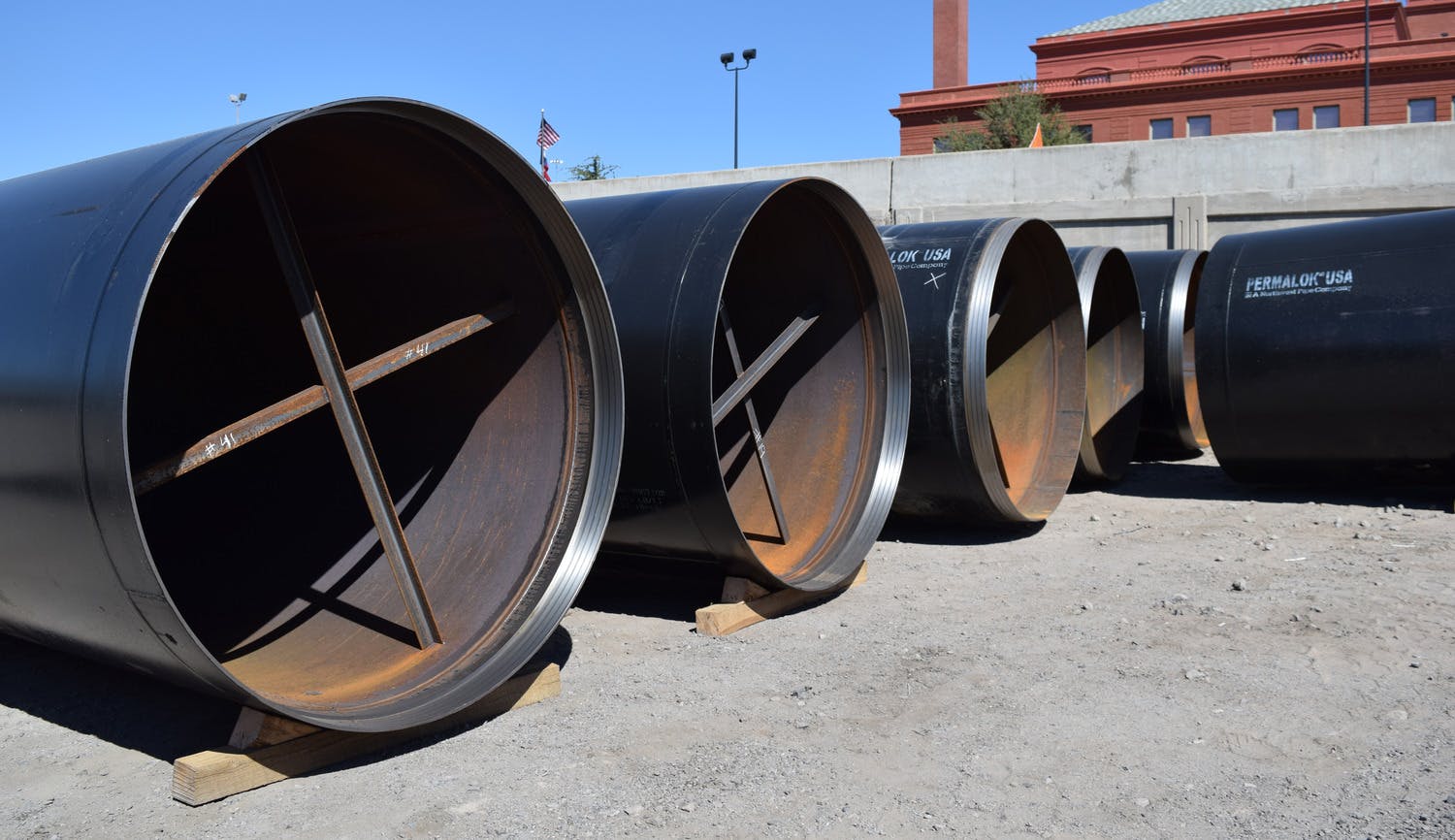
570-foot tunnel and 315-foot tunnel; placement of 66-inch-diameter Permalock casing and 48-inch Northwest Pipe welded steel pipe
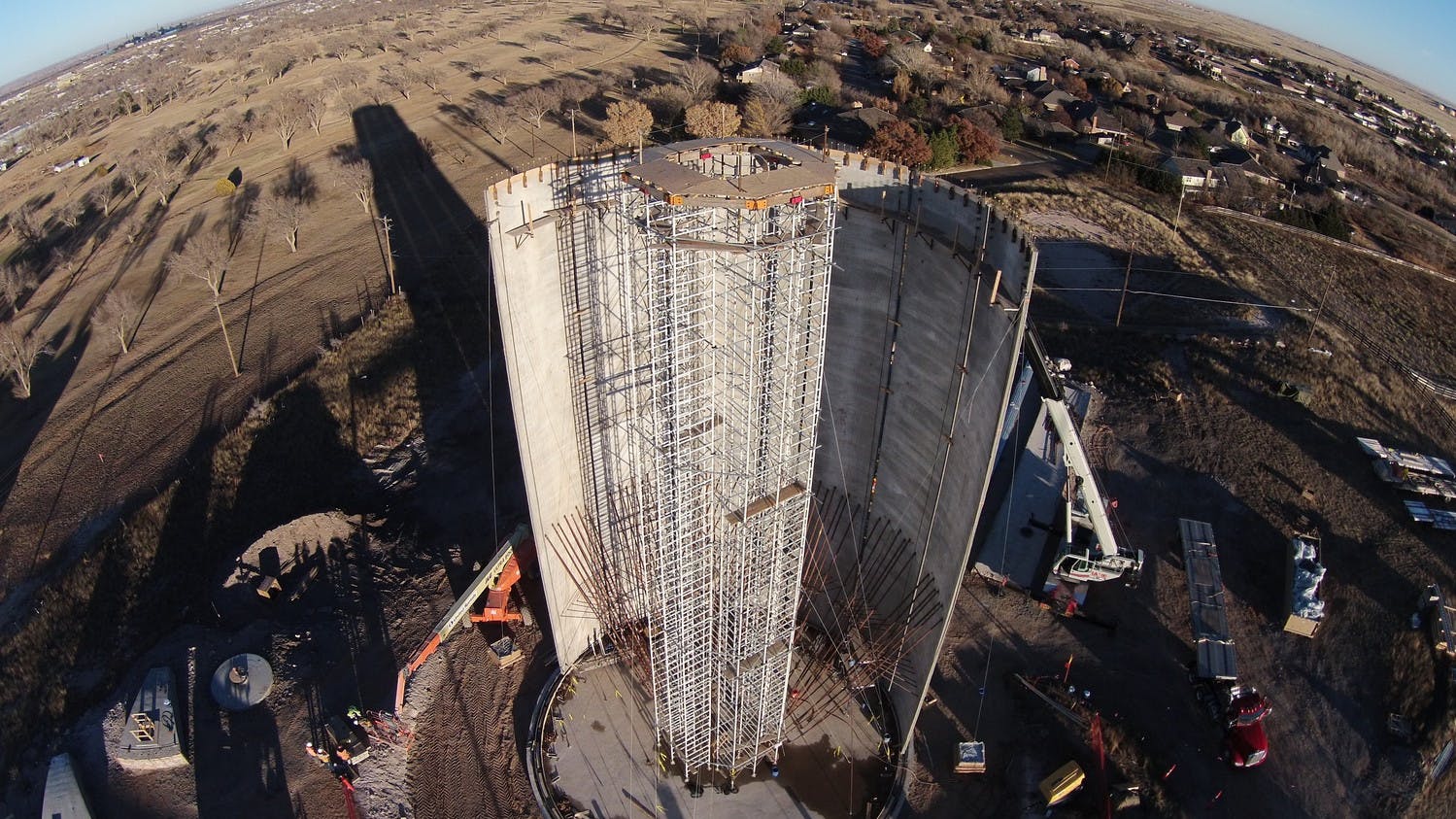
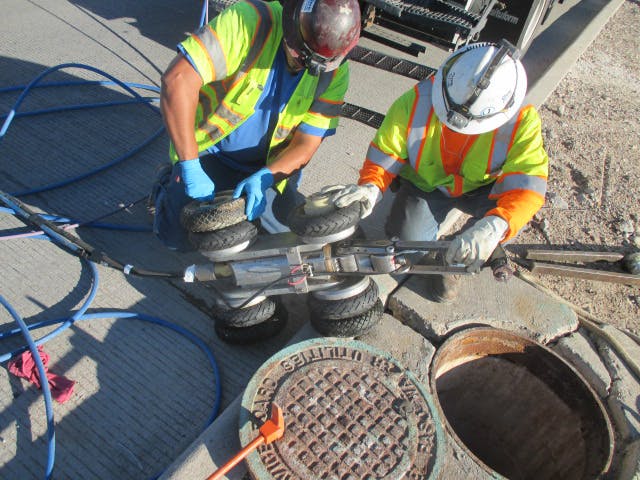
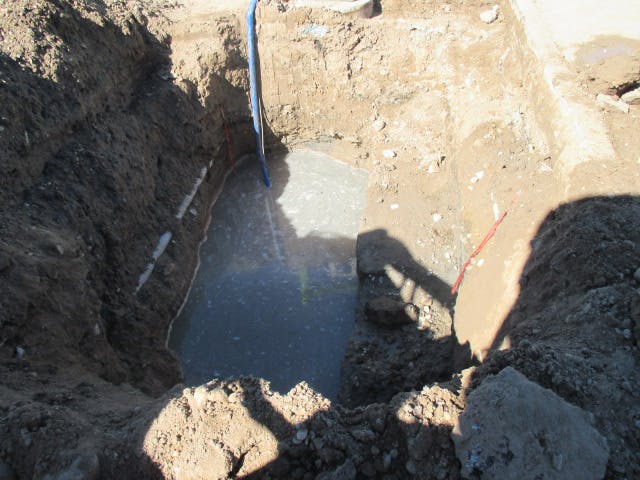
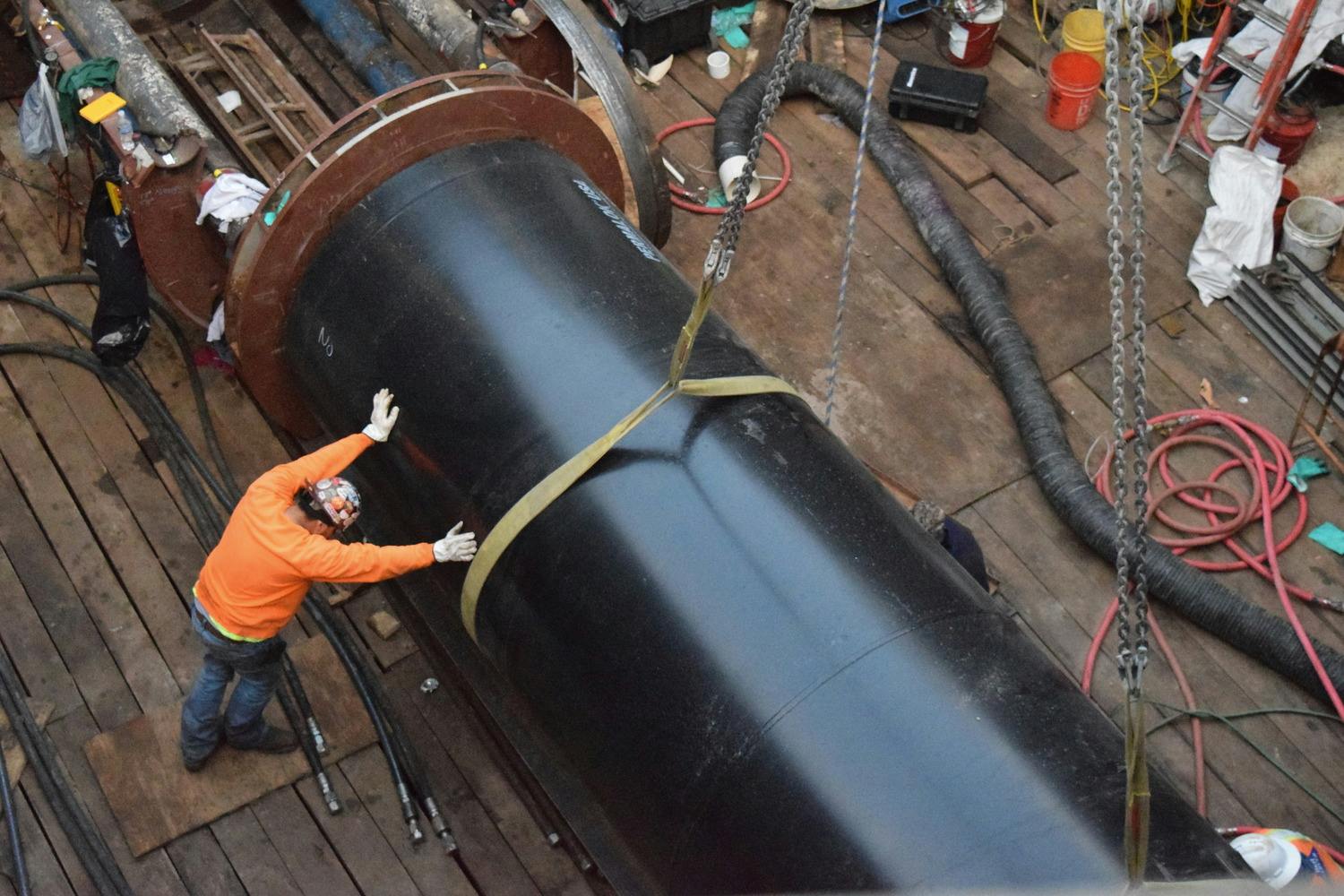
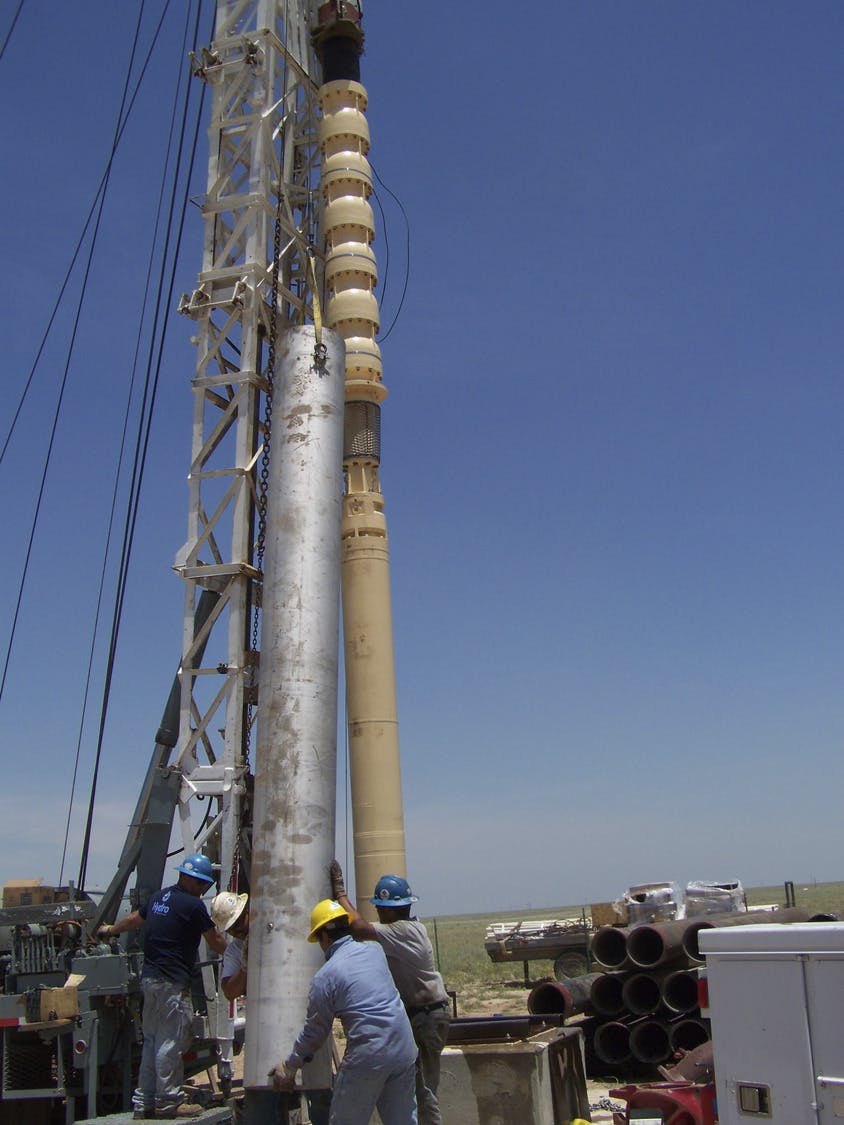
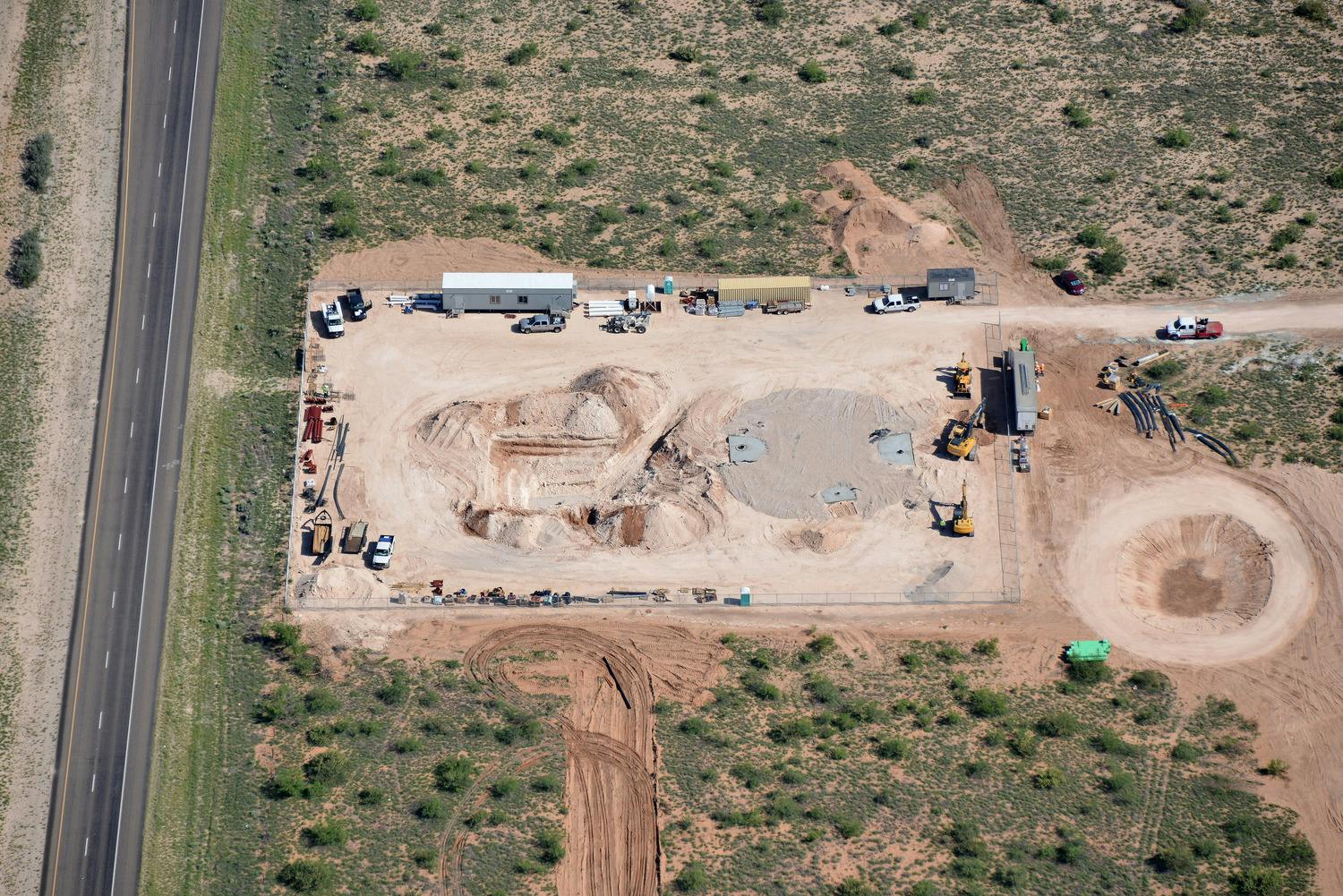
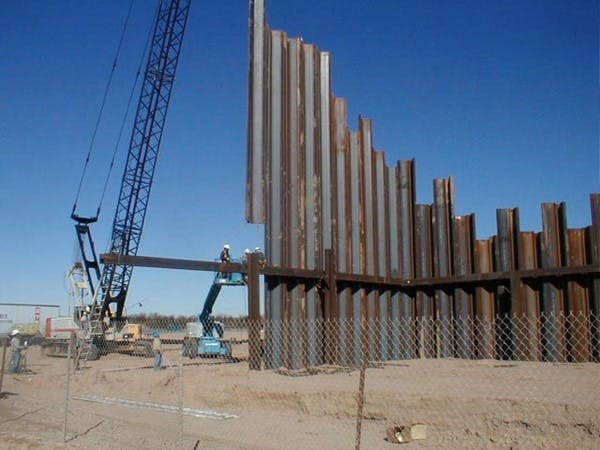
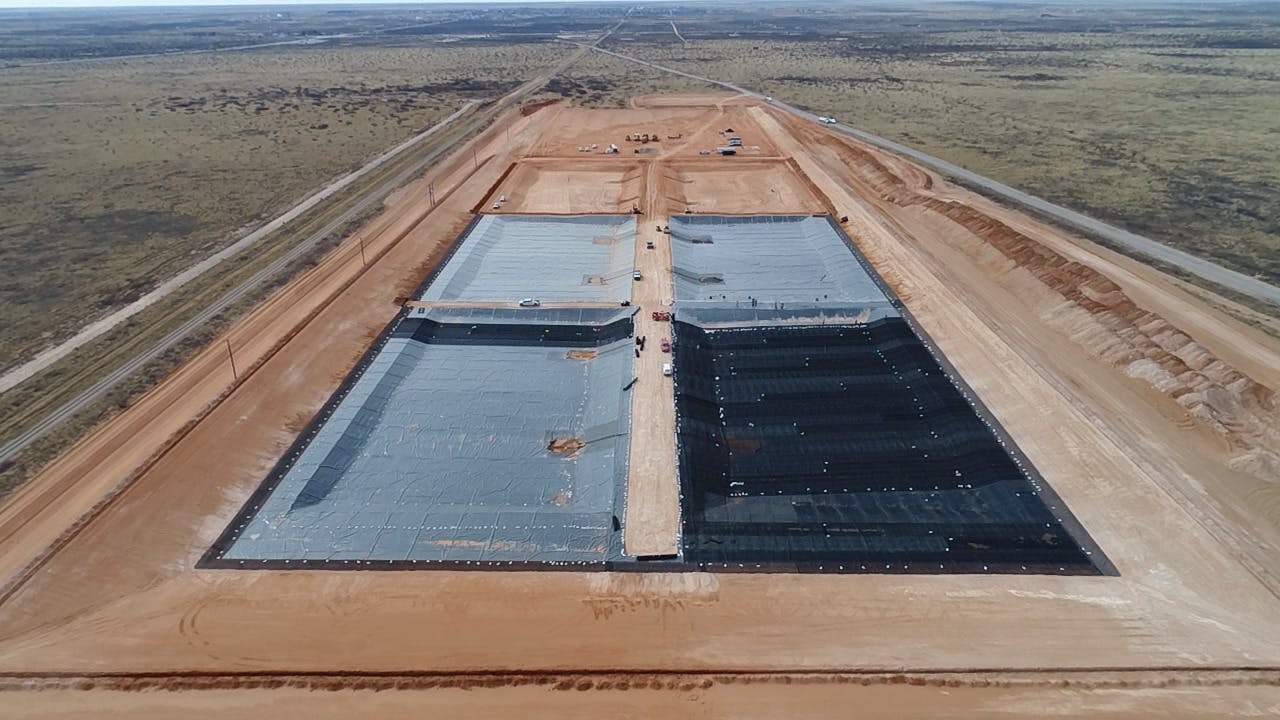
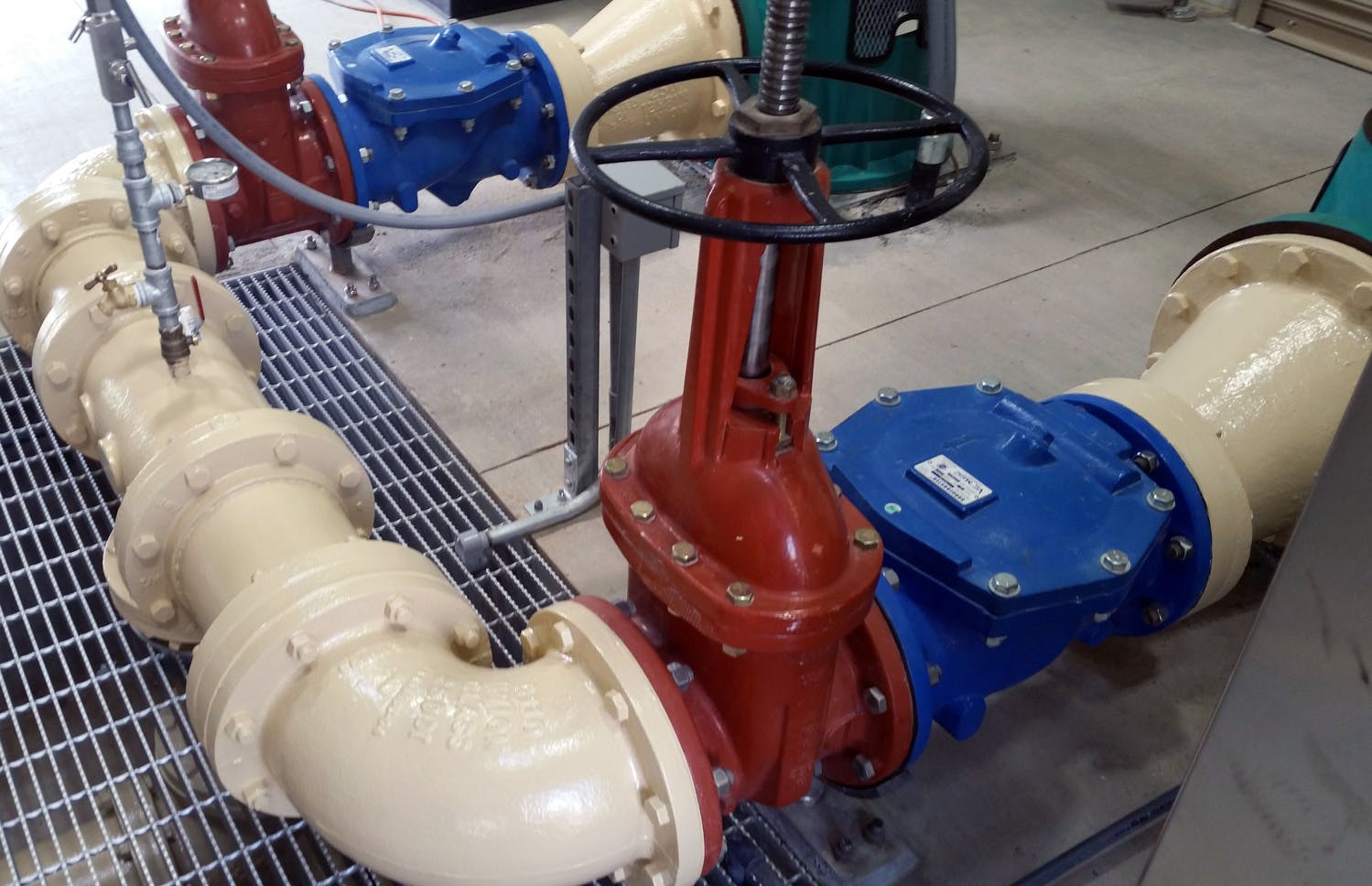
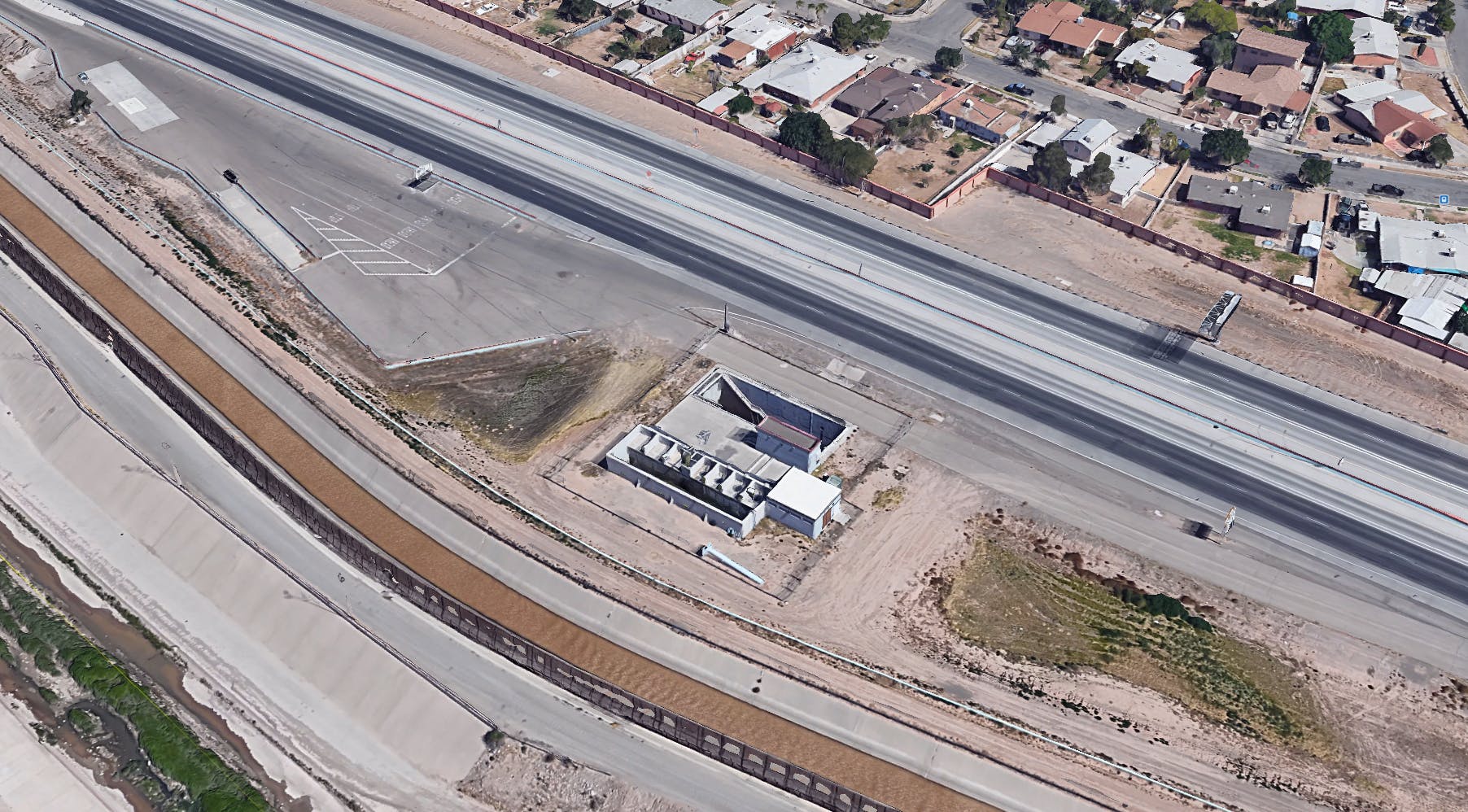
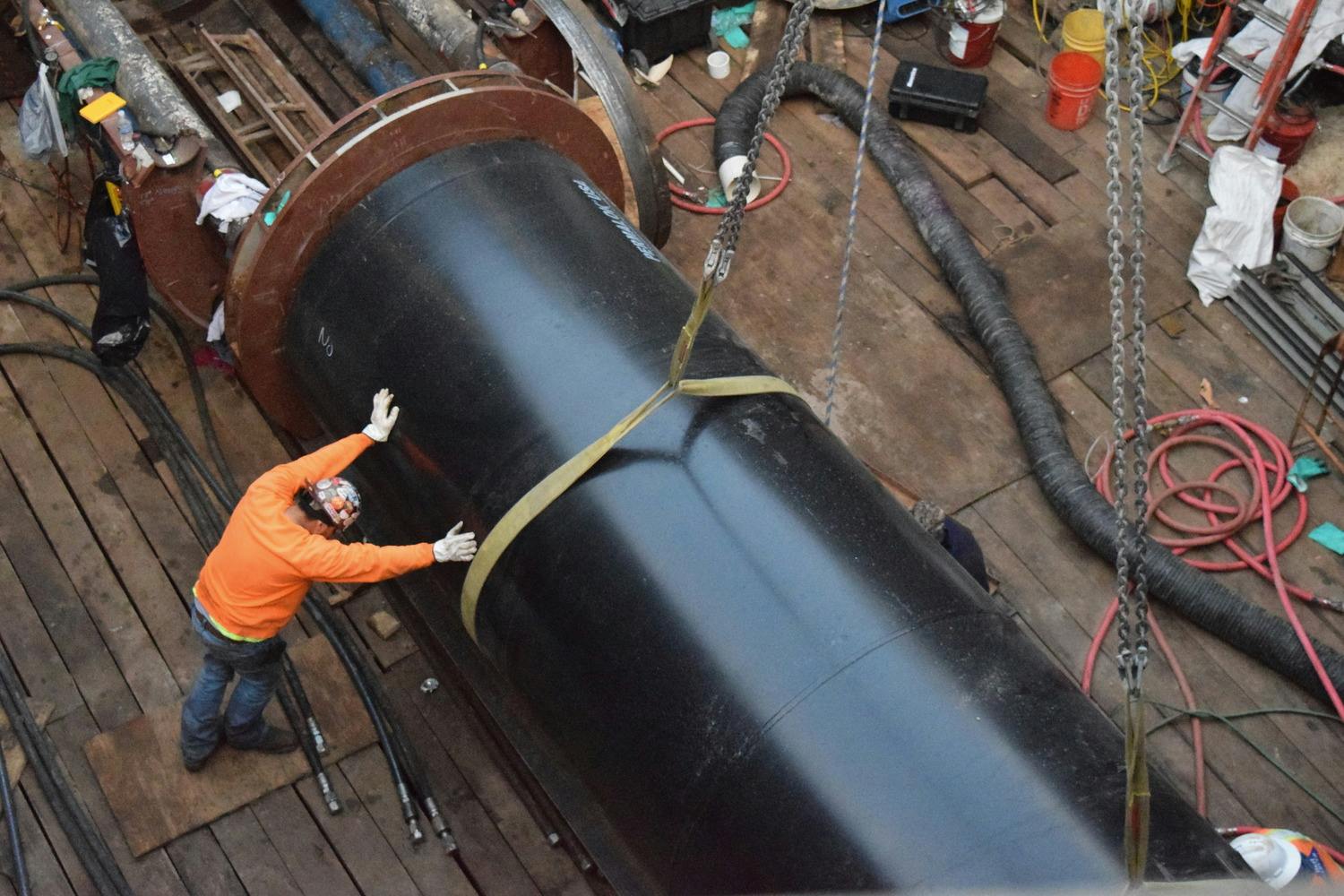
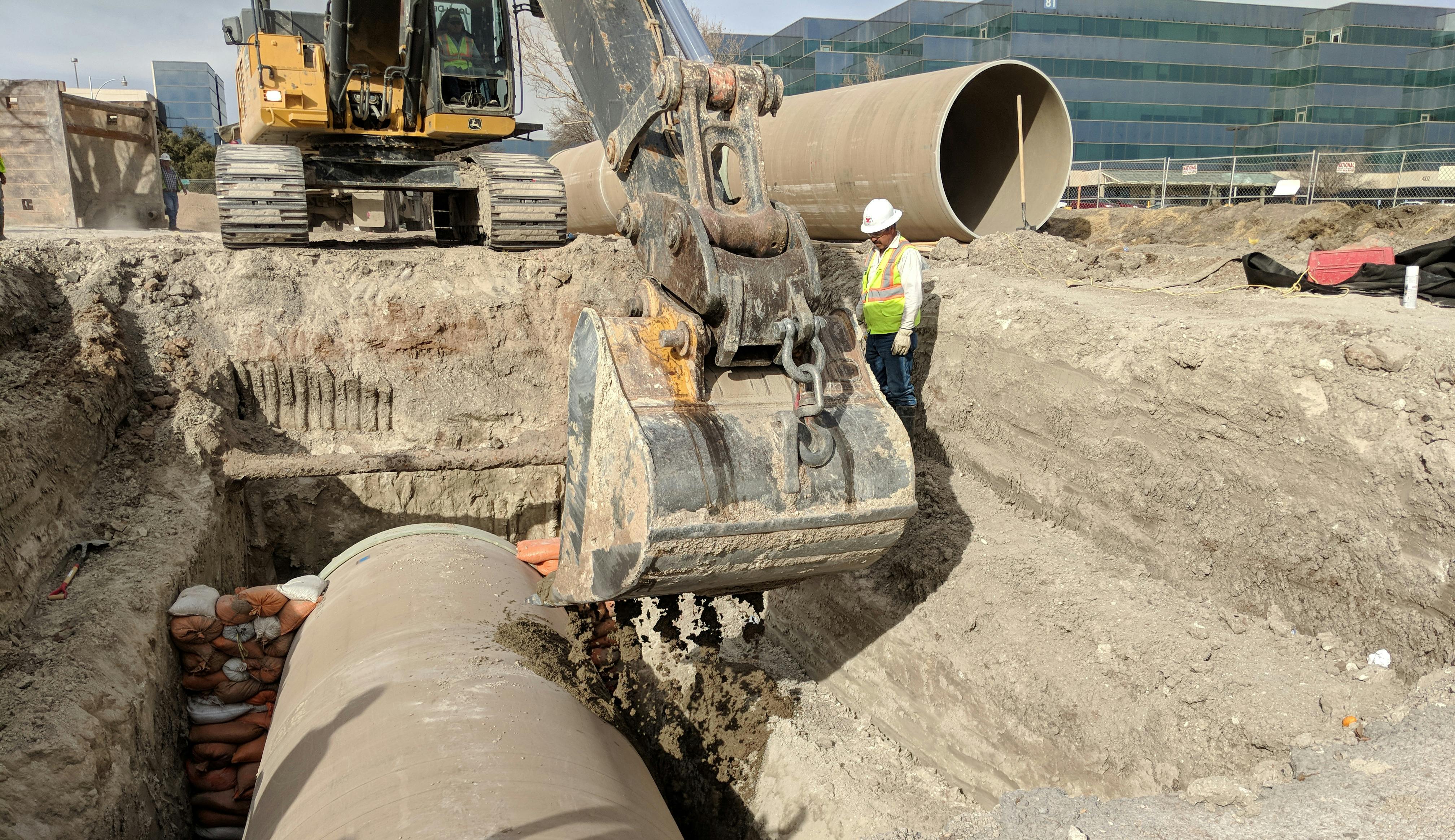
The Robertson Umbenhauer Water Treatment Plant, also referred to as the Canal Water Treatment, is over 75 years old and is located in Downtown El Paso. The plant is located between the Rio Grande River and the BNSF rail yard. The rail yard has been there for over 100 years making any infrastructure improvements near the plant very challenging. To address the aging infrastructure, El Paso Water wanted to replace existing transmission lines from the plant and build a new pump station.
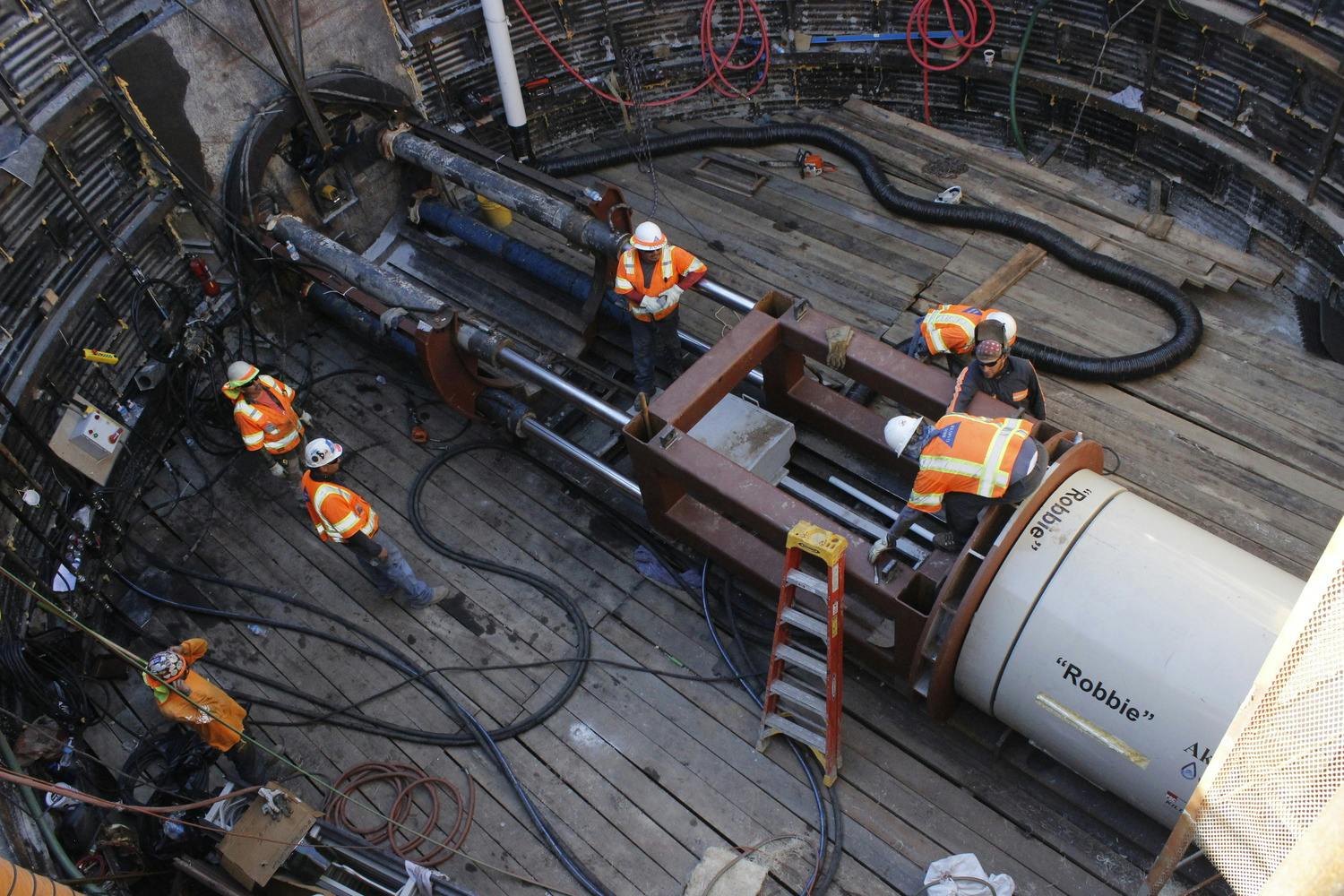
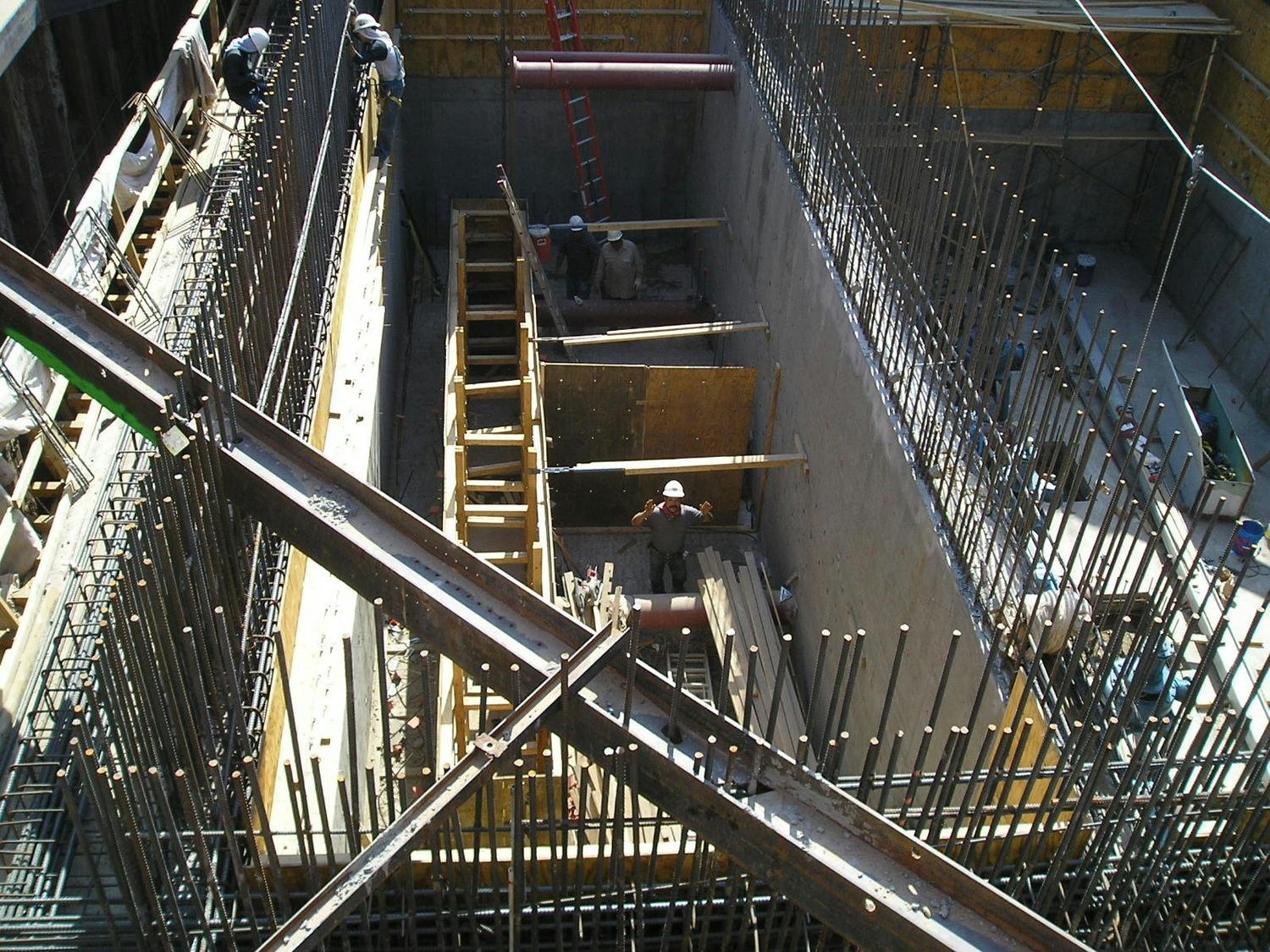
Any pipeline route from the plant required crossing the BNSF rail yard and Paisano Drive, a busy TxDOT controlled roadway. To mitigate risk, El Paso Water elected to use a design-build delivery method on this project. The project required a 66-inch-diameter, 570-foot-long tunnel under 18 active tracks of the rail yard. It also requires a second 315-foot-tunnel across a busy TxDOT roadway. Tunneling was completed using an Akkerman tunnel boring machine. BRH Garver was the prime contractor and the design/build partner on this project.
To facilitate the construction of both tunnels, a single large entry shaft was constructed within the rail yard. This required frequent contact with railroad personnel to coordinate access, safety requirements and storing material and equipment. The project team also had to work creatively to implement and maintain a settlement monitoring plan within the rail yard. Excavation within the rail yard had its complexities because the yard had several abandoned pipelines mixed with active pipelines that had been installed over the yard’s 100-year life. In addition to these challenges, the Border West Highway project by TxDOT had overlapping traffic control with this project.
Time Lapse: “Robbie” the Tunnel Boring Machine from Parkhill on Vimeo.
Awards
- ACEC Texas 2020 Engineering Excellence Awards – Gold Medal Award Recipient
- ACEC 2020 Engineering Excellence Awards – National Recognition Award
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
Canadian River Municipal Water Authority
- water-resources
- Sanford, Texas
Project Size
1,500 to 3,000 gallons-per-minute municipal well
Construction Type
Unit replacements
Project Components
Deep-set line shaft hydrid pumping units, adaptive submersible motor and solid-state soft starters for line shaft hybrid units
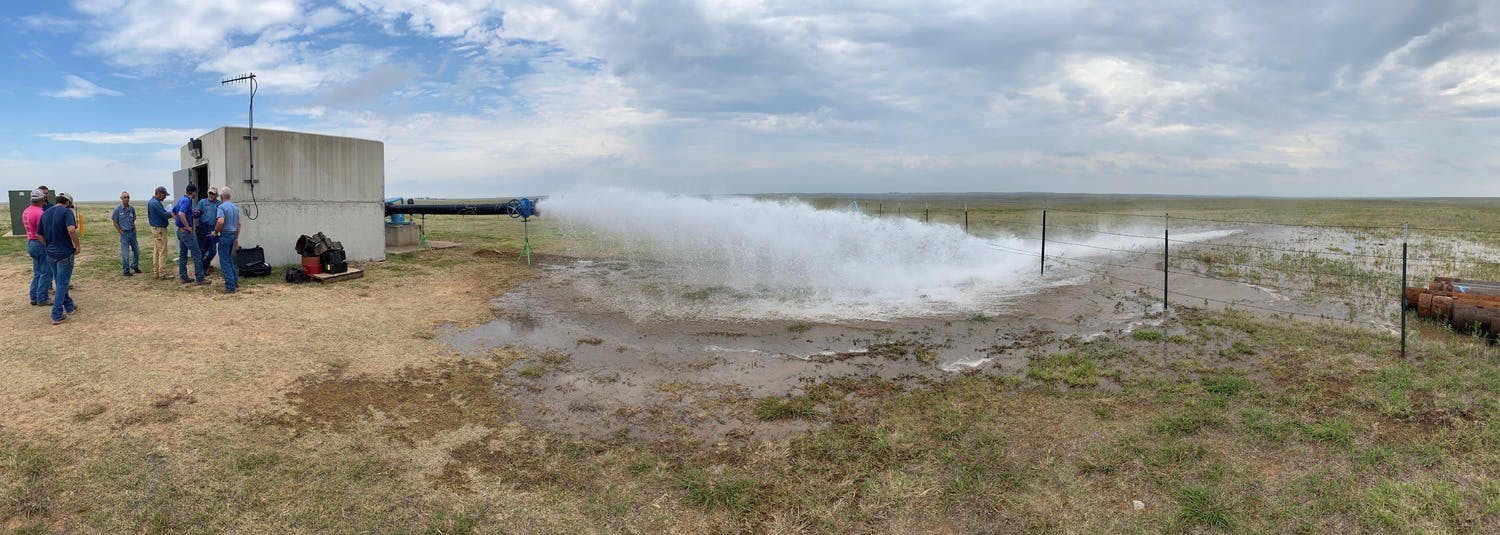
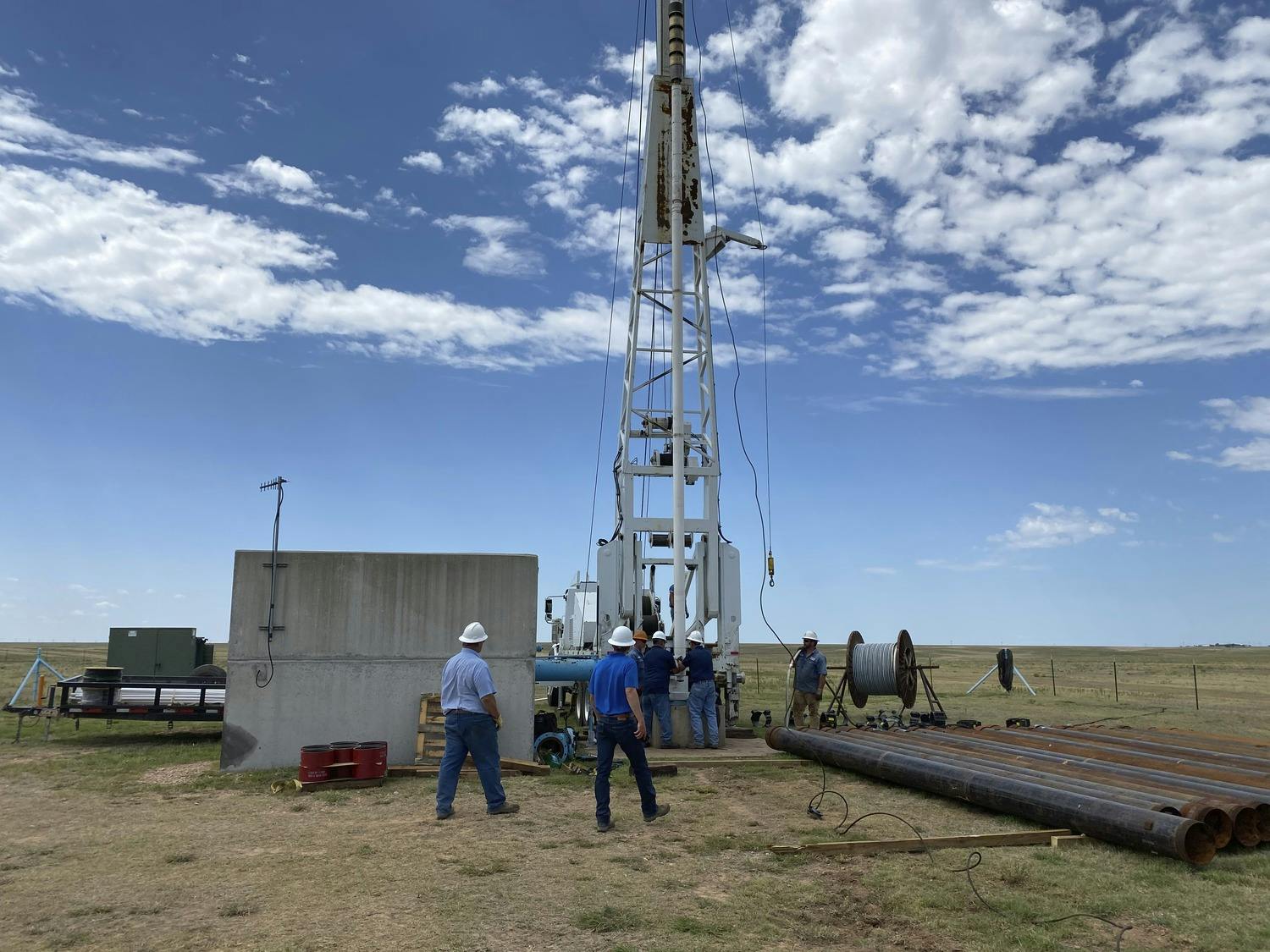
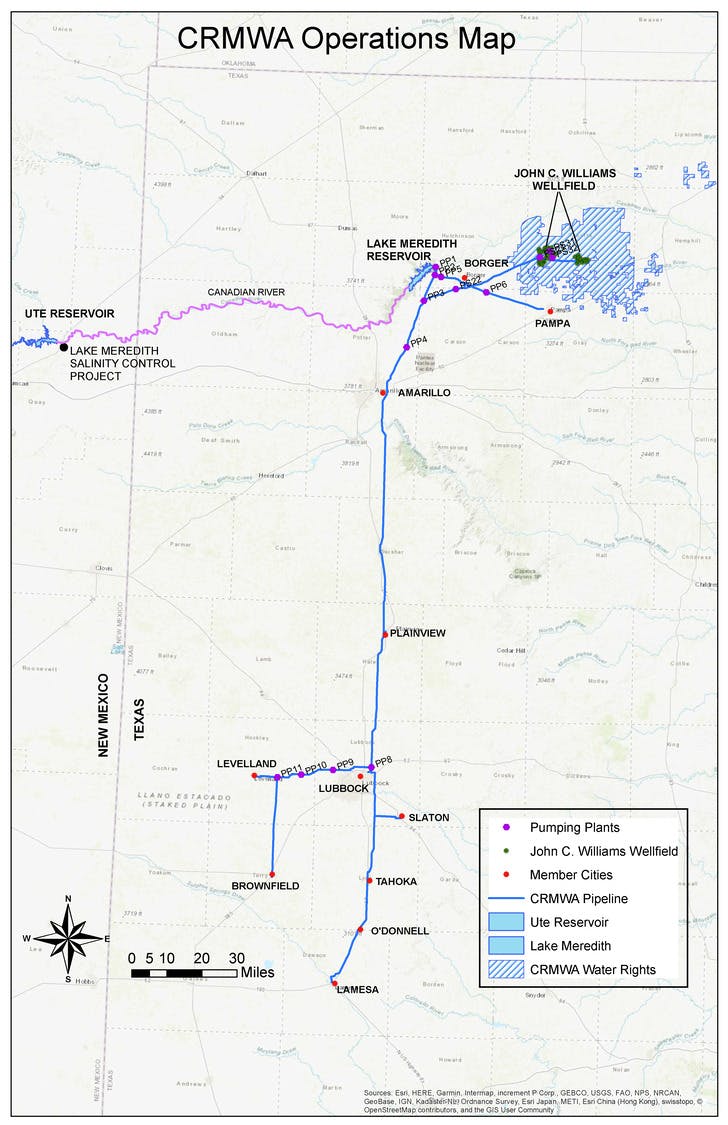
The goal of the CRMWA High Capacity, Deep Well, Beta Pumping Unit Replacements project was to improve the reliability and resiliency of the John C. Williams Wellfield. Three “Beta” sites were selected to replace existing problematic pumping units. One site incorporated the use of a submersible motor application, utilizing adaptive technology typically found in mining and petroleum industries. Achieving the necessary horsepower for the project (600 HP) required several submersible motors to be connected in series. The other two Beta sites utilized hybrid line shaft pumping units challenging those industries' upper limits.
Adapting submersible motor technology to municipal wells for this large horsepower size (600+ HP) and production capacity (1,500 to 3,000 gallons per minute) has essentially provided a new application for this type of equipment and an option for engineers to apply in the municipal discipline. Hybrid deep set line shaft pumping units incorporated into this project have basically raised the upper limit of the industry for this type of configuration. This project set a new standard that will further improve with the attrition of other existing pumping units and the construction of new wells.
The project will also have a significant long-term impact on the water supply and the area’s economy. The project assures the 500,000-plus citizens who are served by CRMWA have a reliable source of potable water, despite times of drought. Economically, the solutions developed for this project should yield considerable savings in maintenance costs to CRMWA and its 11 member cities. Sustainable designs and adaptation of technology in this project will play a large role in the continued success of this wellfield.
Services Provided
Design – adaptive technology from petroleum and mining industry for use in water supply and hybrid deep set line shaft pumping units.
Awards
Silver Medal
2021 Engineering Excellence Awards – ACEC Texas
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
City of Levelland
- water-resources
- Levelland, Texas
Project Size
500,000-Gallon Elevated Storage Tank
Construction Type
Rehabilitation
Project Delivery Method
Design-Bid-Build
Project Components
Exterior – over-coat paint system, new handrail at the top of the bowl, new access hatches, City of Levelland logo painted on the bowl
Interior – epoxy filler
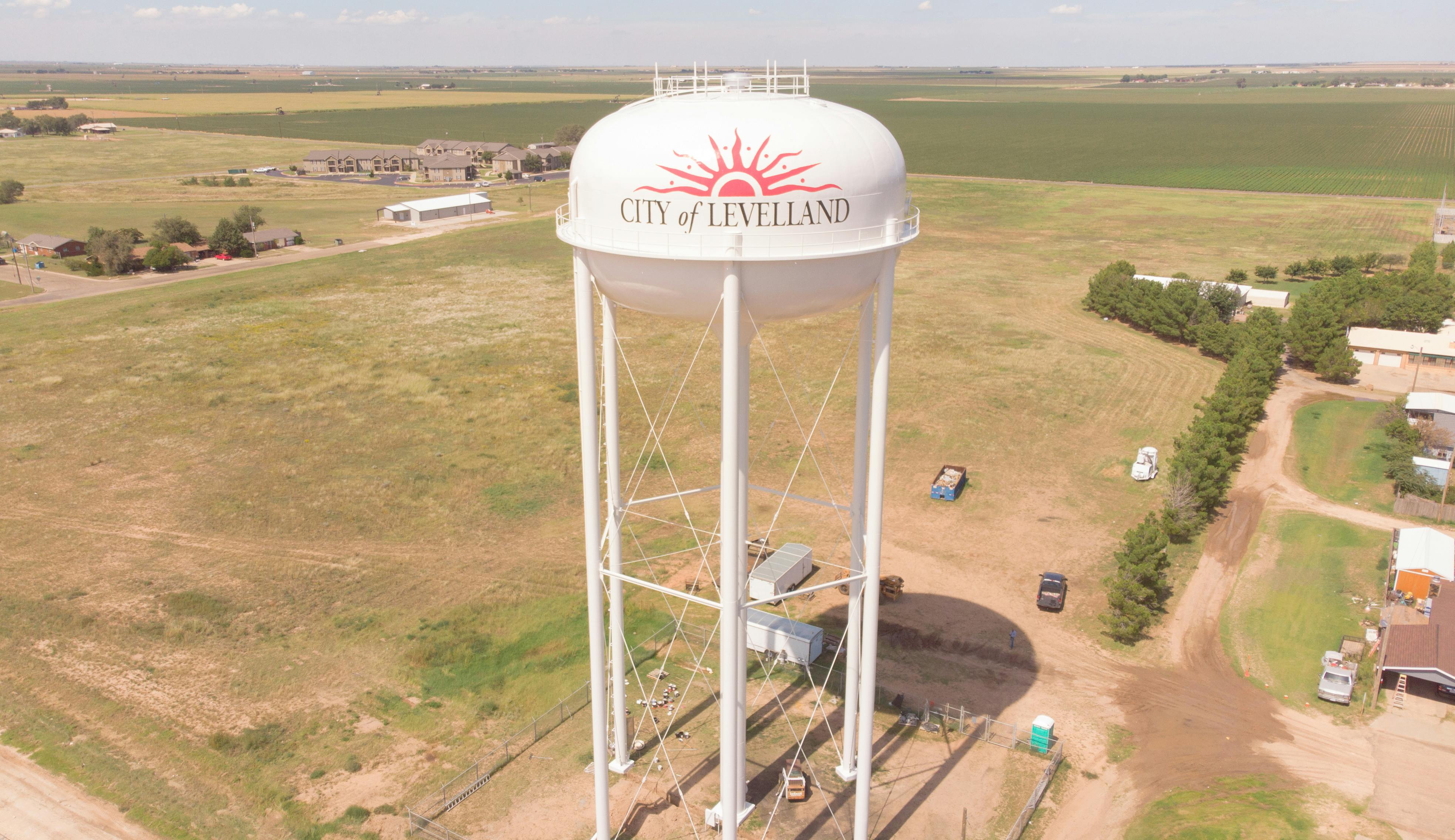
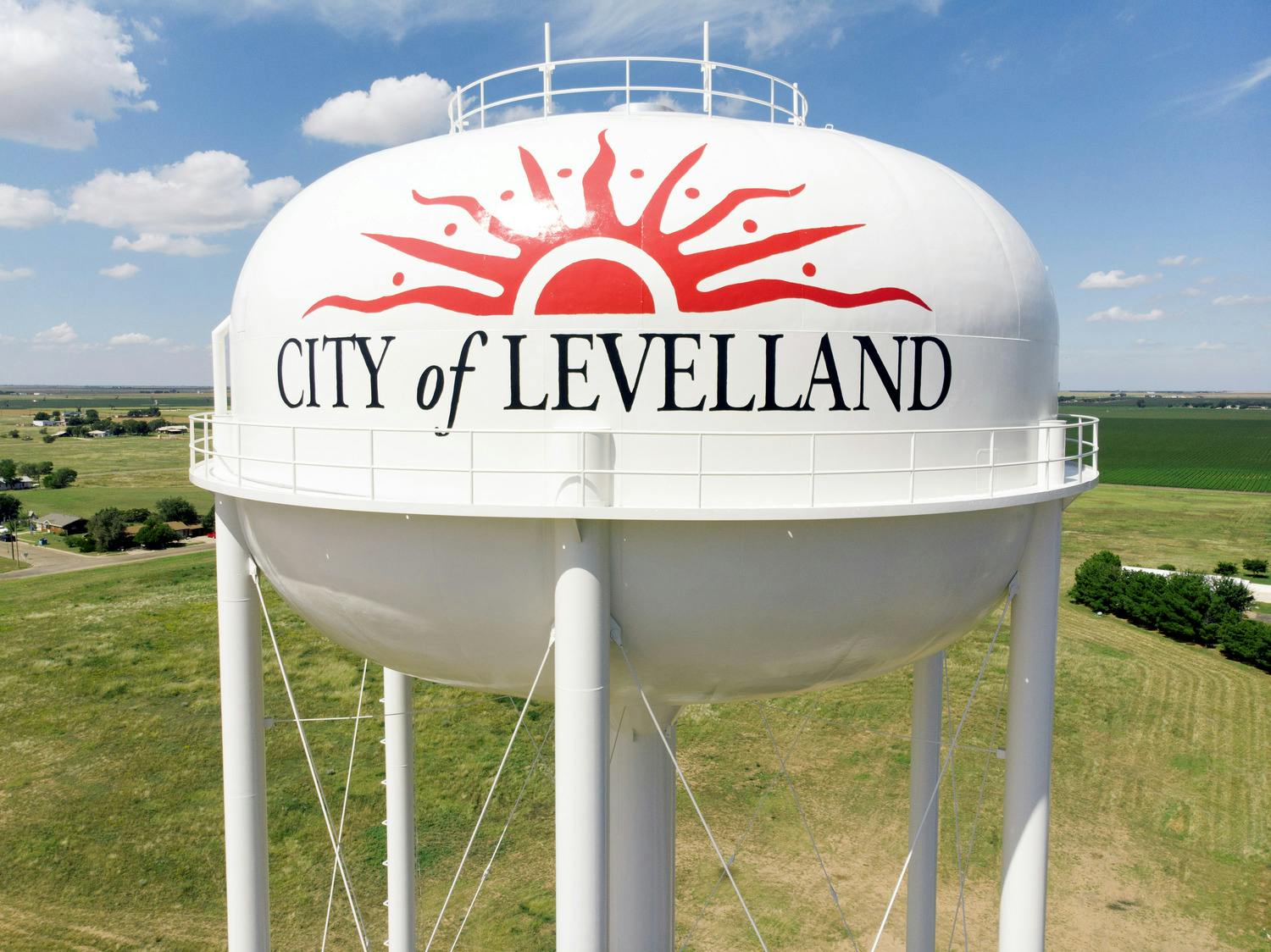
The City of Levelland is a growing community that serves nearly 14,000 West Texans. When driving to Levelland, it is hard to miss their many elevated storage tanks. The water tank that welcomes every resident and visitor is the Adam’s Street EST. This tank has served Levelland for many years and needed a tremendous facelift. Within the last few years, the city has dealt with frequent leaks out of the bowl of the tank. The city’s desire was to fast-track this rehabilitation.
The rehab project consisted of an over-coat paint system, a new handrail at the top of the bowl, new access hatches, adding the city’s logo, and many more necessary updates. After the rehab began, the tank's interior showed the tank was still in great condition but needed extra attention in declining areas. With an epoxy filler, the team brought the tank interior back to life, saving the existing steel from completely deteriorating and leaking. The finishing touch on the tank was painting the city’s official logo, which now faces the city and welcomes every person who passes through the community.
This tank rehabilitation project was a crucial, unexpected project for the city, and Parkhill coordinated taking the tank out of service at the right time of the year. Our contractor was able to get the tank back into services quicker than expected. So this 500,000-gallon water storage tank is now back in service.
See the City of Levelland Adams Street Elevated Storage Project by Parkhill on Vimeo
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
Midland County Fresh Water Supply District No. 1
- water-resources
- Midland, Texas
Project Size
15 miles of transmission line, 12 miles of collection pipeline, 26 potable water wells
Construction Type
Water supply
Project Delivery Method
CMAR
Project Components
Pipeline design, control system design, remote terminal, design, 4MG reservoir design, well design
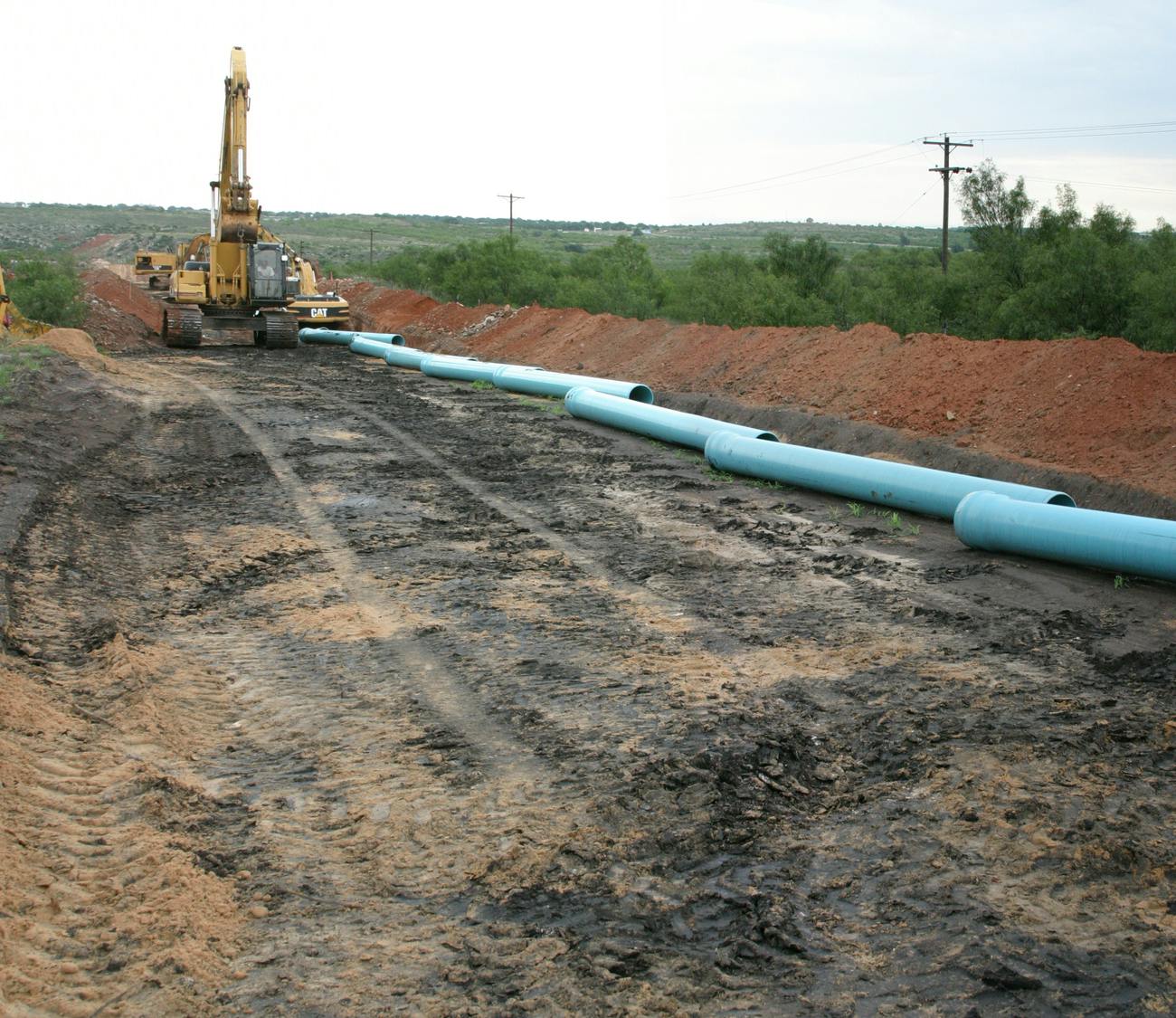
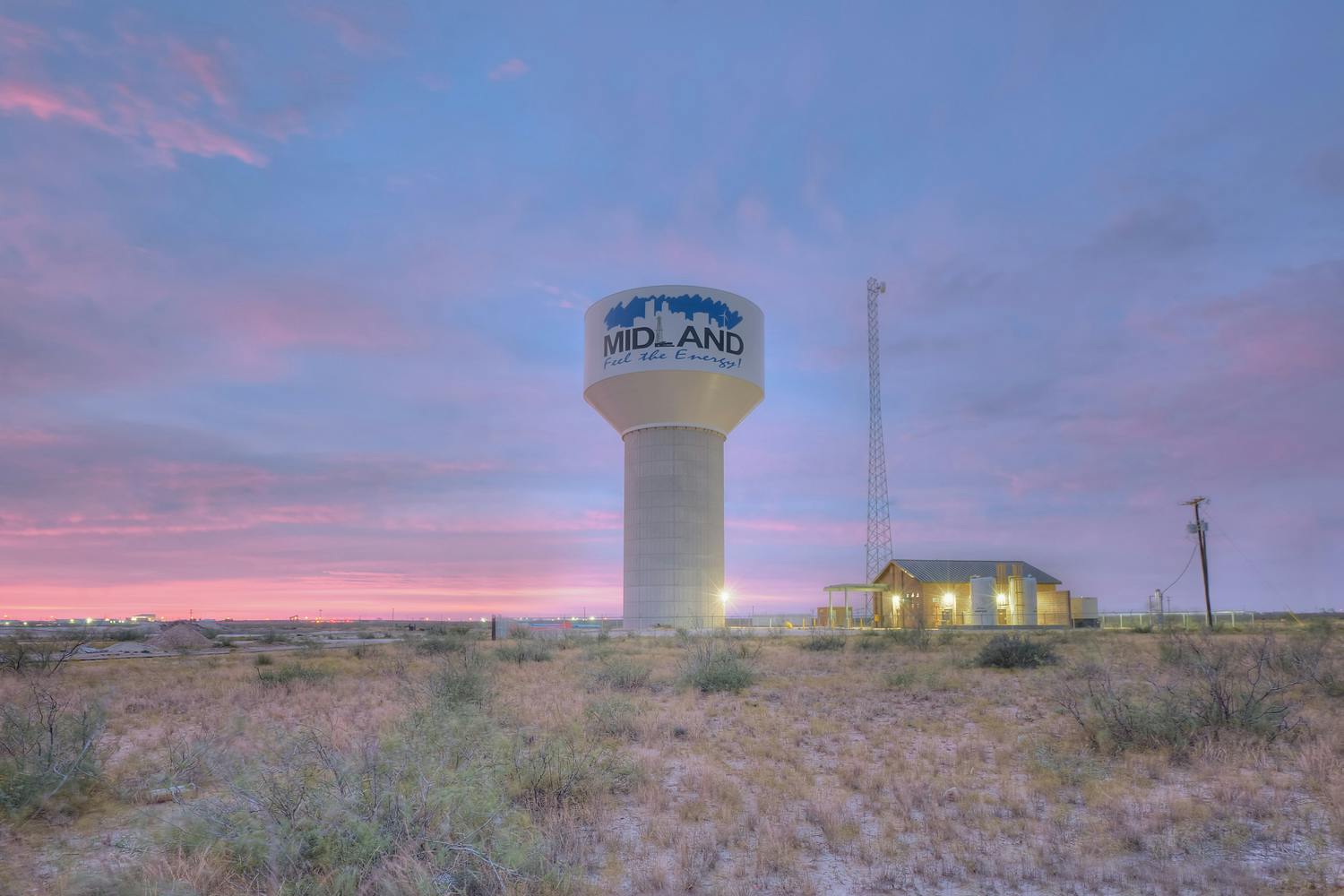
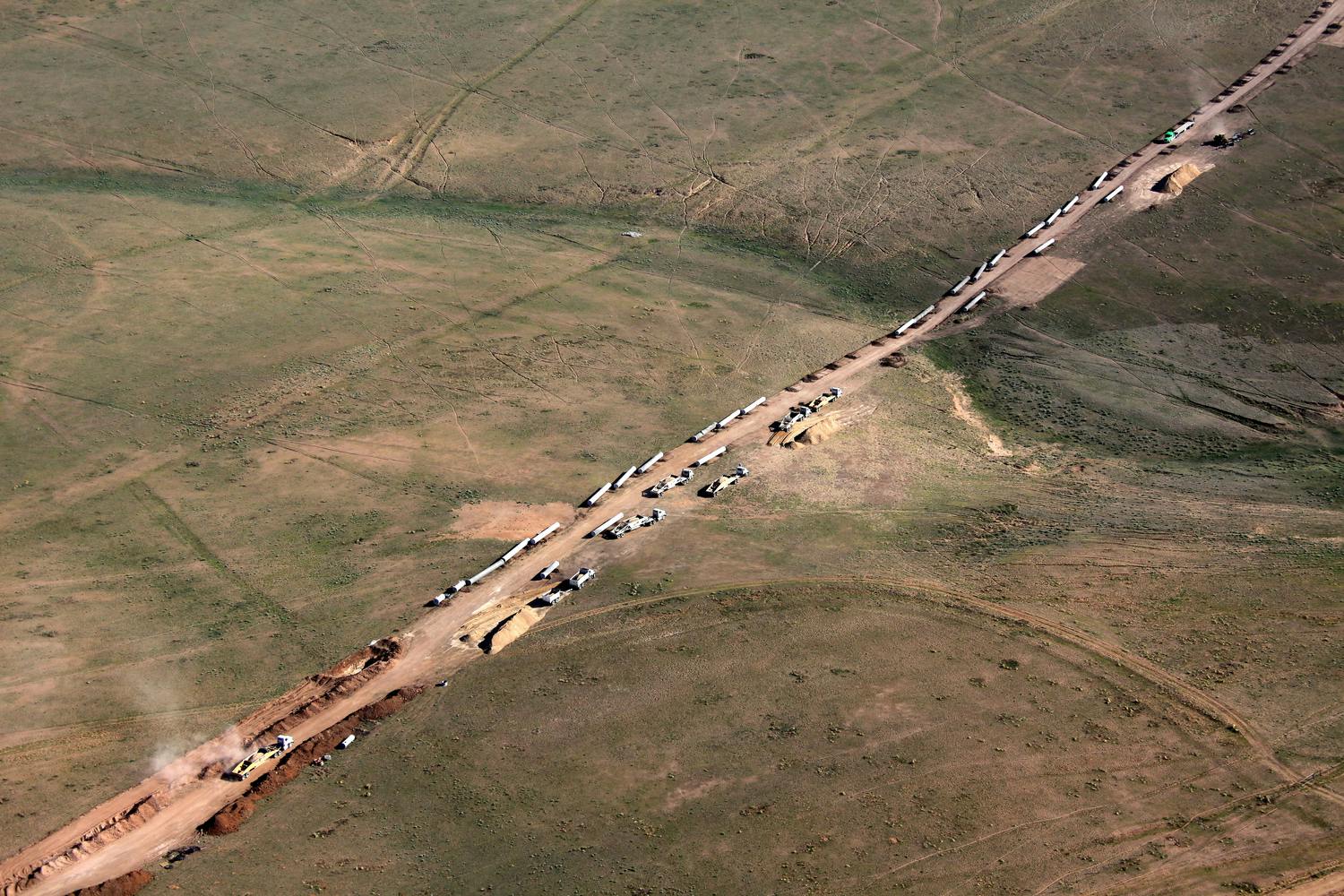
 This project was a follow-up to the T-Bar project. ClearWater Ranch was purchased by the City of Midland to increase its amount of available water supply, while also helping to improve the quality of water delivered from the T-Bar system. The water obtained from the ClearWater Ranch is high quality, which ultimately doubles the pumping capacity of the existing T-Bar ranch because of the ability to blend the two sources. ClearWater Ranch can produce 4 million gallons of water per day, and because of its recharge capabilities, it is expected to last 40 years. The district delivers an average of 3.65 million gallons per day to the city. It is estimated that about 15 percent of the water used daily by Midland water customers is from T-Bar and ClearWater Ranch Projects.
This project was a follow-up to the T-Bar project. ClearWater Ranch was purchased by the City of Midland to increase its amount of available water supply, while also helping to improve the quality of water delivered from the T-Bar system. The water obtained from the ClearWater Ranch is high quality, which ultimately doubles the pumping capacity of the existing T-Bar ranch because of the ability to blend the two sources. ClearWater Ranch can produce 4 million gallons of water per day, and because of its recharge capabilities, it is expected to last 40 years. The district delivers an average of 3.65 million gallons per day to the city. It is estimated that about 15 percent of the water used daily by Midland water customers is from T-Bar and ClearWater Ranch Projects.
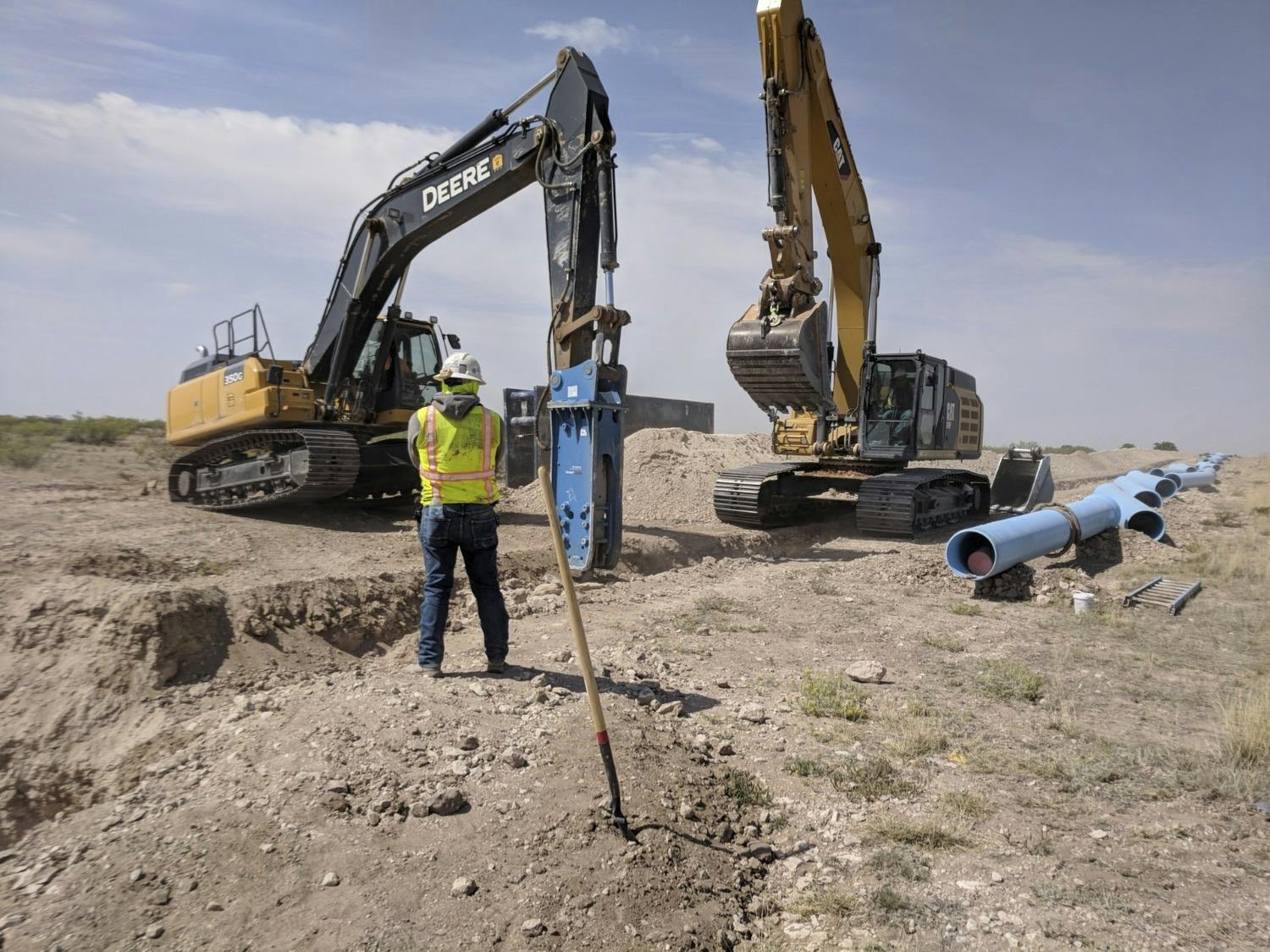
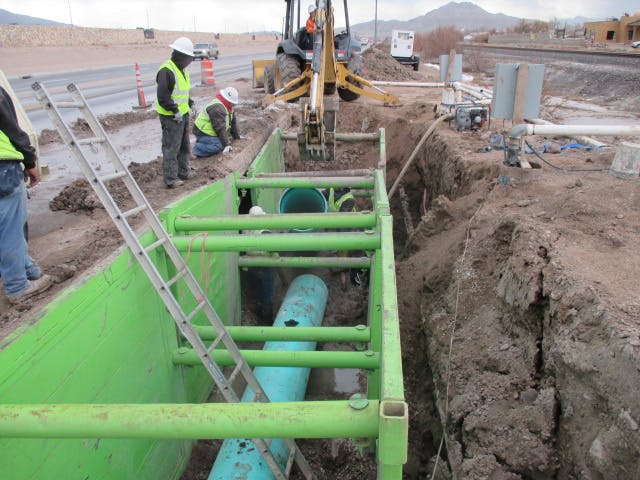
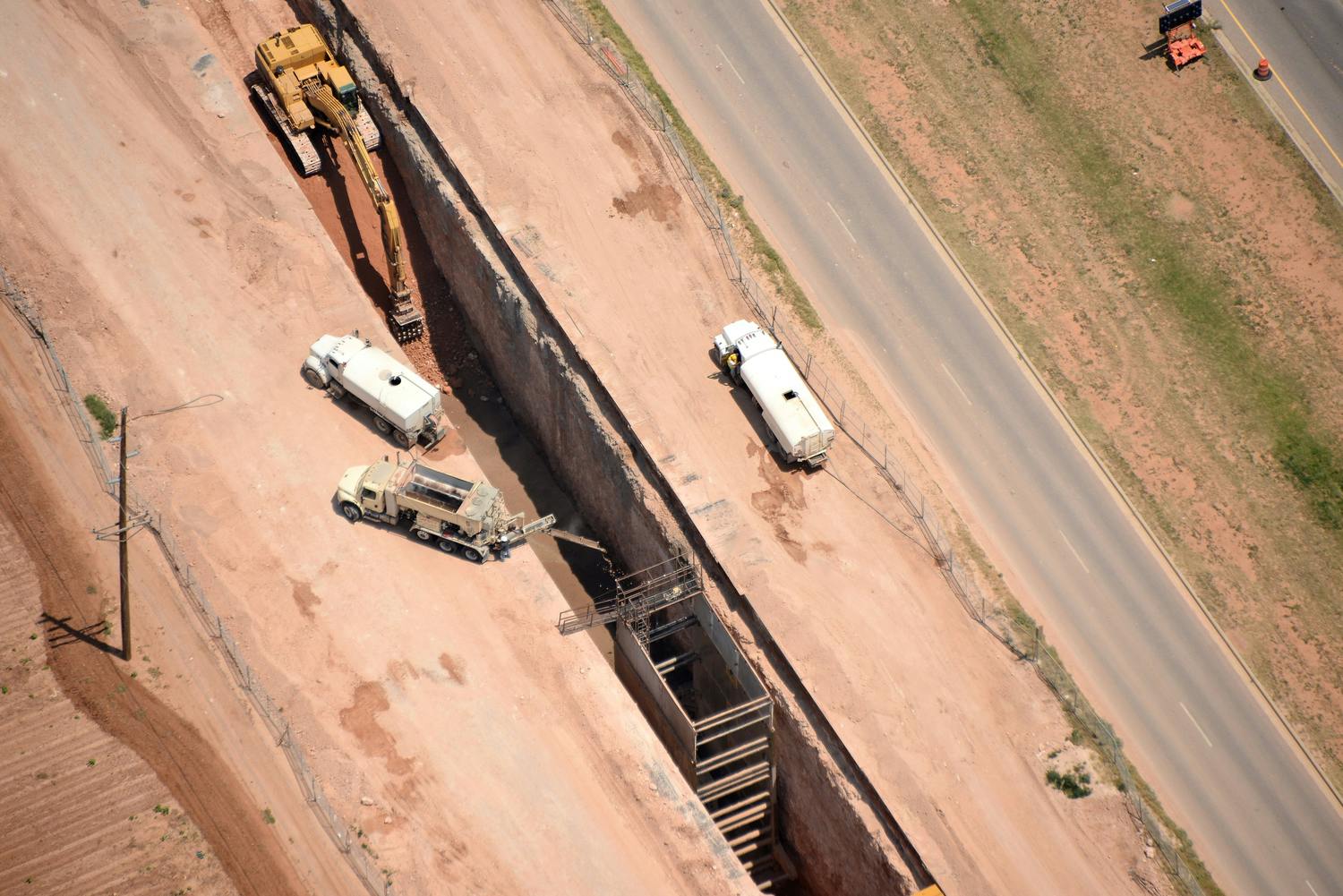
This project was completed under a Construction Manager at Risk contract. As with the T-Bar project, the project schedule was very accelerated. The initial tasks were to determine a tie-in location to the T-Bar system and an alignment from the ClearWater Ranch well field. Based on hydraulics and the capability for mixing, the ClearWater transmission line tied into a 2-million-gallon tank at the T-Bar well field. Parkhill then developed several alternative routes between the T-Bar well field and the ClearWater well field. To analyze the routes, we used a combination of aerial mapping, landowner maps, and hydraulic modeling to determine the most efficient route. The route included a railway crossing, two state highway crossings, and several county road and ranch road crossings. In addition, the land acquisition subconsultant had to coordinate with several landowners to identify specific needs for each landowner.
The alignment was routed near the town of Kermit, so water/wastewater line crossings were minimal. However, because of the oil and gas industry in the area, the project crossed several large gas lines. The gas and oil lines ranged from less than 4” in diameter all the way up to 14” in diameter.
From the time that Parkhill started design work to the time the project was moving water, it took about 18 months.
ClearWater Ranch Project Statistics
- 15 miles of 16” and 18” transmission line
- Ground storage tanks
- 26 new potable water supply wells
- 12 miles of collection piping
- 4 MGD pump station
Awards
2015 Associated Builders & Contractors, Inc. South Texas Chapter
Public Works / Environmental Category
Excellence in Construction
ClearWater Ranch Project
Midland, Texas
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
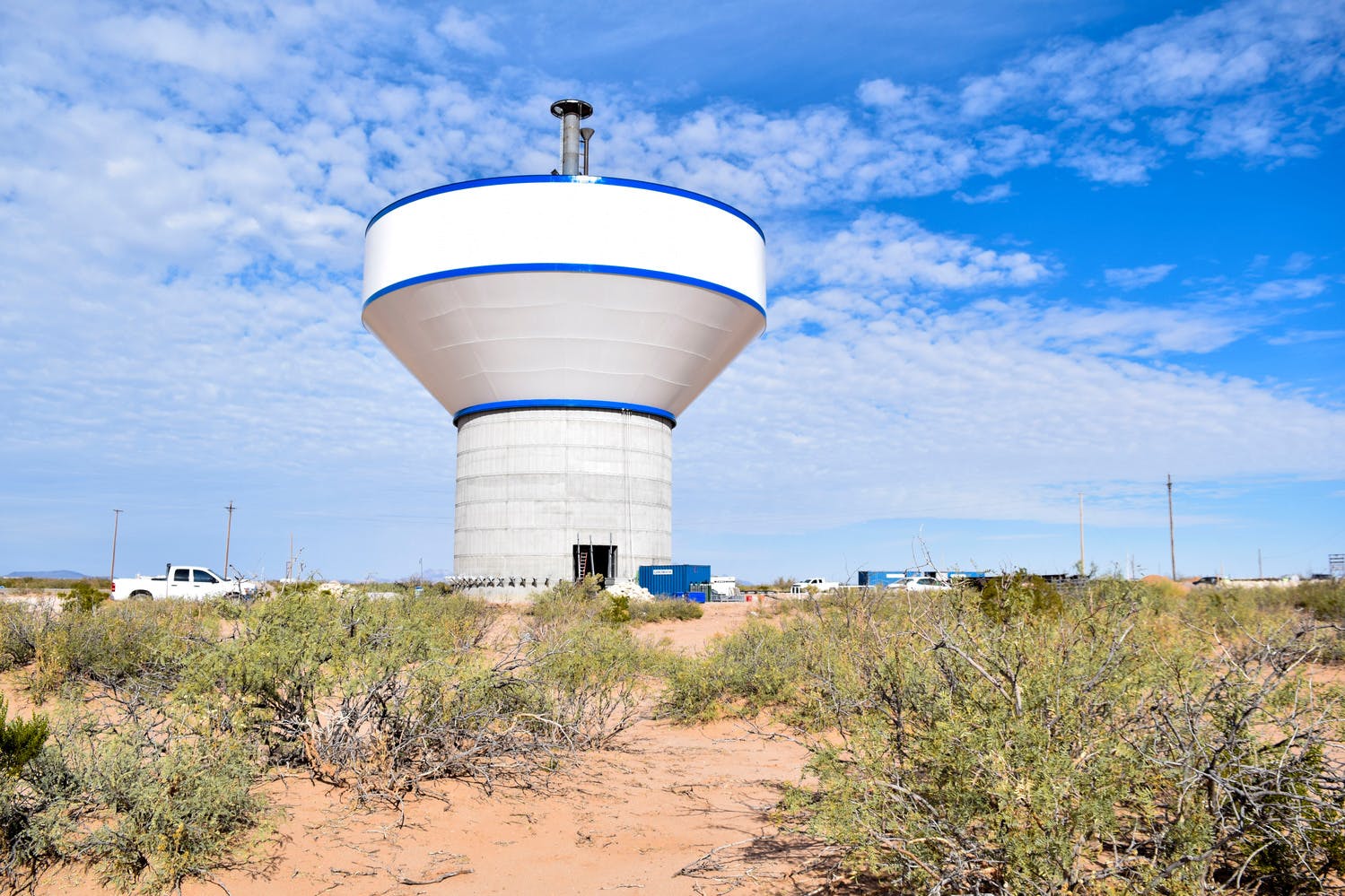
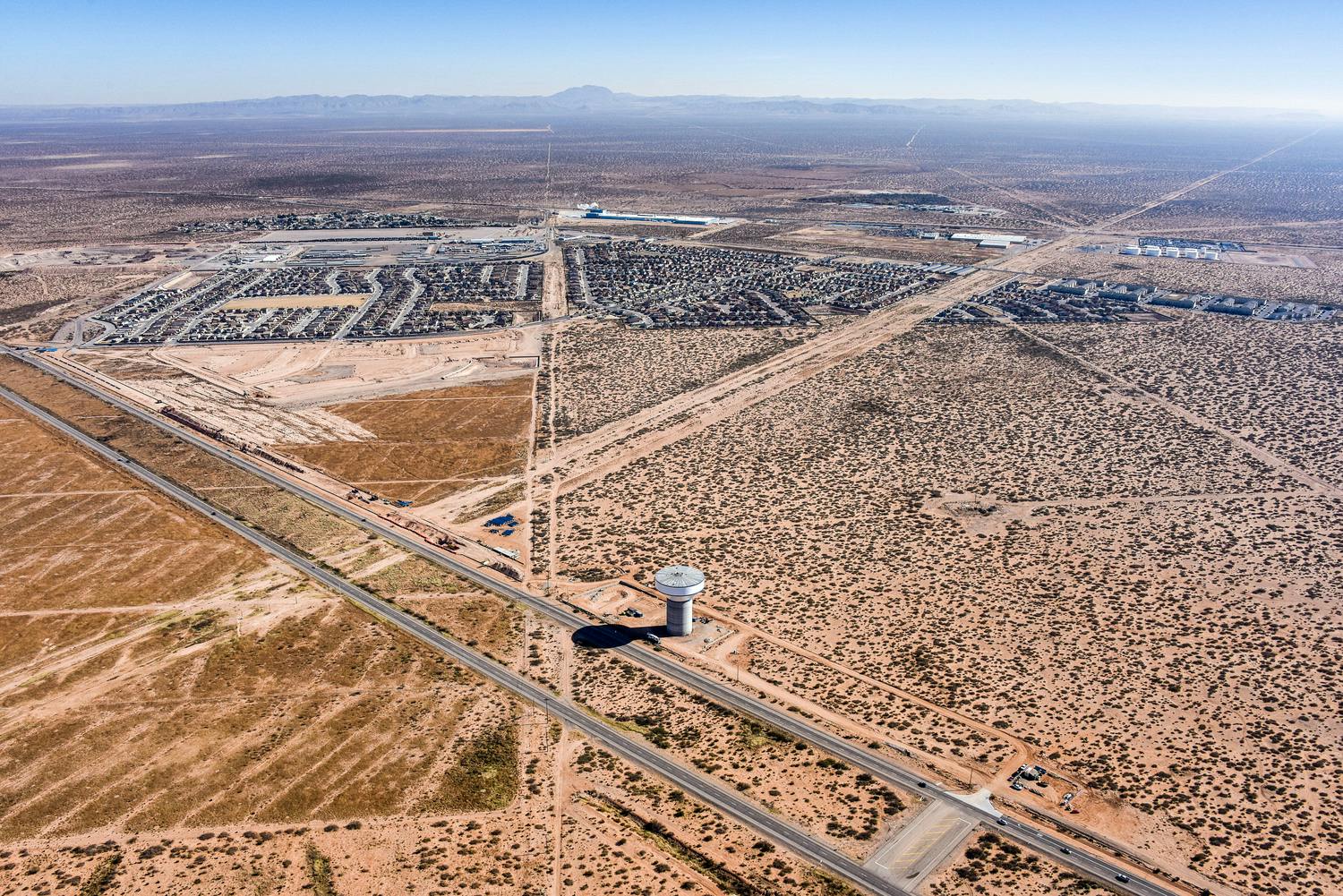
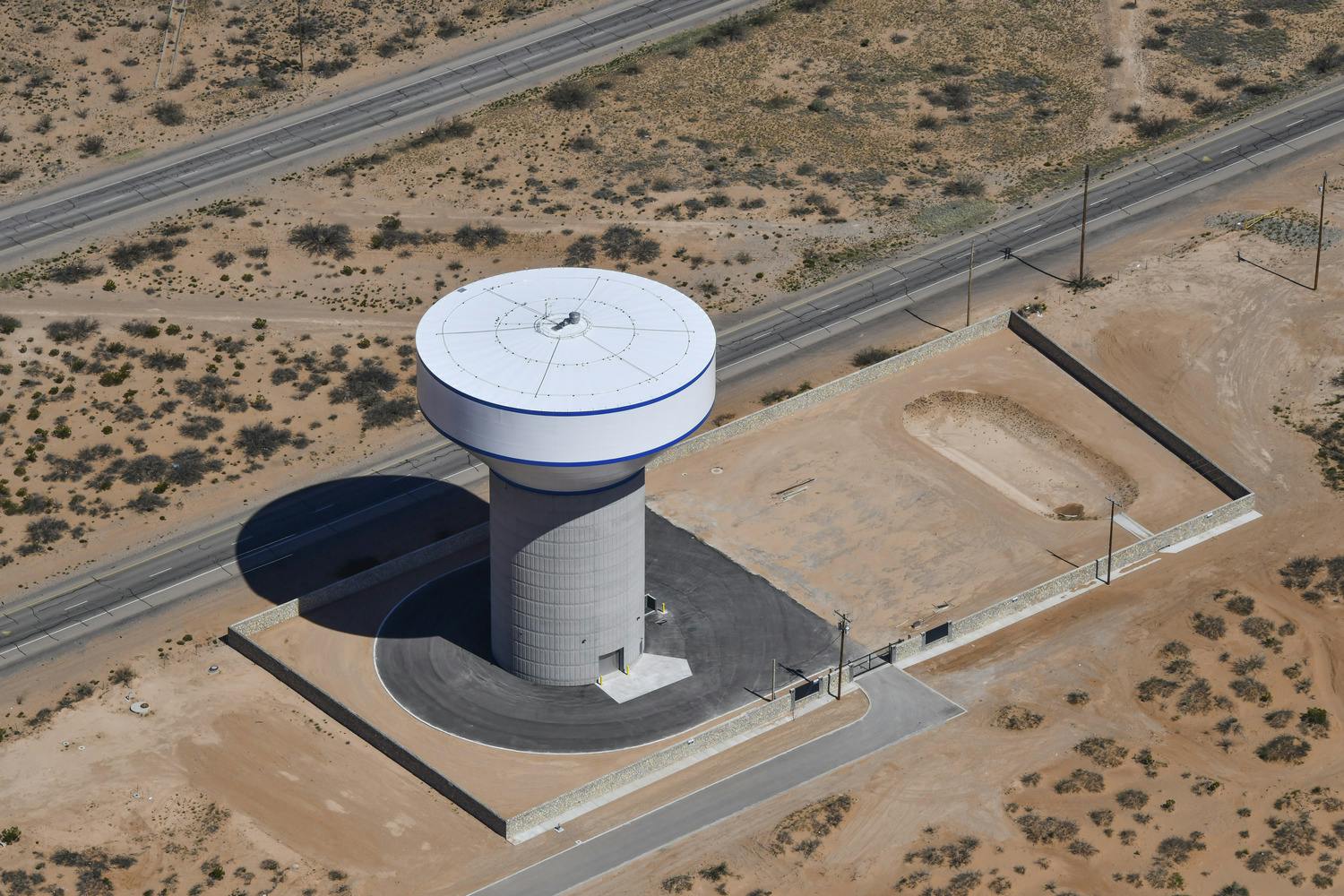
El Paso Water
- water-resources
- El Paso, Texas
Project Size
215 feet tall and holds 3 million gallons
Construction Type
New 3 MG elevated storage tank
Project Delivery Method
Design-Bid-Build
Project Components
Design, excavation and placement of tank foundation, concrete pedestal and steel tank, cathodic protection system, tank painting and logo, site piping with water main tie-ins, site grading, paving and access driveway, deceleration and acceleration lanes in TxDOT right-of-way, overflow basin, rock wall, electrical and instrumentation, disinfection and testing, and other miscellaneous items
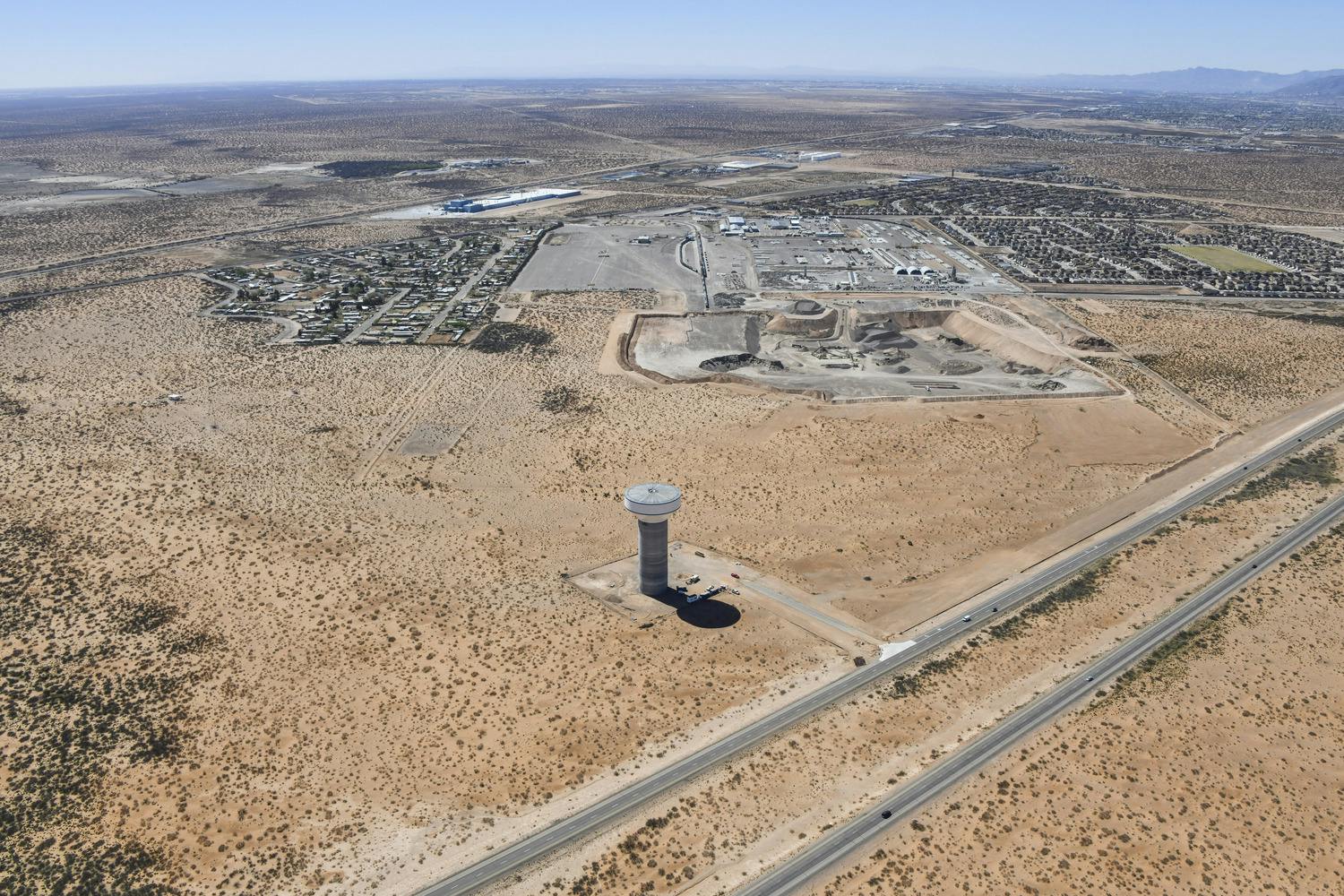
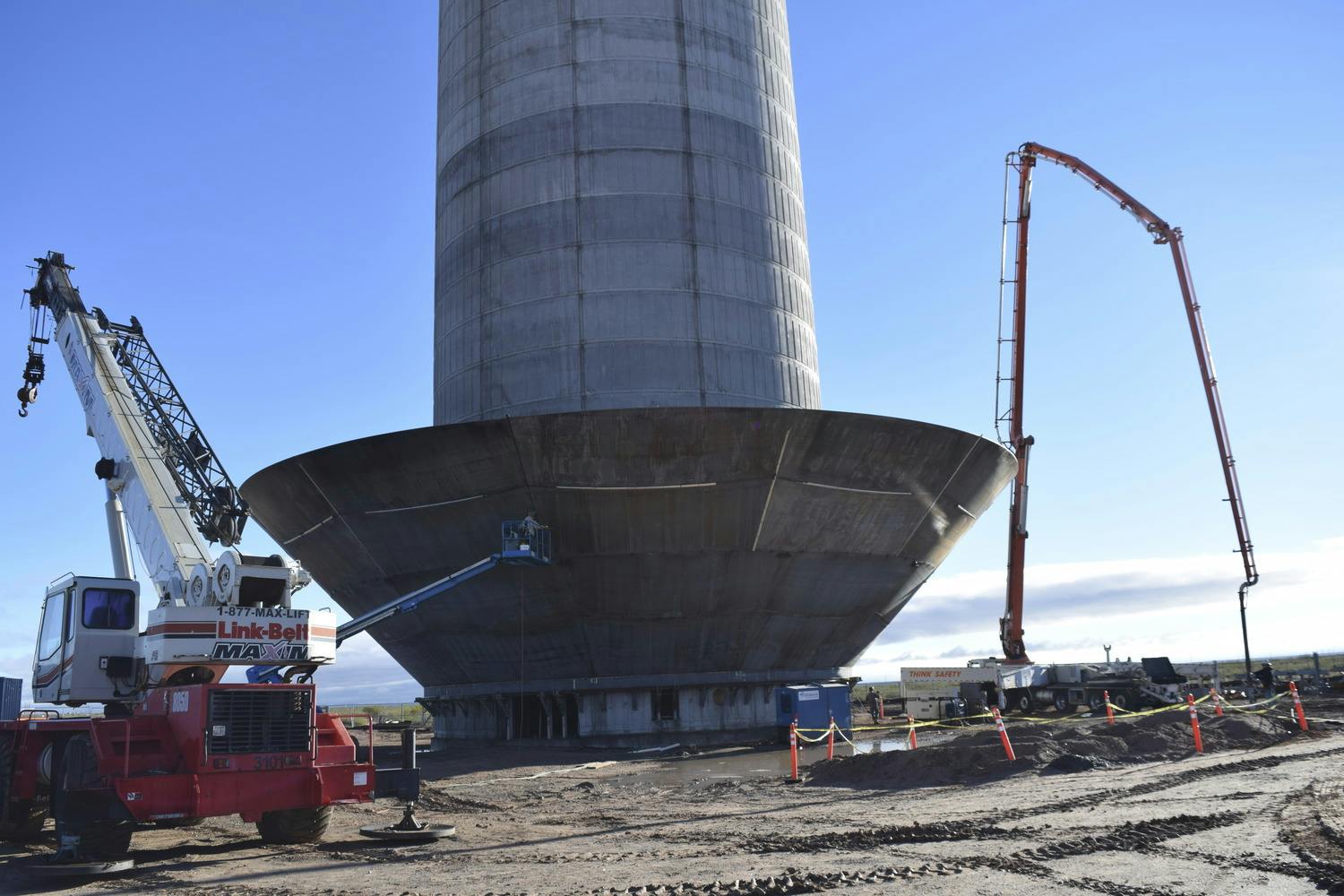
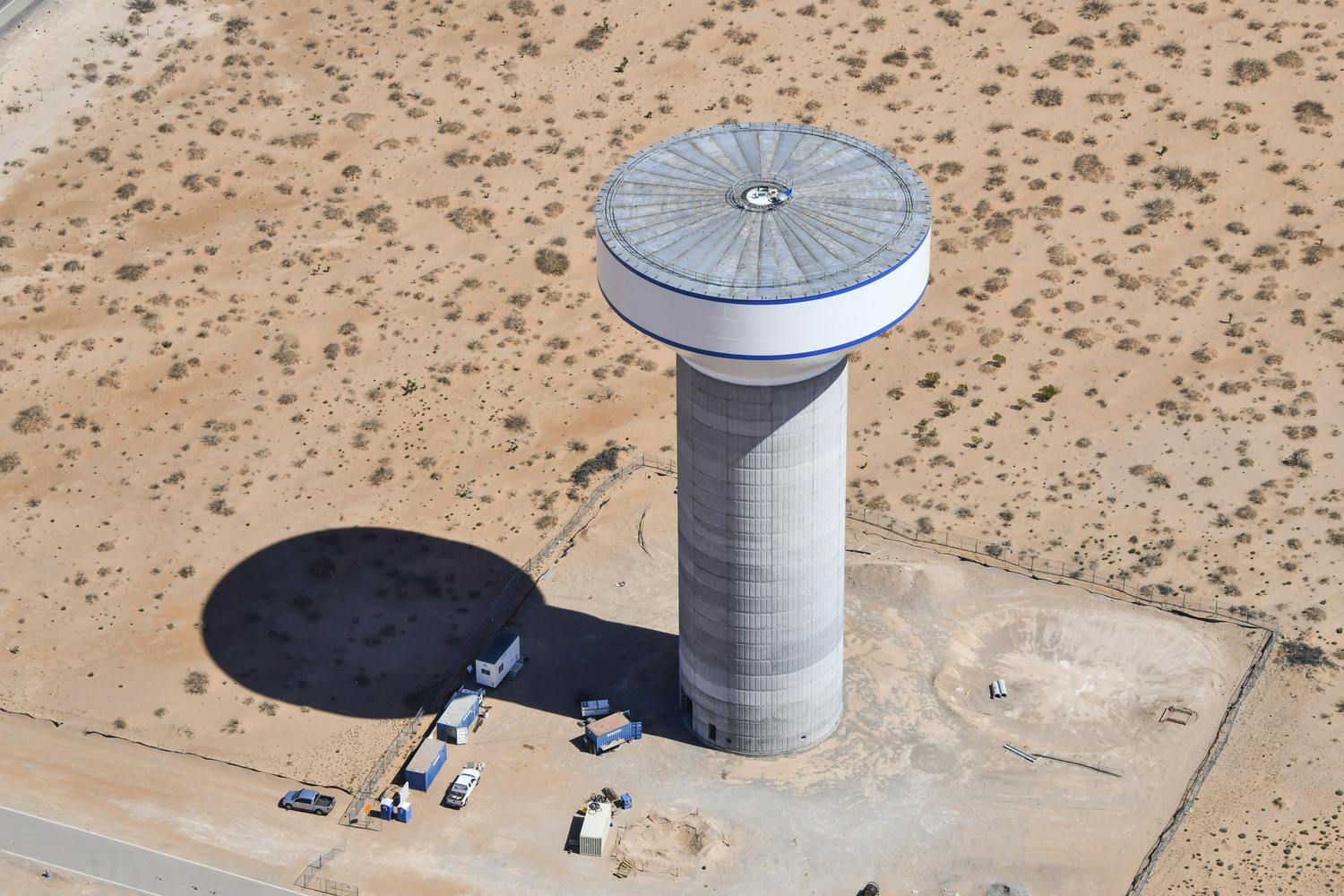
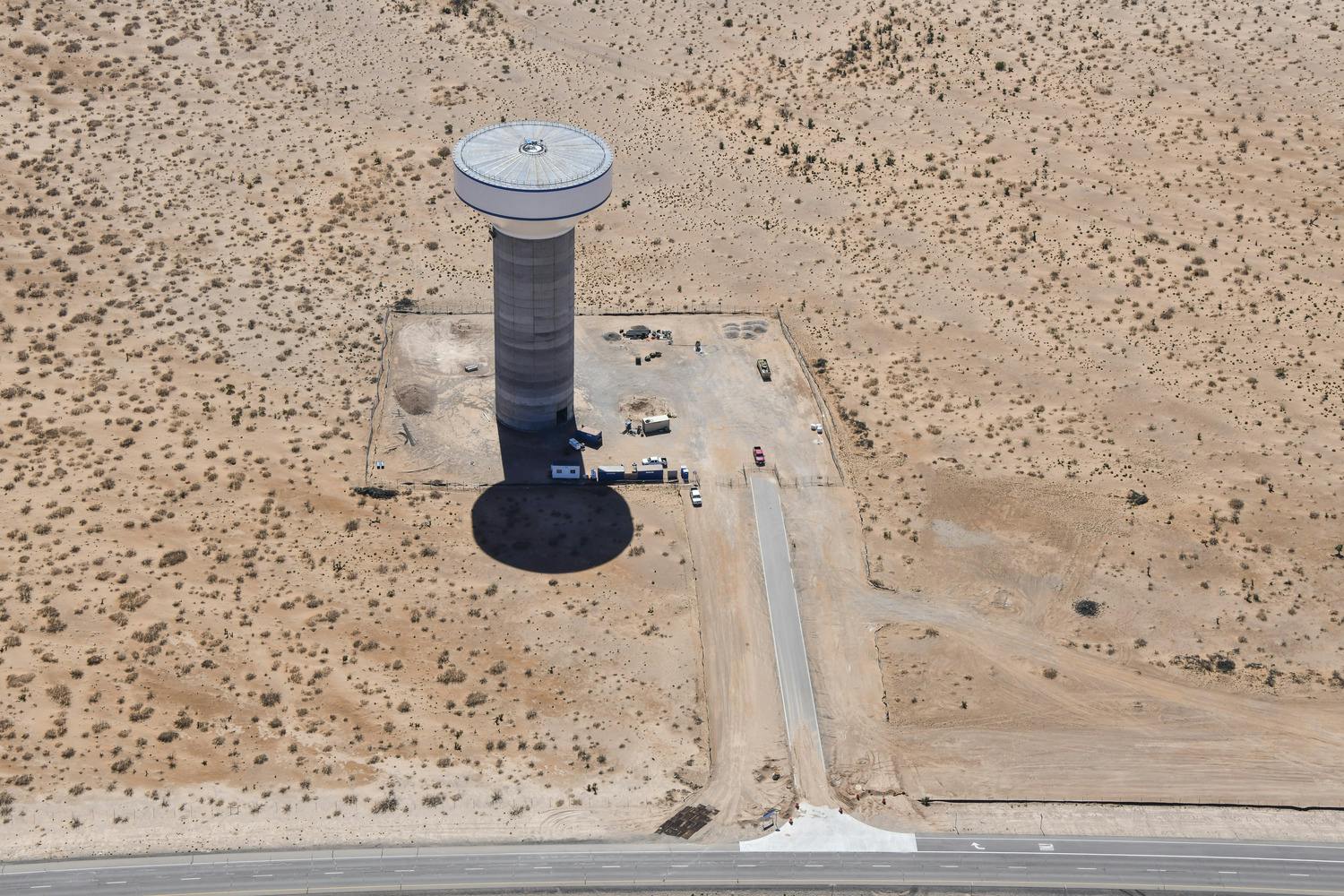
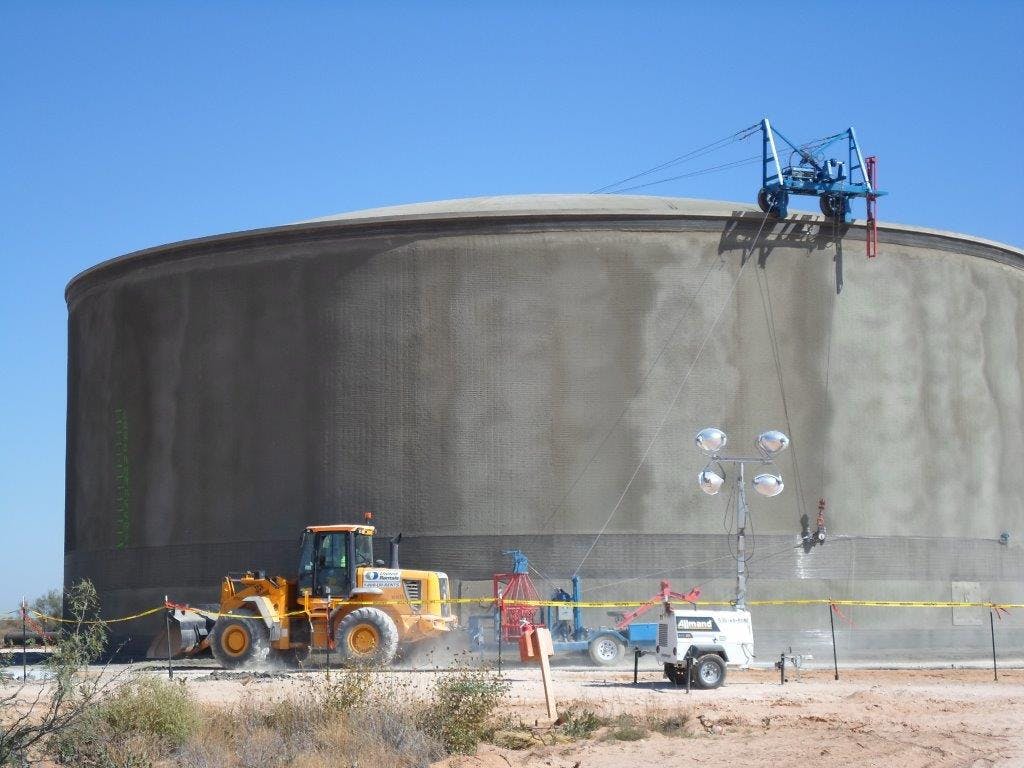
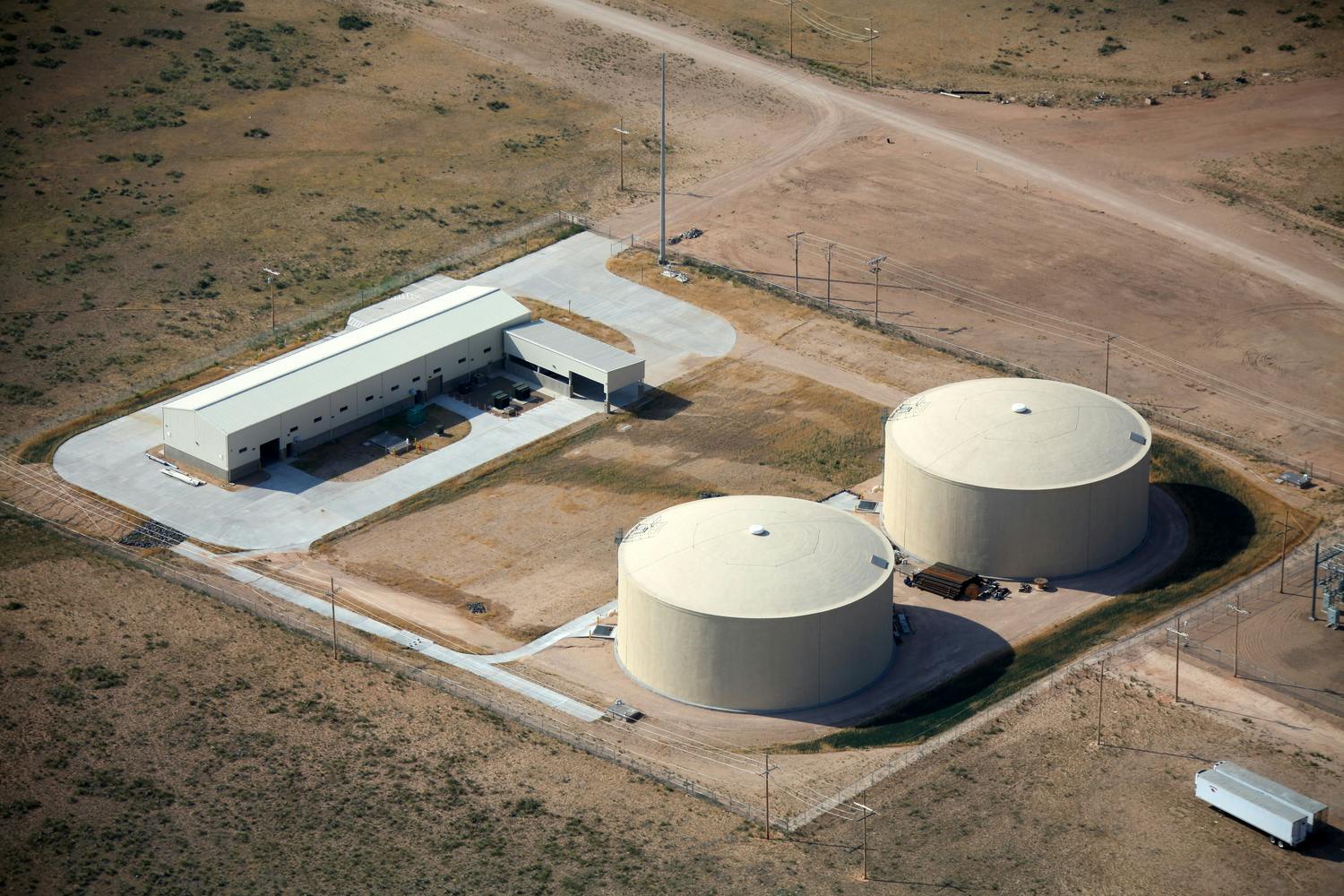
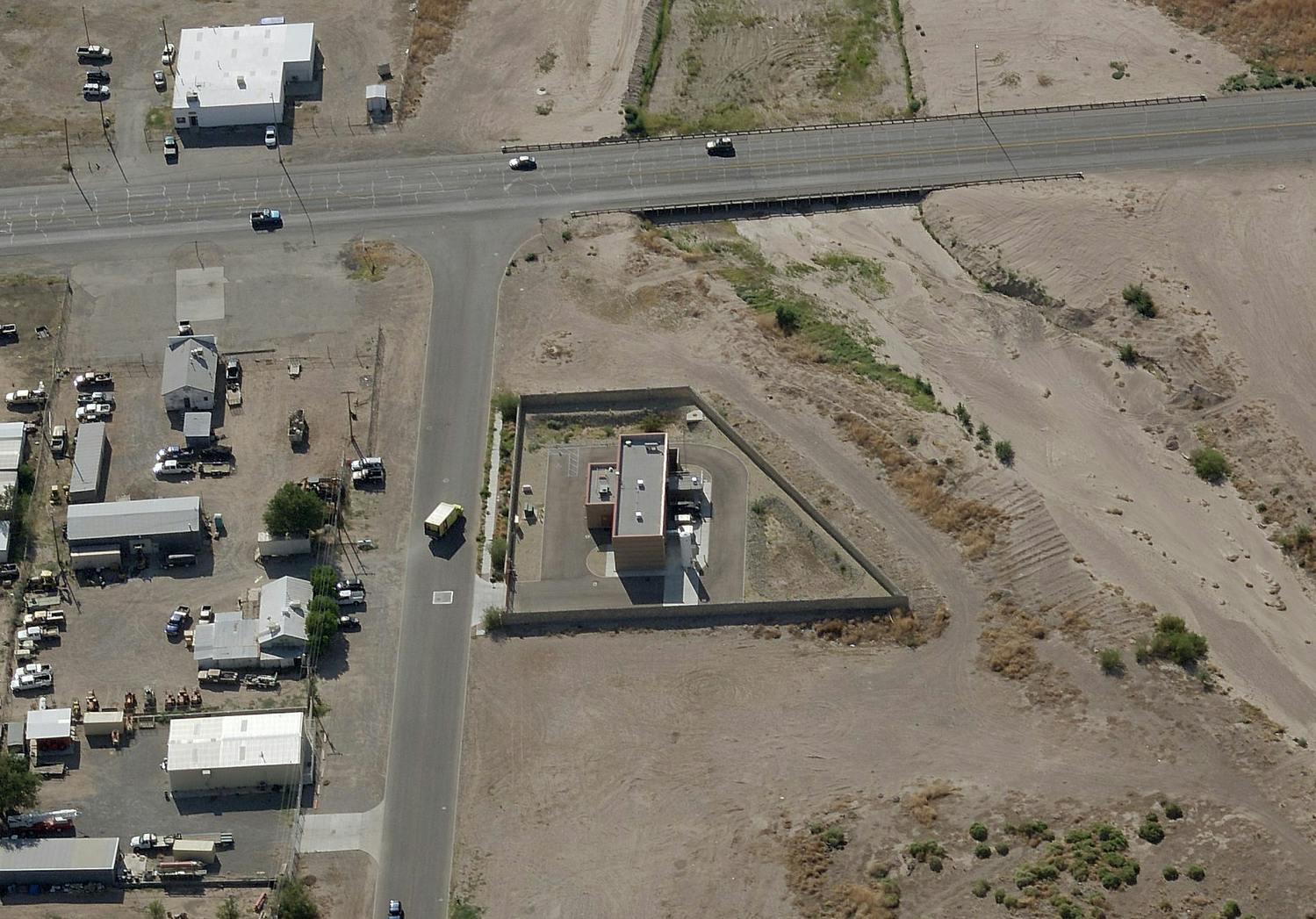
Parkhill provided office engineering and field construction management services for the Franklin 1A Elevated Storage Tank. This 215-foot tank holds 3 million gallons of water and is part of El Paso Water’s Northeast System Expansion. This project entailed design, bid, and construction of the new 3 MG composite concrete pedestal and steel water tank. The elevated storage reservoir for Franklin East 1A will provide elevated storage for future growth in the area, increase local water pressure, and improve the reliability of service for Northeast El Paso.
The construction also included design, excavation and placement of the tank foundation, concrete pedestal and steel tank, cathodic protection system, tank painting and logo, site piping with water main tie-ins, site grading, paving and access driveway, deceleration and acceleration lanes in a TxDOT right-of-way, overflow basin, rock wall, electrical and instrumentation, disinfection and testing, and other miscellaneous items to complete the project. Change orders were involved for additional work and change in scope.
Awards
Part of El Paso Water’s Resiliency Building and Water Storage Project, which was recognized as the Texas Chapter of the American Public Works Association (TPWA) Project of the Year for 2018
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
El Paso Water
- water-resources
- El Paso, Texas
Project Size
3 million gallon water reservoir
Construction Type
New construction
Project Delivery Method
Design-Bid-Build
Project Components
Composite concrete pedestal and steel water tank, cathodic protection system, tank painting, site piping with water main tie-ins, site grading and paving, driveway and deceleration lane, overflow basin rock wall and decorative fencing
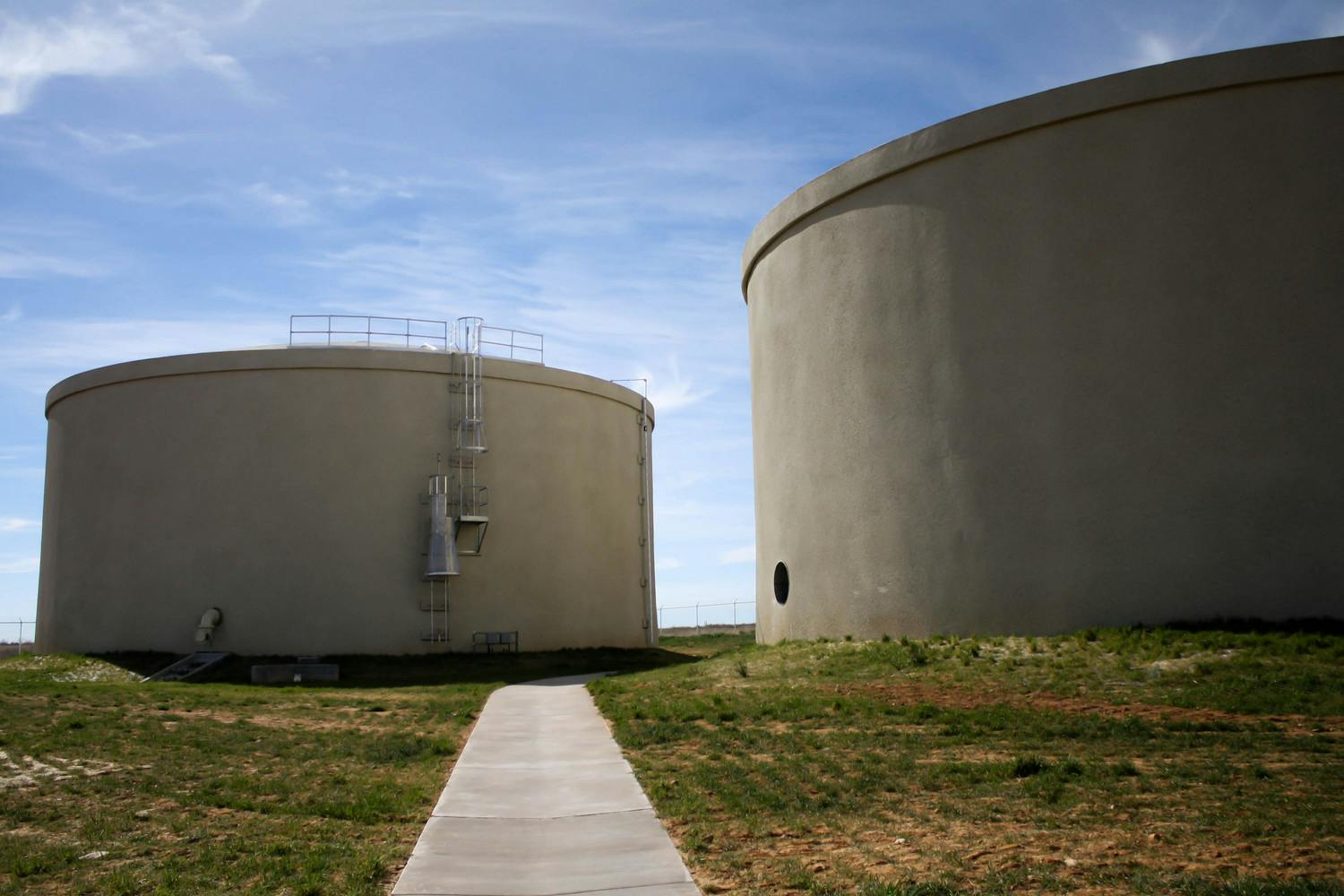
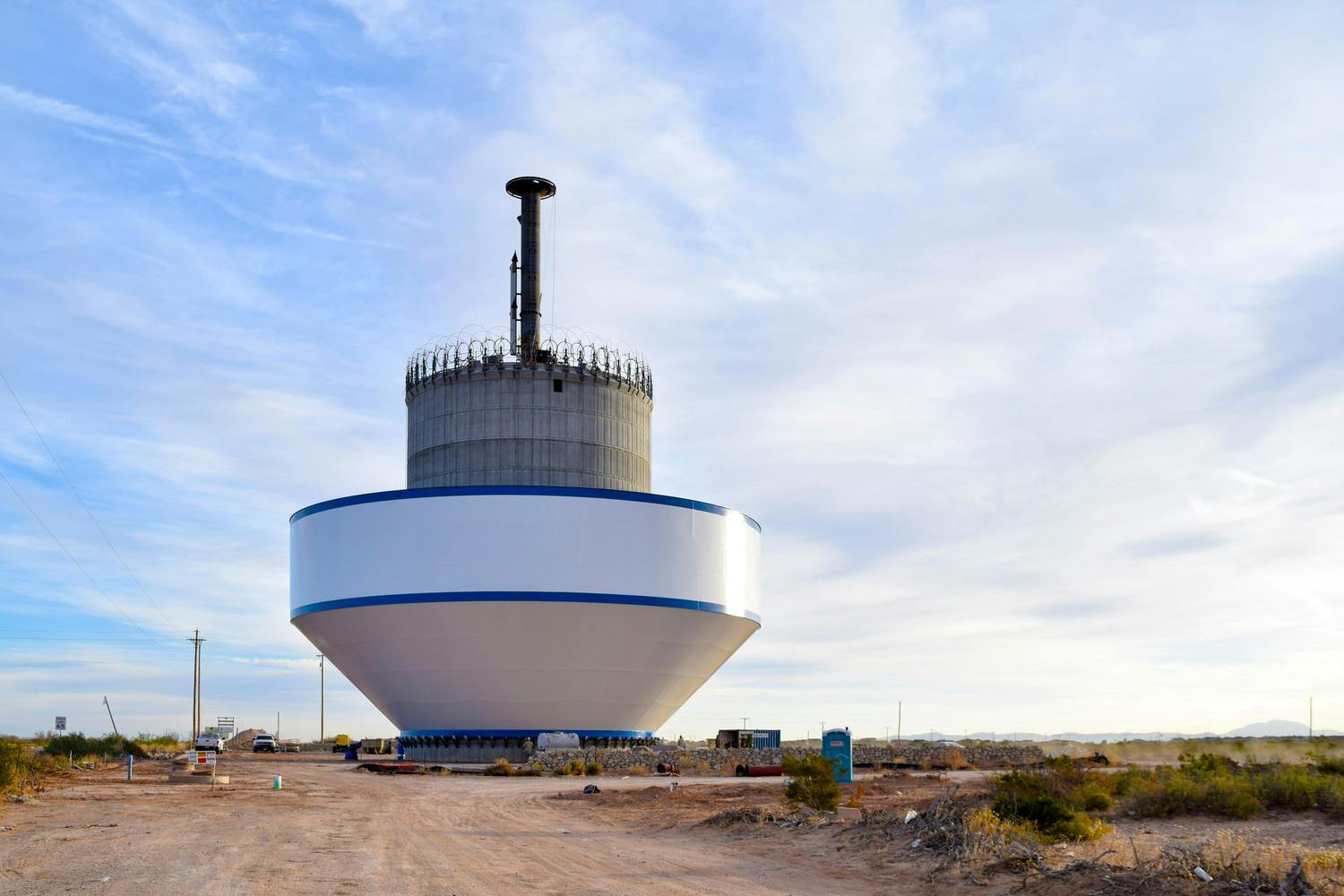
The North 2 Tank is part of the El Paso Water Northeast System Expansion. This 3-million gallon water tank is “one of several pieces of puzzle” for El Paso Water and the northeast part of El Paso, as Parkhill's Mike Ramirez, PE, explains. The project has allowed for several miles of development in the area.
“There’s a lot of discussion where development is happening within El Paso, and the trend is to try to keep from pushing further east and try to move more development to northeast El Paso to try and balance those water resources.”
Parkhill provided design, bid and construction administration services for the construction of the composite concrete pedestal and steel water tank. The construction also included excavation and placement of the tank foundation, concrete pedestal and steel tank, cathodic protection system, tank painting, site piping with water main tie-ins, site grading and paving. The tank is adjacent to US Highway 54 and required an access driveway and deceleration lane in TxDOT Right-of-Way to access the site. Site improvements included an overflow basin a rock wall and decorative fencing at the entrance gate.
Another pump station of the Northeast System Expansion now connects to the North 2 Tank and pumps to a 24-inch line that feeds Franklin 1A tank, another 3-million gallon water tank.
“This is going to be seen by people as they head from Texas to New Mexico,” Ramirez said, “and El Paso Water Utilities is very happy to have this up. It took a long time to get this going, and this is a big moment for them.”
Awards
El Paso Water’s Resiliency Building & Water Storage Project was recognized as the Texas Chapter of the American Public Works Association (TPWA) Project of the Year for 2018
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
City of Midland
- water-resources
- Midland, Texas
Construction Type
New construction
Project Components
Well field, well field collection piping, well field storage reservoir, high service pump station, transmission pipeline, intermediate storage reservoir, chlorine feed facility, terminal facilities, instrumentation, controls, and communications system
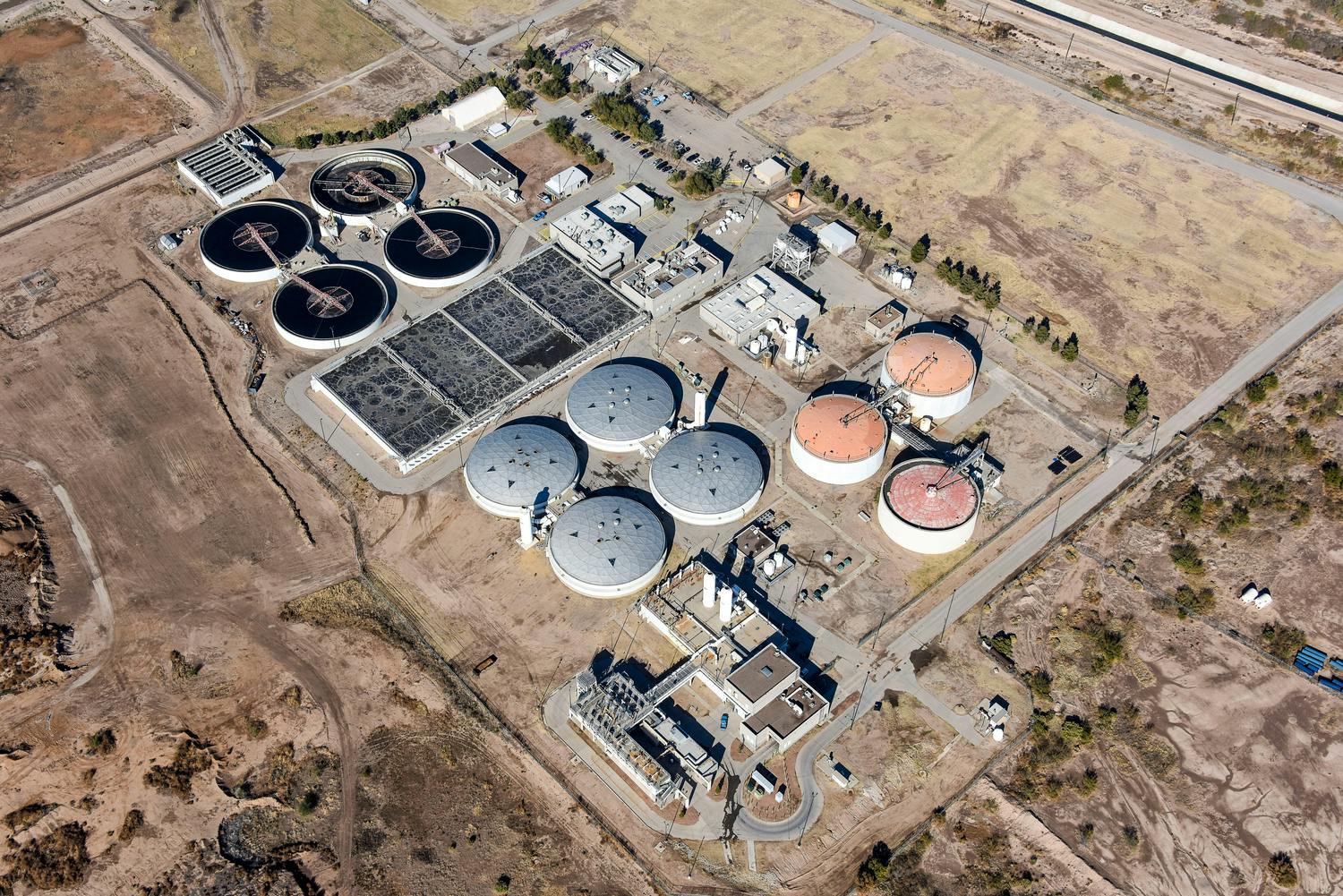
The City of Midland contracted with the Midland County Fresh Water Supply District No. 1 (FWSD1), forming a public-to-public partnership to design, build, operate, and finance the development of the T-Bar Ranch project. Under the water supply contract, the district agreed to provide water to the city from the T-Bar Ranch well field.
The project consists of the following major components:
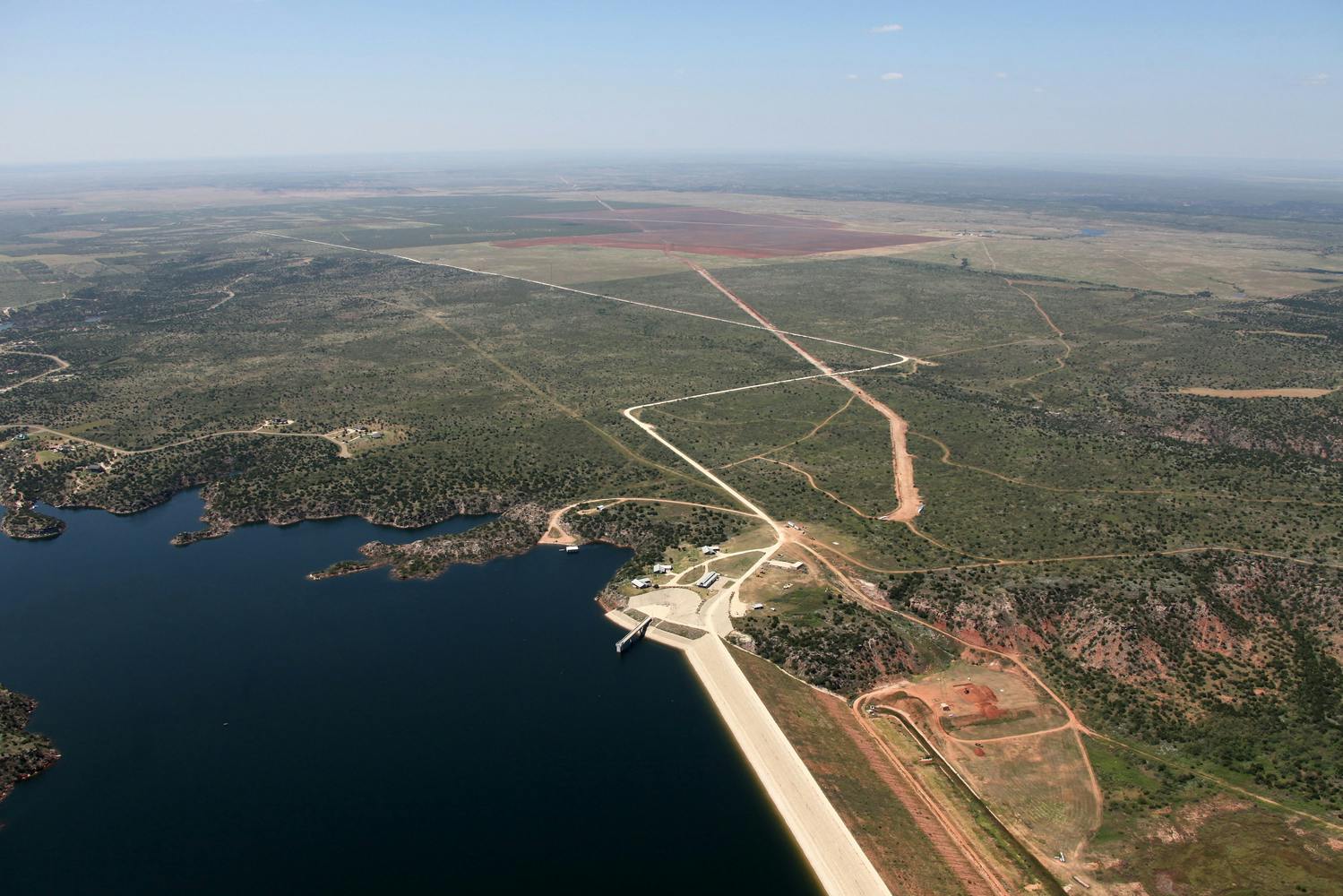
Well Field – 45 wells (approximately 550-feet deep) are located on the T-Bar Ranch in Winkler County and will produce a peak flow of 20-million gallons per day. Site work includes 15-miles of well access roads and 12.5Kv overhead power distribution system.
Well Field Collection Piping – A network of well field collection pipelines, varying from 6 to 36 inches in diameter.
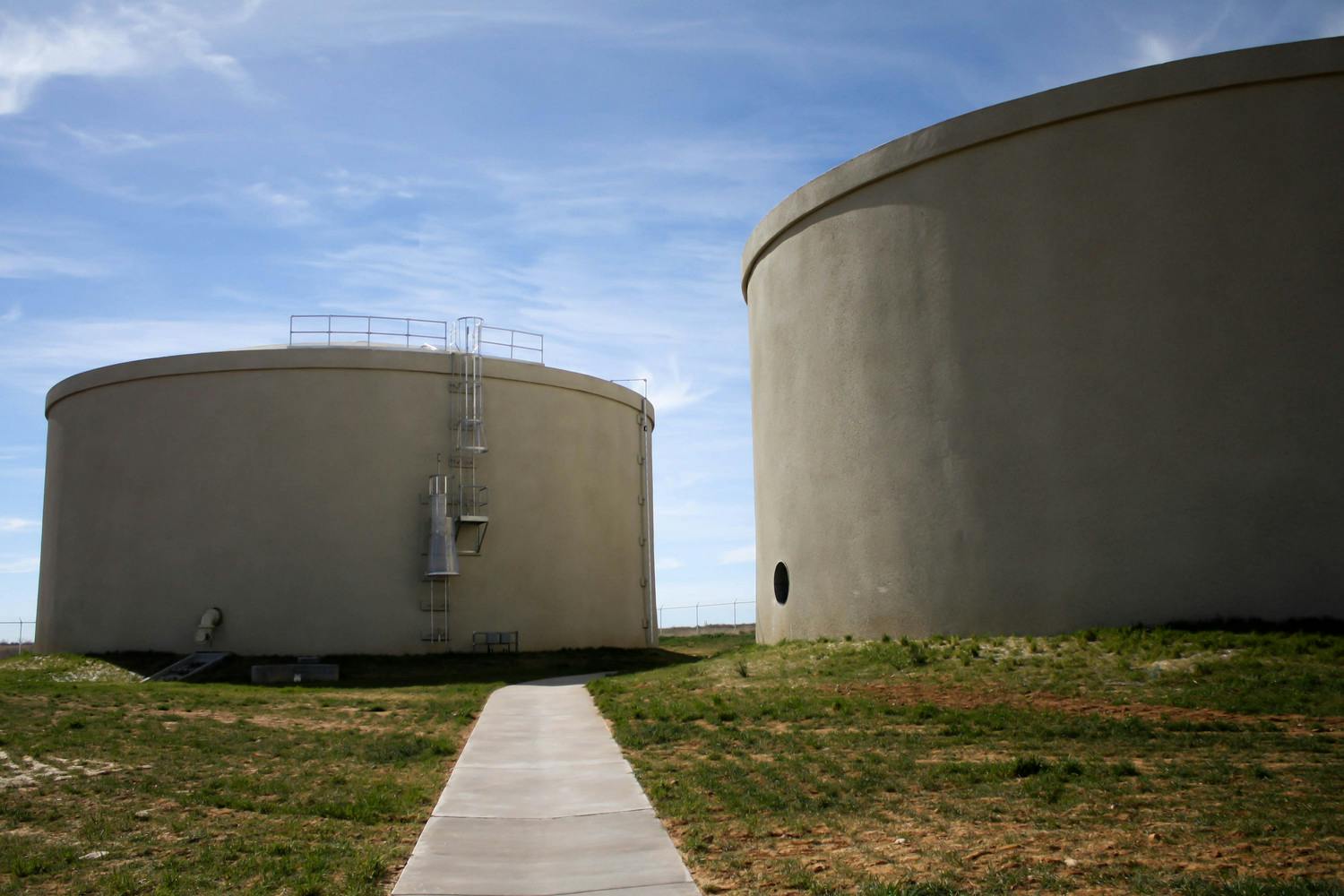
Well Field Storage Reservoir – A two-million-gallon, pre-stressed concrete covered ground storage reservoir adjacent to the High Service Pump Station.
High Service Pump Station – Four 900 horsepower, high-service vertical turbine pumps with a firm capacity of 20 MGD located inside a precast concrete building. Site work includes 12.5kV power drop to a substation transformer providing 4,160 and 480-volt power.
Transmission Pipeline – 59 miles of 48-inch diameter transmission pipeline from the T Bar Ranch Well Field to the Terminal Point within the City of Midland. The first 25-miles are uphill to the Intermediate Storage Reservoir, with the remaining 34 miles downhill to the City of Midland.
Intermediate Storage Reservoir – A five-million-gallon, pre-stressed concrete covered reservoir at the high point of the pipeline, 500-feet above the Well Field/High Service Pump Station. Site work includes 12.5kV power drop to substation transformer to provide 4,160 or 480 volts power to site facilities.
Chlorine Feed Facility – A precast concrete chlorination building will house electrical and chlorine feed equipment, an outdoor covered storage area for ton containers, and a chlorine gas scrubber system at the intermediate storage reservoir site to provide the contact time (CT) prior to use by the City of Midland.
Terminal Facilities – The terminal facility will include a pressure reducer/flow meter/control station and 2-MG elevated storage reservoir.
Instrumentation, Controls, and Communications System – Complete Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system will include microwave radio communication towers at the High service Pump Station, Intermediate Storage Reservoir, and Terminal Facility.
Awards
- Award of Merit – Design Build Institute of America
- Award of Merit – Best Projects – ENR Texas & Louisiana
- Infrastructure Project Award – National Public-Private Partnerships
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
City of Amarillo
- water-resources
- Amarillo, Texas
Project Size
20 MGD initial production capacity; facility designed for maximum future capacity of 30 MGD
Construction Type
New construction
Project Delivery Method
Design-Bid-Construct
Project Components
21 wells, 21 miles of collection pipelines, pump station, and 21 miles of transmission pipeline
Reacting to increased reductions in surface water allocations from the Canadian River Municipal Water Authority, population growth, increased water demand and groundwater depletion, the City of Amarillo began master planning efforts with Parkhill in the development of the Potter County Well Field.
The Potter County Well Field was master-planned for an initial capacity of 20 million gallons per day (MGD) with an ultimate capacity of 30 MGD. The firm capacity of 20 MGD allows for 10 percent of the wells to be out of service. Constructing this project required 21 wells, approximately 21 miles of collection pipelines, a pump station, and approximately 21 miles of transmission pipeline. The basic design of the collection system routing attempted to utilize existing pasture roads to reduce surface damages and enhance access to the property by the owner. The routing of the collection system coincides with the location of the access roadways and the overhead electric power distribution system forming a utility corridor.
The master-planning of the collection system places the largest pipelines needed for the full development of the well field in their appropriate location. Well buildings have been designed to include a durable pre-cast structure to house the motor control equipment and the instrumentation. Also included in the design is a pump station and power coordination.
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
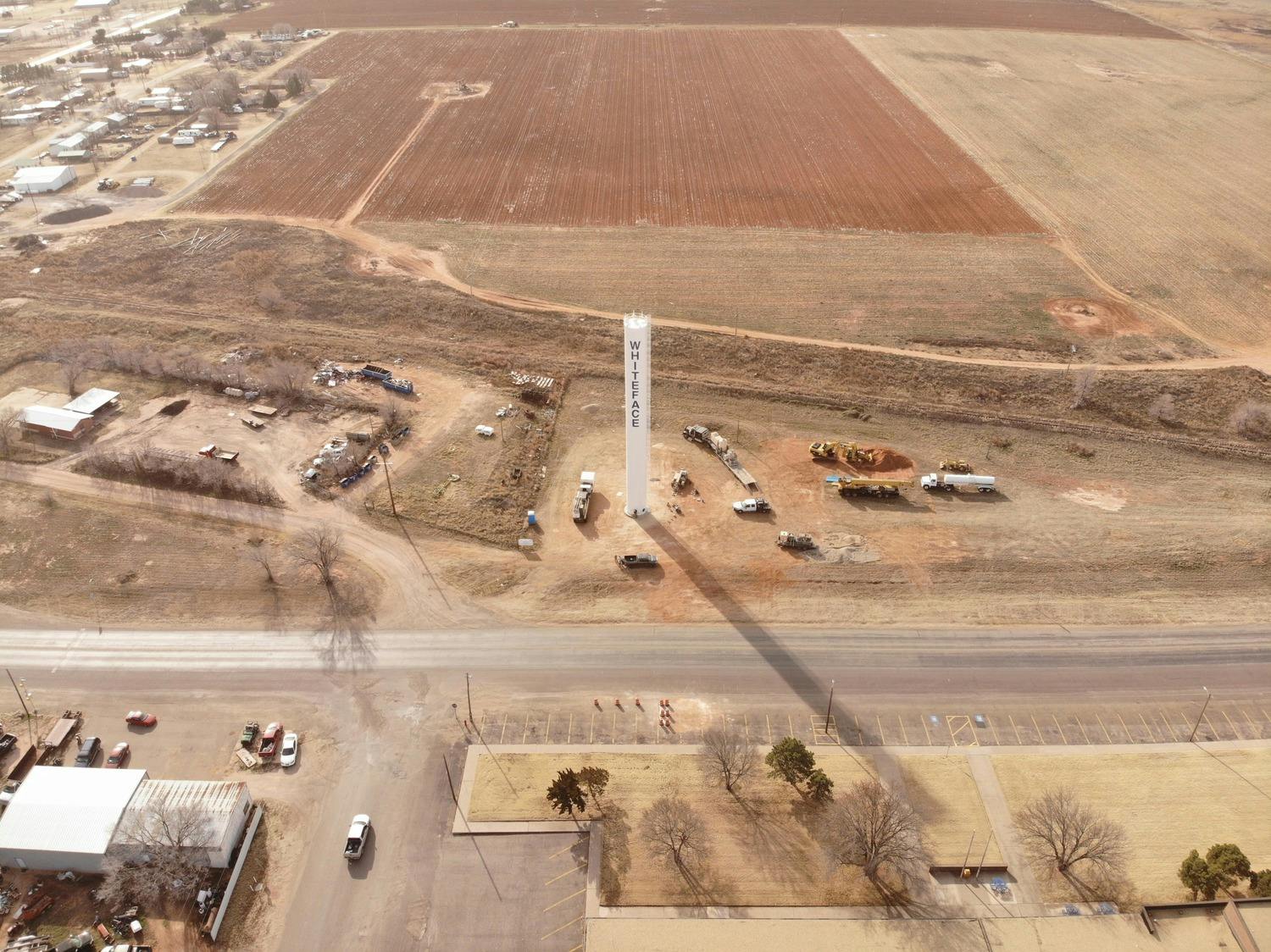
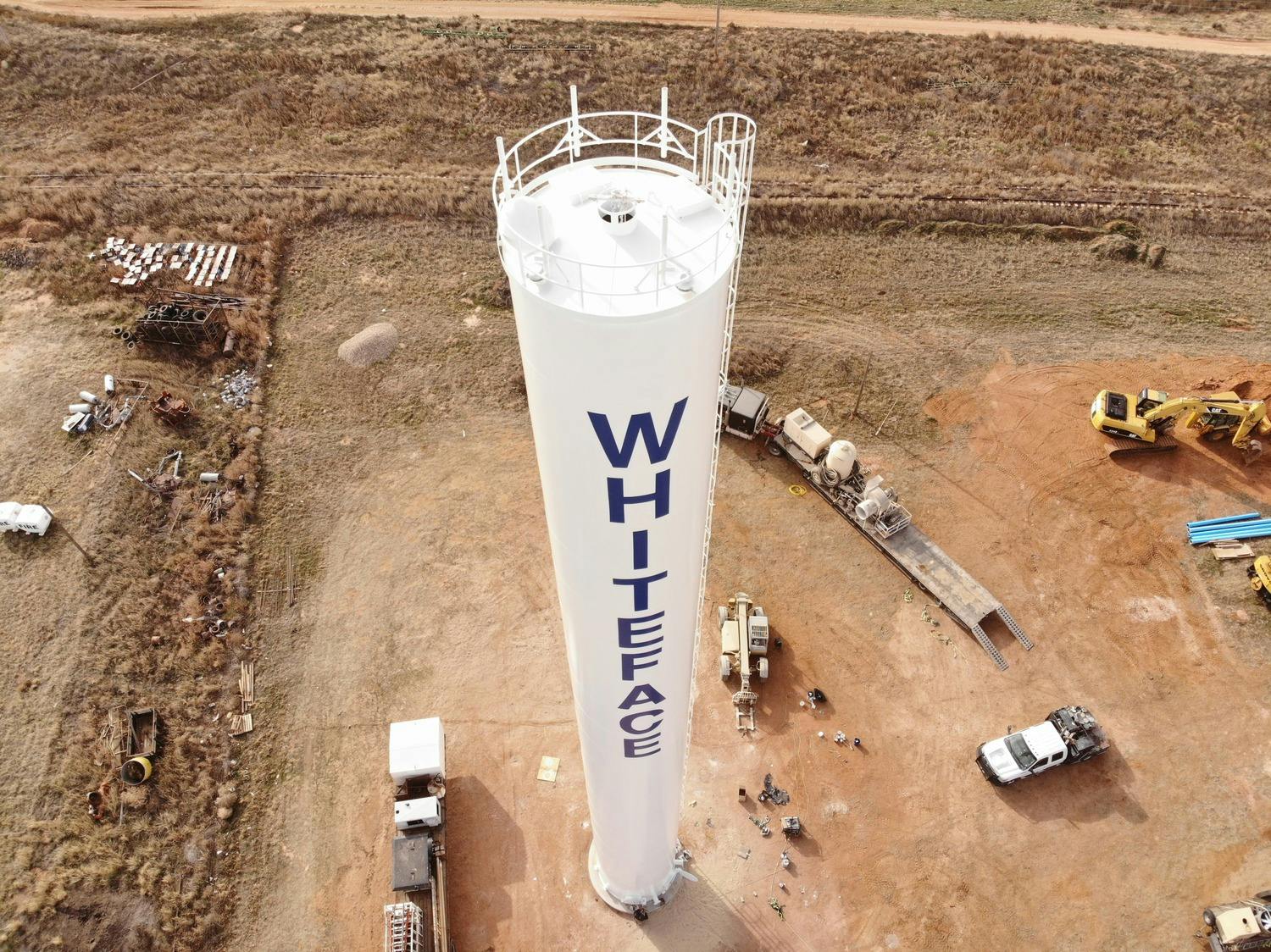
City of Whiteface
- water-resources
- Whiteface, Texas
Project Size
103,000-gallon water storage tank
Construction Type
New Construction
Project Delivery Method
Design-Bid-Build
Project Components
Concrete foundation, steel tank, TNEMEC interior and exterior coating system, underground waterline piping and new meter/valve box, site improvements (fencing, access road, site gravel); this project also included a water meter replacement component.
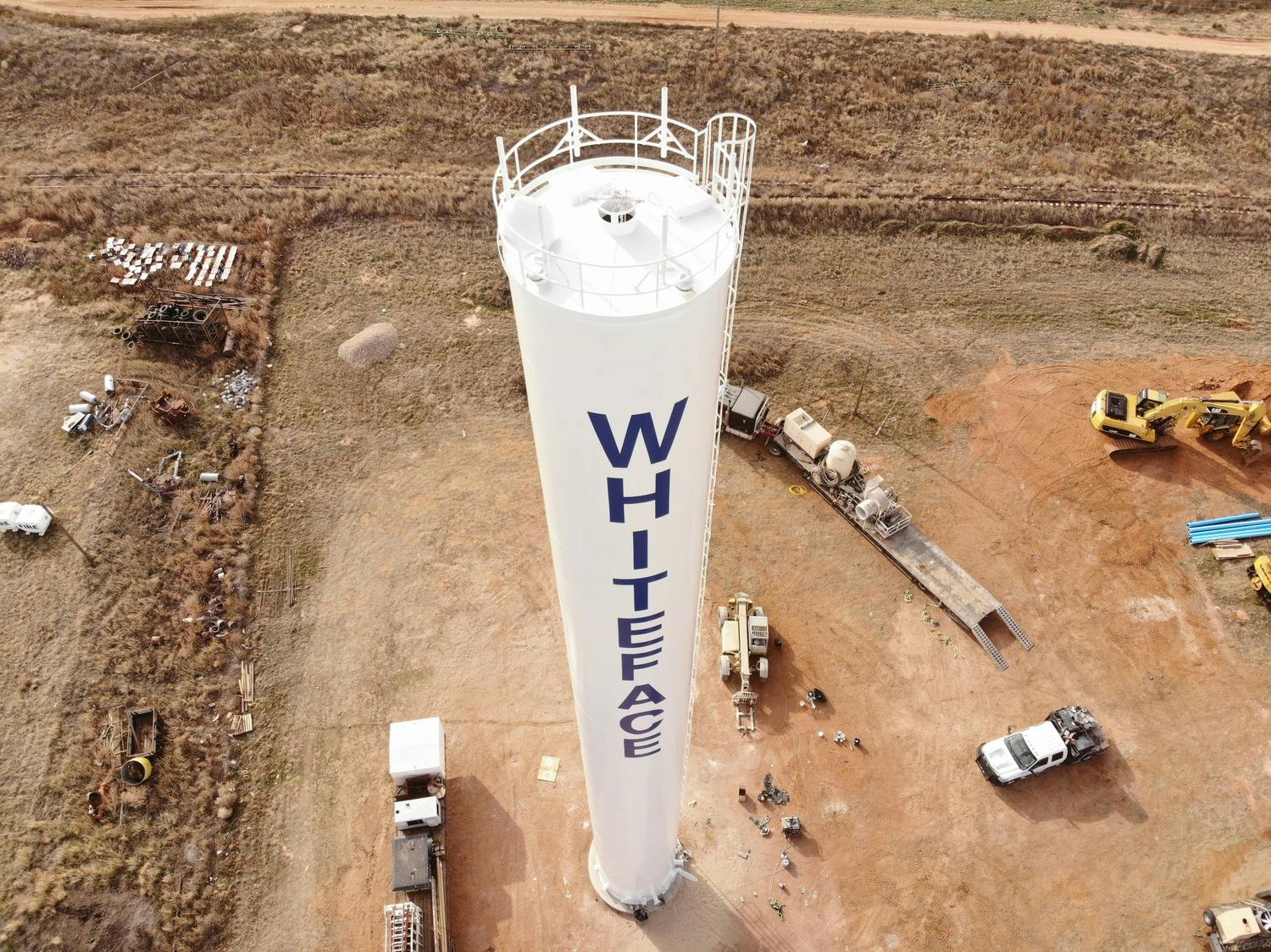
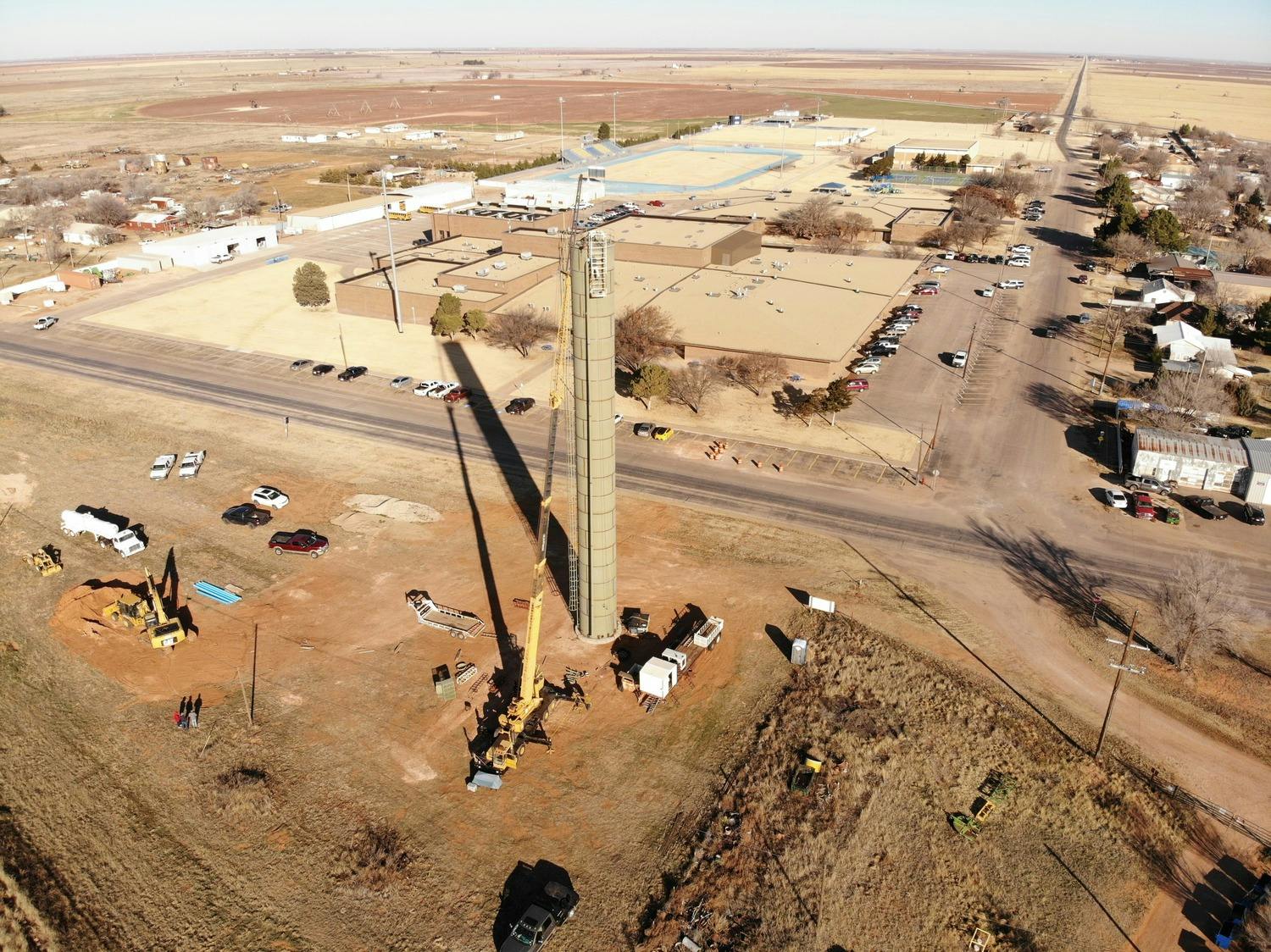
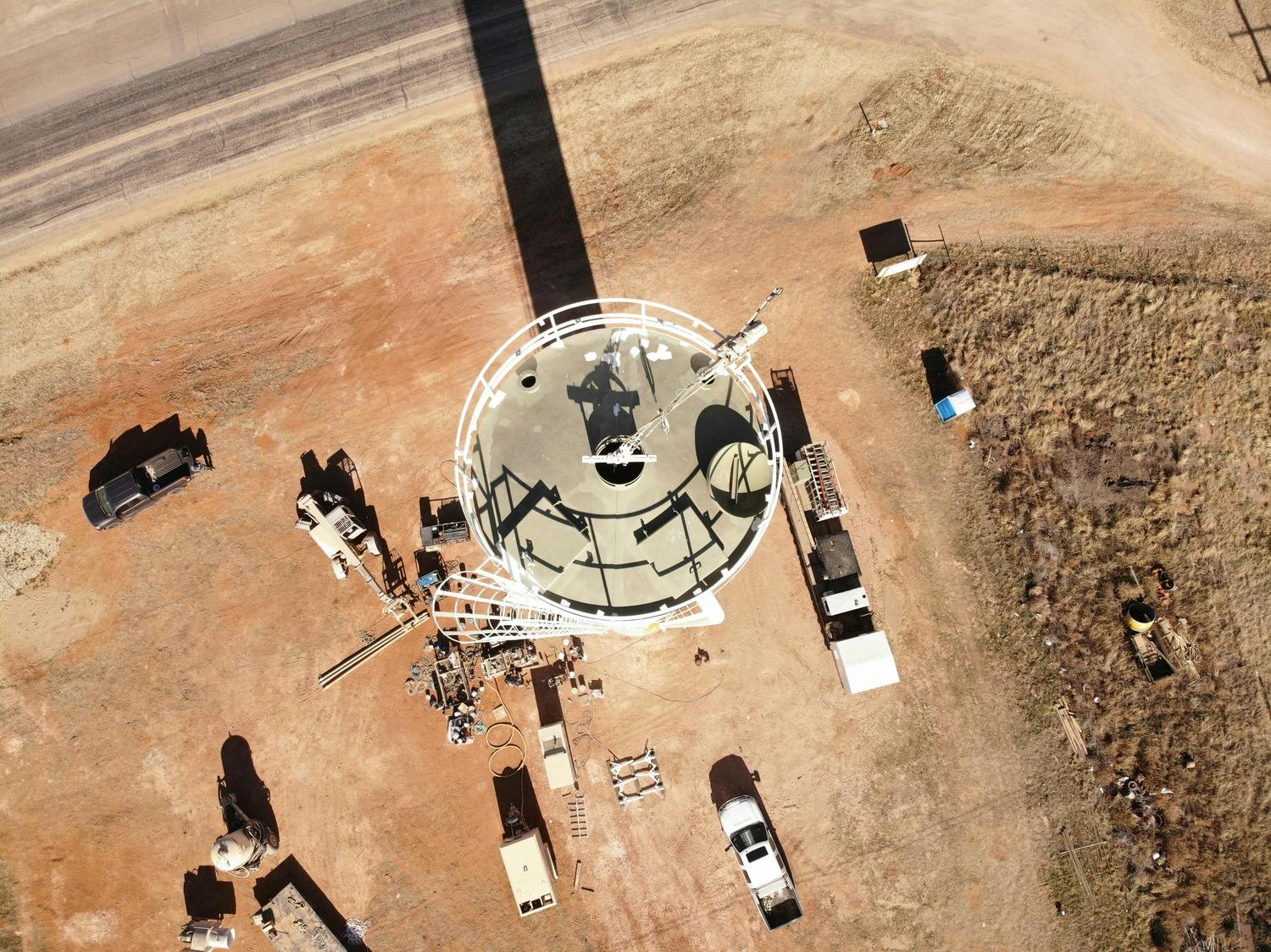
The City of Whiteface contracted Parkhill to design and build a new water storage tank for the Whiteface Water System Improvements. Their existing elevated storage tank was hit by a tornado in the late 1970s and was not structurally sound to continue operations. As with all West Texas communities, the functionality and reliability of a water tank are critical to the survival of the town.
Parkhill helped the City of Whiteface secure dual funding sources through the Texas Department of Agriculture and Texas Water Development Board in 2018 and the project moved forward to the design phase in 2019. Construction of the project began in September 2019 and was completed in December 2019.
Parkhill designed a standpipe, which minimizes the footprint of the project while still allowing for ample water storage capacity. At maximum capacity, this tank stores 103,000 gallons. The new standpipe proudly stands at 122 feet above the West Texas plains and is a beacon for the City of Whiteface.
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
Winkler Services
- water-resources
- Winkler, Texas
Project Size
18-mile pipeline to serve companies with water for their oil and gas operations
Construction Type
New pipeline
Project Delivery Method
Design-Build
Project Components
Boundary surveying, easement descriptions, construction staking
The West Texas oil and gas industries are still relying on water, a finite resource in the Permian Basin.
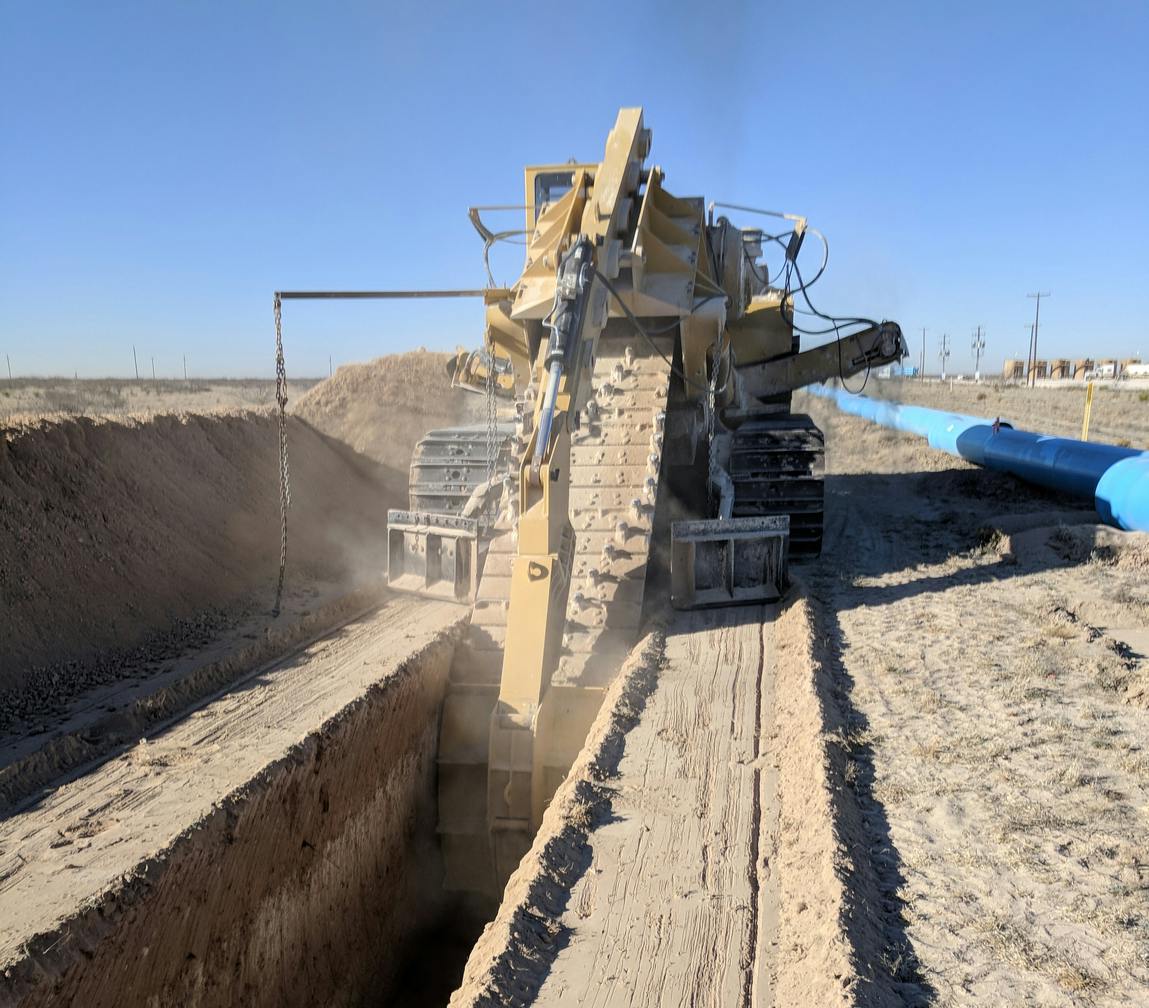
 Typically, water delivery systems to oil and gas operations aren’t permanent and don’t focus on efficiency. Parkhill developed a system that allows water to be conveyed efficiently and safely, encouraging industry growth. Parkhill and Garney Construction teamed to design the $14,500,000 water transmission system to deliver a max flow rate of 250,000 barrels per day to support oil and gas operations. The project was fast-tracked, so the team had to engineer solutions to deliver this system from concept to operation in fewer than 200 days. Services included a survey of more than 50 sections of land in both the Public School Land Survey System and the University Land System in Winkler and Loving counties. Using these survey relocations, our team prepared survey easement exhibits to submit to the University Land System and staked out a pipeline alignment in the field. Survey coordination with the contractor allowed an accelerated timeline and deliverables on schedule.
Typically, water delivery systems to oil and gas operations aren’t permanent and don’t focus on efficiency. Parkhill developed a system that allows water to be conveyed efficiently and safely, encouraging industry growth. Parkhill and Garney Construction teamed to design the $14,500,000 water transmission system to deliver a max flow rate of 250,000 barrels per day to support oil and gas operations. The project was fast-tracked, so the team had to engineer solutions to deliver this system from concept to operation in fewer than 200 days. Services included a survey of more than 50 sections of land in both the Public School Land Survey System and the University Land System in Winkler and Loving counties. Using these survey relocations, our team prepared survey easement exhibits to submit to the University Land System and staked out a pipeline alignment in the field. Survey coordination with the contractor allowed an accelerated timeline and deliverables on schedule.
Services Provided
Survey, civil
Project Leadership
At Parkhill, We're Designing and Building for
Your Tomorrow
El Paso Water
- water-resources
- El Paso, Texas
Project Size
20 MGD System
Construction Type
Water – Dist – Trans
Project Delivery Method
Design-Bid-Build
Project Components
One large lift station consolidating five stations, multiple complex permitting applications, and SCADA
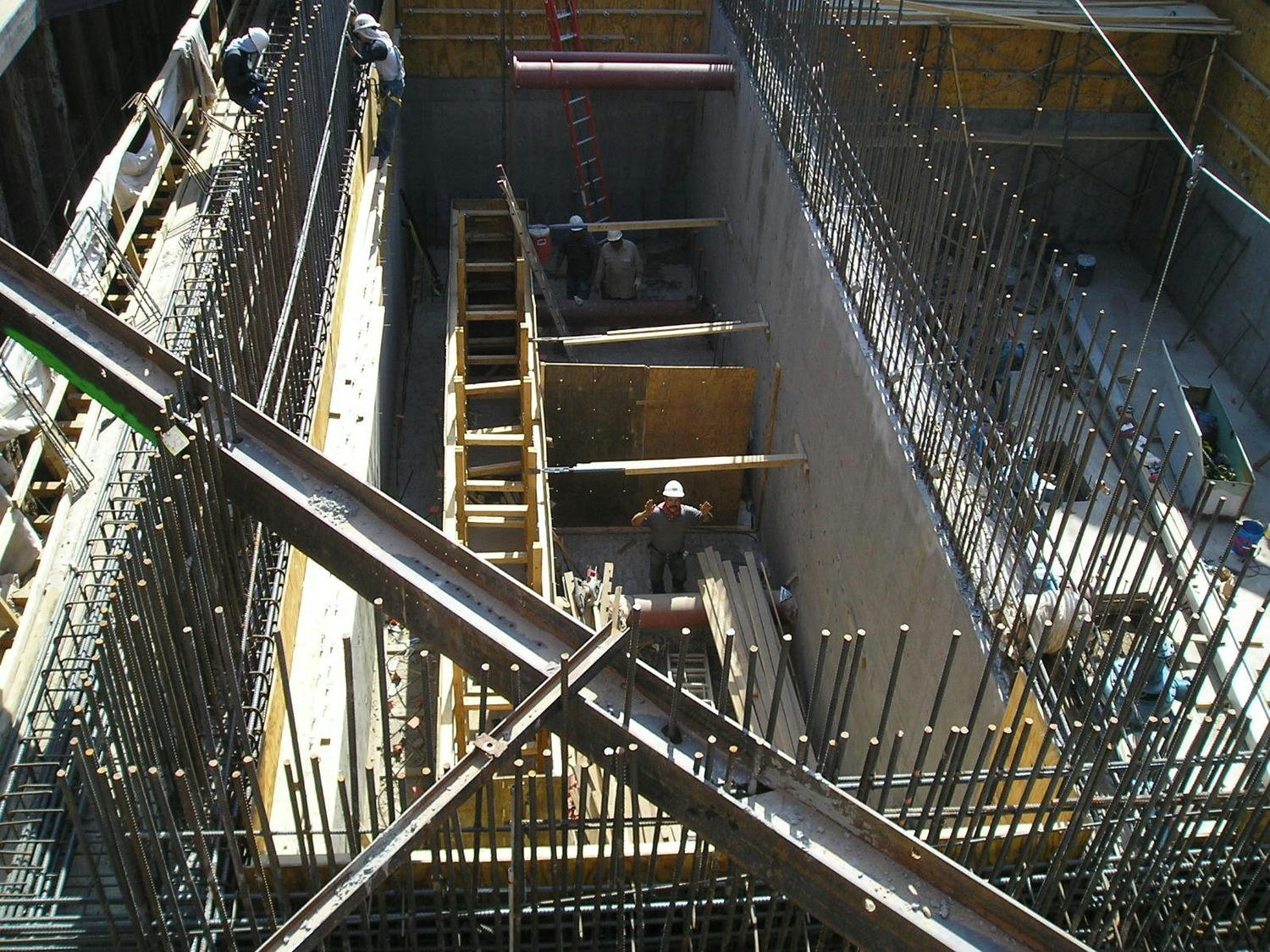
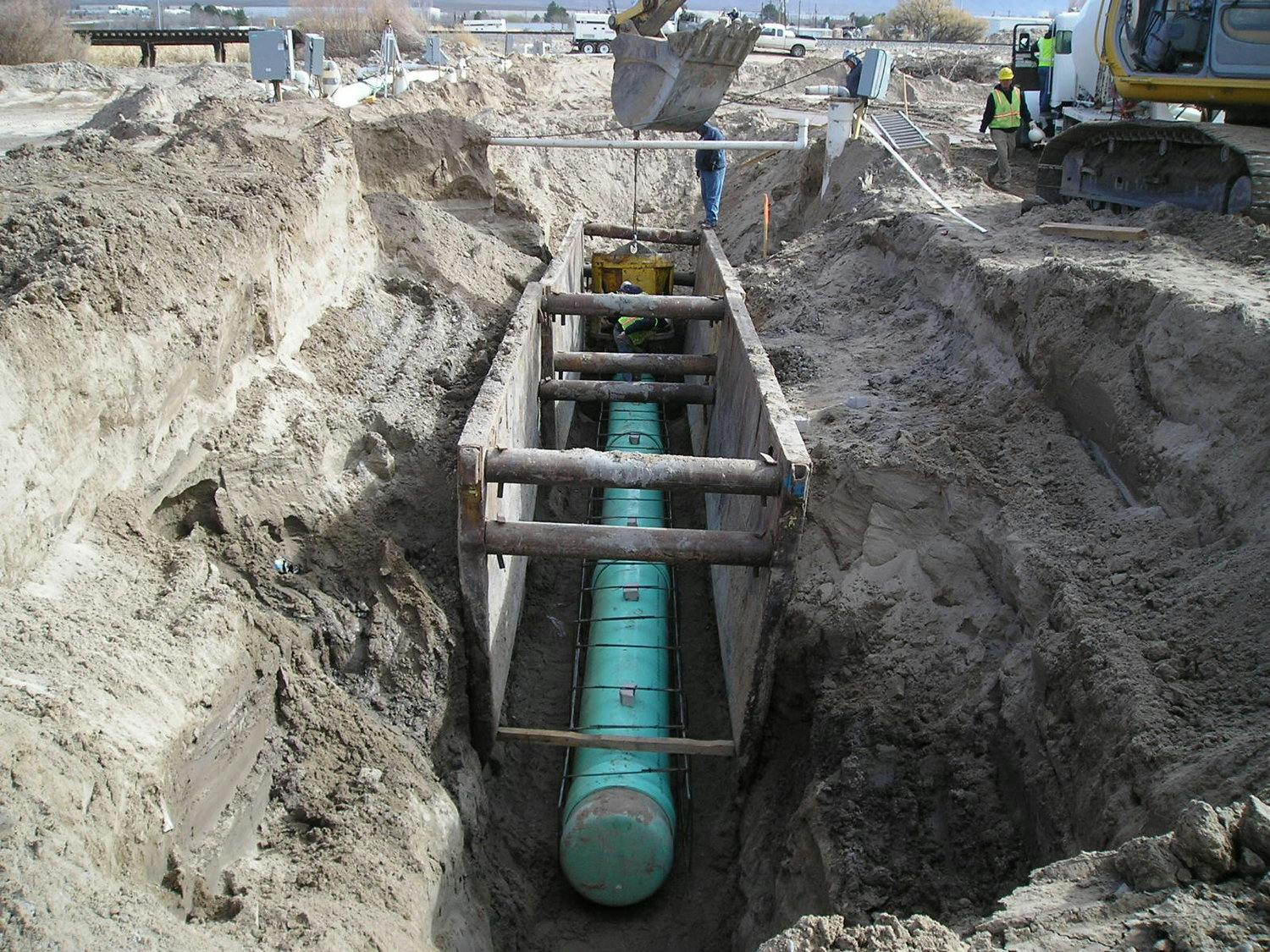
The Easy Way II Force Main Interceptor and Lift Station project exhibits Parkhill’s capability to design major interceptors and lift stations that include complex strategies and challenges. Two of those challenges were to route a pipeline under the Rio Grande and across I-10. The project provides major wastewater infrastructure improvements to serve rapidly developing areas and future development in West and Northwest El Paso.
The anticipated growth in the area would have surcharged the existing Artcraft, Westport, and El Paso West Lift Stations. During the planning, El Paso Water also asked Parkhill to incorporate the existing Easy Way Lift Station into the proposed improvements. The result was the construction of a large lift station that consolidated the existing stations – Artcraft, Westport, El Paso West, and Easy Way Lift stations – plus a future proposed lift station into one large station.
Using Geographic Information System (GIS) maps to determine the most desirable lift station location and pipeline route, we developed alternatives and worked with El Paso Water to develop a decision matrix. The matrix included factors such as constructibility, property, easement and permit acquisition, public acceptance, utility infrastructure conflicts, accessibility, maintenance, and capital costs.
The Easy Way II Lift Station is a wet well/dry well configuration with four 125-horsepower variable speed pumps. The station is approximately 45 feet deep and located in groundwater. Because of the topography in the area, the station employs a unique hydraulic operation using a combination of gravity lines, gravity force mains, and force mains. This system has the capacity to convey approximately 20 MGD and only pump 13 MGD. Our design was able to use the difference in elevation within the service area to push flow into the force main via a gravity force main. This project was featured at an American Society of Civil Engineers conference.